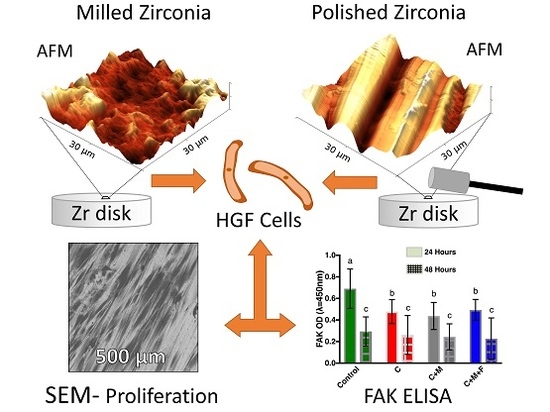
Effect of Clinically Relevant CAD/CAM Zirconia Polishing on Gingival Fibroblast Proliferation and Focal Adhesions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Fabrication
2.2. Specimen Polishing and Finishing
- 1
- Control: 320-grit sanded;
- 2
- Coarse (C): Finishing (ZilMaster Coarse (green), Bullet Shape, Shofu Dental Corp., Kyoto, Japan);
- 3
- Coarse plus Medium (C+M): Finishing (as previously described for Group C) and polishing (ZilMaster Medium (blue), Bullet Shape, Shofu Dental Corp., Kyoto, Japan);
- 4
- Coarse plus Medium plus Fine (C+M+F): Finishing and polishing (both as previously described for Group C+M) and final polishing (ZilMaster Fine (yellow), Bullet Shape, Shofu Dental Corp., Kyoto, Japan).
2.3. Optical Profilometry, Atomic Force Microscopy, and Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cell Seeding
2.6. FAK ELISA
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Zr Microscale Topography, SEM and OP
3.2. Zr Nanoscale Topography, AFM
3.3. FAK ELISA
3.4. Mean Cell Count and Cellular Morphology
4. Discussion
4.1. Zr Topography
4.2. Cellular Adhesion
4.3. Other Considerations for Zr
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J. Peri-implant diseases: Diagnosis and risk indicators. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Glantz, P.O.; Lindhe, J. The mucosal attachment at different abutments: An experimental study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, K.; Lopez, B.S.; Hultenby, K.; Wennerberg, A.; Arvidson, K. Attachment and proliferation of human oral fibroblasts to titanium surfaces blasted with TiO2 particles. A scanning electron microscopic and histomorphometric analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1998, 9, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kanno, T.; Milleding, P.; Ortengren, U. Zirconia as a dental implant abutment material: A systematic review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 23, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pabst, A.M.; Walter, C.; Grassmann, L.; Weyhrauch, M.; Brüllmann, D.D.; Ziebart, T.; Scheller, H.; Lehmann, K.M. Influence of CAD/CAM all-ceramic materials on cell viability, migration ability and adenylate kinase release of human gingival fibroblasts and oral keratinocytes. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.; Weber, H.P.; Donath, K.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Paquette, D.W.; Williams, R.C. Soft tissue reactions to non-submerged unloaded titanium implants in beagle dogs. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könönen, M.; Hormia, M.; Kivilahti, J.; Hautaniemi, J.; Thesleff, I. Effect of surface processing on the attachment, orientation, and proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts on titanium. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pae, A.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kwon, Y.-D.; Woo, Y.-H. Attachment and growth behaviour of human gingival fibroblasts on titanium and zirconia ceramic surfaces. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, S.; Truffa Giachet, F.; Miola, M.; Bertone, E.; Varesano, A.; Vineis, C.; Cochis, A.; Sorrentino, R.; Rimondini, L.; Spriano, S. Nanogrooves and keratin nanofibers on titanium surfaces aimed at driving gingival fibroblasts alignment and proliferation without increasing bacterial adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, M.J.; Giannaras, D.; Riehle, M.O.; Gadegaard, N.; Affrossman, S.; Curtis, A.S.G. Rapid fibroblast adhesion to 27 nm high polymer demixed nano-topography. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, C.J.; Wen, W.; Hamilton, D.W. Role of titanium surface topography and surface wettability on focal adhesion kinase mediated signaling in fibroblasts. Materials 2011, 4, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltriukienė, D.; Sabaliauskas, V.; Balčiūnas, E.; Melninkaitis, A.; Liutkevičius, E.; Bukelskienė, V.; Rutkūnas, V. The effect of laser-treated titanium surface on human gingival fibroblast behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkunas, V.; Bukelskiene, V.; Sabaliauskas, V.; Balciunas, E.; Malinauskas, M.; Baltriukiene, D. Assessment of human gingival fibroblast interaction with dental implant abutment materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, T.; Wen, J.; Xu, L.; Zeng, D.; Wu, Q.; Cao, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Selective responses of human gingival fibroblasts and bacteria on carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone with multilevel nanostructured TiO2. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, R.N.; Oda, D.; Quaranta, V.; Plopper, G.; Lambert, R.; Glaser, S.; Jones, J.C. Coating of titanium alloy with soluble laminin-5 promotes cell attachment and hemidesmosome assembly in gingival epithelial cells: Potential application to dental implants. J. Periodontal Res. 1997, 32, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Pareja, N.; Salvagni, E.; Guillem-Marti, J.; Aparicio, C.; Ginebra, M.P. Collagen-functionalised titanium surfaces for biological sealing of dental implants: Effect of immobilisation process on fibroblasts response. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Alfonso-Rodriguez, C.A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Espana-Lopez, A.; Jimenez-Guerra, A.; Garzon, I.; Alaminos, M.; Gil, F.J. Relevant aspects in the surface properties in titanium dental implants for the cellular viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.-Q.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, X.; Li, H.-P.; Tan, J.-G. Enhanced biological behavior of in vitro human gingival fibroblasts on cold plasma-treated zirconia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunzler, T.P.; Drobek, T.; Schuler, M.; Spencer, N.D. Systematic study of osteoblast and fibroblast response to roughness by means of surface-morphology gradients. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampin, M.; Warocquier-Clerout, R.; Legris, C.; Degrange, M.; Sigot-Luizard, M.F. Correlation between substratum roughness and wettability, cell adhesion, and cell migration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 36, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, A.; Walter, C.; Bell, A.; Weyhrauch, M.; Schmidtmann, I.; Scheller, H.; Lehmann, K. Influence of CAD/CAM zirconia for implant-abutment manufacturing on gingival fibroblasts and oral keratinocytes. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 20, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treccani, L.; Yvonne Klein, T.; Meder, F.; Pardun, K.; Rezwan, K. Functionalized ceramics for biomedical, biotechnological and environmental applications. Acta. Biomater. 2013, 9, 7115–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.B.; Ha, S.R. Effects of surface treatments on the translucency, opalescence, and surface texture of dental monolithic zirconia ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.R.; Nishimura, I.; Campbell, S.D. Ceramics in dentistry: Historical roots and current perspectives. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 75, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.; Swain, M. A critical review of dental implant materials with an emphasis on titanium versus zirconia. Materials 2015, 8, 932–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Hotta, Y.; Kunii, J.; Kuriyama, S.; Tamaki, Y. A review of dental CAD/CAM: Current status and future perspectives from 20 years of experience. Dent. Mater. J. 2009, 28, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruse, N.D.; Sadoun, M.J. Resin-composite blocks for dental CAD/CAM applications. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1232–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zembic, A.; Bösch, A.; Jung, R.E.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Sailer, I. Five-year results of a randomized controlled clinical trial comparing zirconia and titanium abutments supporting single-implant crowns in canine and posterior regions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Pajares, S.P.; Ritter, A.V.; Vera Resendiz, C.; Henson, B.R.; Culp, L.; Donovan, T.E. Effect of finishing and polishing on the surface roughness of four ceramic materials after occlusal adjustment. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happe, A.; Röling, N.; Schäfer, A.; Rothamel, D. Effects of different polishing protocols on the surface roughness of Y-TZP surfaces used for custom-made implant abutments: A controlled morphologic SEM and profilometric pilot study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavali, R.; Lin, C.P.; Lawson, N.C. Evaluation of different polishing systems and speeds for dental zirconia. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 26, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.J.; Thangavel, A.K.; Rolton, S.B.; Guazzato, M.; Klineberg, I.J. Clinical and laboratory surface finishing procedures for zirconia on opposing human enamel wear: A laboratory study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 50, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.G.; Tsujimoto, A.; Baruth, A. Effects of polishing bur application force and re-use on sintered zirconia surface topography. Oper. Dent. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Heintze, S.D.; Forjanic, M.; Rousson, V. Surface roughness and gloss of dental materials as a function of force and polishing time in vitro. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grössner-Schreiber, B.; Herzog, M.; Hedderich, J.; Dück, A.; Hannig, M.; Griepentrog, M. Focal adhesion contact formation by fibroblasts cultured on surface-modified dental implants: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, M.; Murphy, M.F.; Lilley, F.; French, P.W.; Burton, D.R.; Dixon, S.; Sharp, M.C. The use of abrasive polishing and laser processing for developing polyurethane surfaces for controlling fibroblast cell behaviour. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Oranization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 4288: 1996 (EN) Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Surface Texture: Profile Method-Rules and Procedures for the Assessment of the Surface Texture; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cerutis, D.R.; Dreyer, A.; Cordini, F.; McVaney, T.P.; Mattson, J.S.; Parrish, L.C.; Romito, L.; Huebner, G.R.; Jabro, M. Lysophosphatidic acid modulates the regenerative responses of human gingival fibroblasts and enhances the actions of platelet-derived growth factor. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Her, S.B.; Chang, W.G.; Lim, B.S. Effects of surface treatments on the susceptibilities of low temperature degradation by autoclaving in zirconia. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, M.S.; Cerutis, D.R.; Miyamoto, T.; Nunn, M.E. Cell attachment following instrumentation with titanium and plastic instruments, diode laser, and titanium brush on titanium, titanium-zirconium, and zirconia surfaces. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2016, 31, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatomo, K.; Komaki, M.; Sekiya, I.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Oda, S.; Muneta, T.; Ishikawa, I. Stem cell properties of human periodontal ligament cells. J. Periodontal Res. 2006, 41, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Edmiston, K.H.; Carpenter, C.; Gaffney, E.; Ryan, C.; Ward, R.; White, S.; Memeo, L.; Colarossi, C.; Petricoin, E.F.; et al. One-step preservation of phosphoproteins and tissue morphology at room temperature for diagnostic and research specimens. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicilia, A.; Cuesta, S.; Coma, G.; Arregui, I.; Guisasola, C.; Ruiz, E.; Maestro, A. Titanium allergy in dental implant patients: A clinical study on 1500 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomason, J.M.; Kelly, S.A.M.; Bendkowski, A.; Ellis, J.S. Two implant retained overdentures—A review of the literature supporting the McGill and York consensus statements. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Vijayanarayanan, R.P.; Pachter, D.; Coulthard, P. Oral health-related quality of life: Pre-and post-dental implant treatment. Oral Surg. 2015, 8, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.K.; Hanson, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.J.; Donais, K.; Whitmore, L.A.; Thomas, S.M.; Turner, C.E.; Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.F. FAK–Src signalling through paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bian, Z.C.; Yee, K.; Chen, B.P.C.; Chien, S.; Guan, J.L. Identification of transcription factor KLF8 as a downstream target of focal adhesion kinase in its regulation of cyclin D1 and cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.D. FAK and paxillin: Regulators of N-cadherin adhesion and inhibitors of cell migration? J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt, E.G.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase signaling in unexpected places. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 45, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franková, J.; Pivodová, V.; Růžička, F.; Tománková, K.; Šafářová, K.; Vrbková, J.; Ulrichová, J. Comparing biocompatibility of gingival fibroblasts and bacterial strains on a different modified titanium discs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, K.; Odén, A.; Wennerberg, A.; Hultenby, K.; Arvidson, K. The influence of surface topography of ceramic abutments on the attachment and proliferation of human oral fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunette, D.M.; Chehroudi, B. The effects of the surface topography of micromachined titanium substrata on cell behavior in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomech. Eng. 1999, 121, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, P.; Zara, S.; De Colli, M.; Radunovic, M.; Lazovic, V.; Ettorre, V.; Di Crescenzo, A.; Piattelli, A.; Cataldi, A.; Fontana, A. Graphene oxide improves the biocompatibility of collagen membranes in an in vitro model of human primary gingival fibroblasts. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutis, D.R.; Weston, M.D.; Alnouti, Y.; Bathena, S.P.; Nunn, M.E.; Ogunleye, A.O.; Mcvaney, T.P.; Headen, K.V.; Miyamoto, T. A major human oral lysophosphatidic acid species, LPA 18:1, regulates novel genes in human gingival fibroblasts. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.-L.; Ohura, K.; Fujii, T.; Oido-Mori, M.; Kowashi, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Suetsugu, Y.; Tanaka, J. DNA microarray analysis of human gingival fibroblasts from healthy and inflammatory gingival tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlady, V.; Buijs, J. Protein adsorption on solid surfaces. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1996, 7, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.J.; Clegg, R.E.; Leavesley, D.I.; Pearcy, M.J. Mediation of biomaterial–cell interactions by adsorbed proteins: A review. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Cassinelli, C.; Götz, W.; Tarnow, D. Plasma of argon accelerates murine fibroblast adhesion in early stages of titanium disk colonization. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubu, E.; Hamilton, D.W.; Inoue, T.; Brunette, D.M. Modulation of human gingival fibroblast adhesion, morphology, tyrosine phosphorylation, and ERK 1/2 localization on polished, grooved and SLA substratum topographies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 91, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Wen, W.; Prowse, P.; Hamilton, D.W. Regulation of matrix remodelling phenotype in gingival fibroblasts by substratum topography. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Suggested guidelines for the topographic evaluation of implant surfaces. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2000, 15, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kournetas, N.; Spintzyk, S.; Schweizer, E.; Sawada, T.; Said, F.; Schmid, P.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Eliades, G.; Rupp, F. Comparative evaluation of topographical data of dental implant surfaces applying optical interferometry and scanning electron microscopy. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, e317–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, L.; Oliva, A.; Basile, M.A.; Giordano, M.; Nastri, L.; Annunziata, M. Human gingival fibroblast functions are stimulated by oxidized nano-structured titanium surfaces. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrukhov, O.; Huber, R.; Shi, B.; Berner, S.; Rausch-Fan, X.; Moritz, A.; Spencer, N.D.; Schedle, A. Proliferation, behavior, and differentiation of osteoblasts on surfaces of different microroughness. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keselowsky, B.G.; Collard, D.M.; García, A.J. Surface chemistry modulates focal adhesion composition and signaling through changes in integrin binding. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5947–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Haj Husain, N.; Camilleri, J.; Özcan, M. Effect of polishing instruments and polishing regimens on surface topography and phase transformation of monolithic zirconia: An evaluation with XPS and XRD analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 64, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, P.; Tabellion, A.; Fischer, C. Microscopical and chemical surface characterization of CAD/CAM zircona abutments after different cleaning procedures. A qualitative analysis. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotfredsen, K.; Nimb, L.; Hjorting-hansen, E.; Jensen, J.S.; Holmen, A. Histomorphometric and removal torque analysis for TiO2-blasted titanium implants. An experimental study on dogs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1992, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, K.T.; Keller, J.C.; Randolph, B.A.; Wick, D.G.; Michaels, C.M. Optimization of surface micromorphology for enhanced osteoblast responses in vitro. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1992, 7, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denry, I.; Kelly, J.R. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denry, I.; Holloway, J.A. Ceramics for dental applications: A review. Materials 2010, 3, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işeri, U.; Özkurt, Z.; Yalniz, A.; Kazazoglu, E. Comparison of different grinding procedures on the flexural strength of zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazzawi, T.F.; Lemons, J.; Liu, P.R.; Essig, M.E.; Bartolucci, A.A.; Janowski, G.M. Influence of low-temperature environmental exposure on the mechanical properties and structural stability of dental zirconia. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 21, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsias, M.E.; Silva, N.R.; Pines, M.; Stappert, C.; Thompson, V.P. Reliability and fatigue damage modes of zirconia and titanium abutments. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 23, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Wille, S.; Al-Alhali, M.; Kern, M. Effect of fatigue loading on the fracture strength and failure mode of lithium disilicate and zirconia implant abutments. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauser, R.; Sailer, I.; Wohlwend, A.; Studer, S.; Schibli, M.; Scharer, P. Experimental zirconia abutments for implant-supported single-tooth restorations in esthetically demanding regions: 4-year results of a prospective clinical study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herzl, C.; Kaizer, M.; Chughtai, A.; Tong, H.; Tanaka, C.; Zhang, Y. On the interfacial fracture resistance of resin-bonded zirconia and glass-infiltrated graded zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsayar, M.M.; Park, P. Modified maximum tangential stress criterion for fracture behavior of zirconia/veneer interfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 59, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, N.G.; Wong, J.; Baruth, A.; Cerutis, D.R. Effect of Clinically Relevant CAD/CAM Zirconia Polishing on Gingival Fibroblast Proliferation and Focal Adhesions. Materials 2017, 10, 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121358
Fischer NG, Wong J, Baruth A, Cerutis DR. Effect of Clinically Relevant CAD/CAM Zirconia Polishing on Gingival Fibroblast Proliferation and Focal Adhesions. Materials. 2017; 10(12):1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121358
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Nicholas G., Jeffrey Wong, Andrew Baruth, and D. Roselyn Cerutis. 2017. "Effect of Clinically Relevant CAD/CAM Zirconia Polishing on Gingival Fibroblast Proliferation and Focal Adhesions" Materials 10, no. 12: 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121358
APA StyleFischer, N. G., Wong, J., Baruth, A., & Cerutis, D. R. (2017). Effect of Clinically Relevant CAD/CAM Zirconia Polishing on Gingival Fibroblast Proliferation and Focal Adhesions. Materials, 10(12), 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121358