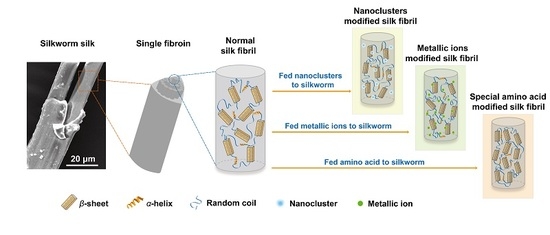
Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. ICP-MS Measurements
2.3. FTIR Analysis
2.4. XRD Analysis
2.5. TGA Analysis
2.6. Mechanical Properties of the Silk Fibers
2.7. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contents of Metal Elements in Silk Fibers
3.2. Secondary Structure of Silk Fibers
3.3. Thermal Stabilities of Silk Fibers
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Silk Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. New opportunities for an ancient material. Science 2010, 329, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Silk materials—A road to sustainable high technology. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2824–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, L.D.; Cheng, Y.; Teng, C.P.; Khin, Y.W.; Loh, X.J.; Tee, S.Y.; Low, M.; Ye, E.; Yu, H.D.; Zhang, Y.W. Structures, mechanical properties and applications of silk fibroin materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 46, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Viney, C.; Llorca, J.; Elices, M. Silkworm silk as an engineering material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Viney, C.; Llorca, J.; Elices, M. Mechanical properties of single-brin silkworm silk. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 75, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Vollrath, F. Materials: Surprising strength of silkworm silk. Nature 2002, 418, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, B.; Holland, C.; Vollrath, F. Forced reeling of Bombyx mori silk: Separating behavior and processing conditions. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, B.; Guan, J.; Holland, C.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Linking naturally and unnaturally spun silks through the forced reeling of Bombyx mori. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Y. Feeding single-walled carbon nanotubes or graphene to silkworms for reinforced silk fibers. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6695–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Dai, F.; Zhao, H. Characterization of silkworm larvae growth and properties of silk fibres after direct feeding of copper or silver nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2017, 129, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardo, A.; Pantano, M.F.; Pugno, N.M. Slip knots and unfastening topologies enhance toughness without reducing strength of silk fibroin fibres. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20150060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, M.F.; Berardo, A.; Pugno, N.M. Tightening slip knots in raw and degummed silk to increase toughness without losing strength. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Dai, F. Natural Silkworm Cocoon Composites with High Strength and Stiffness Constructed in Confined Cocooning Space. Polymers 2018, 10, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Du, L.; Shen, T.; Li, F.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, D. Structure and properties of silkworm cocoon (Bombyx mori) treated by hot pressing. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Effect of various dissolution systems on the molecular weight of regenerated silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2012, 14, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.Z. Luminescent golden silk and fabric through in situ chemically coating pristine-silk with gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials 2015, 36, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; He, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, P.; Xie, J.; Lu, Z. Controllable in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on multilayered film-coated silk fibers for antibacterial application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Construction of high strength hollow fibers by self-assembly of a stiff polysaccharide with short branches in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Sezutsu, H.; Tatematsu, K.I.; Kobayashi, I.; Yonemura, N.; Uchino, K.; Nakajima, K.; Kojima, K.; Takabayashi, C.; Machii, H. Colored fluorescent silk made by transgenic silkworms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5232–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yuan, L.; Ding, H.; Song, C.; Ma, S.; Peng, Z.; Peng, Z. Advanced silk material spun by a transgenic silkworm promotes cell proliferation for biomedical application. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4947–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Yi, Q.; Ma, S.; Xie, K.; Chen, H.; Xia, Q. Modifying the mechanical properties of silk fiber by genetically disrupting the ionic environment for silk formation. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, O.J.; Kim, S.-W.; Ki, C.S.; Chao, J.R.; Yoo, H.; Yoon, S.-I.; Lee, J.E.; Park, Y.R.; Kweon, H. Novel fabrication of fluorescent silk utilized in biotechnological and medical applications. Biomaterials 2015, 70, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansil, N.C.; Li, Y.; Koh, L.D.; Peng, T.C.; Win, K.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Han, M.Y. The use of molecular fluorescent markers to monitor absorption and distribution of xenobiotics in a silkworm model. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9576–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansil, N.C.; Koh, L.D.; Han, M.Y. Functional silk: Colored and luminescent. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisal, A.; Trivedy, K.; Mohammad, H.; Panneri, S.; Sen Gupta, S.; Lele, A.; Manchala, R.; Kumar, N.S.; Gadgil, M.; Khandelwal, H. Uptake of Azo dyes into silk glands for production of colored silk cocoons using a green feeding approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Li, L.L.; Feng, L.; Li, J.F.; Jiang, L.H.; Shen, Q. Directly obtaining pristine magnetic silk fibers from silkworm. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 63, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Shen, Q. Directly obtaining high strength silk fiber from silkworm by feeding carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Reinforced and ultraviolet resistant silks from silkworms fed with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Song, P.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Huang, H.M.; Zhao, H.P.; Wang, N.N.; Zhu, Y.Q. Robust composite silk fibers pulled out of silkworms directly fed with nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, H.; Kojima, K. Production of Bombyx mori silk fibroin incorporated with unnatural amino acids. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Nicodemo, D.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, F.; Fidelis, M.; Silva, L.; Tonoli, G. Enhanced silk performance by enriching the silkworm diet with bordeaux mixture. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansil, N.C.; Li, Y.; Teng, C.P.; Zhang, S.; Win, K.Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Han, M.Y. Intrinsically colored and luminescent silk. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, Z.; Ban, H.; Liu, L. Effects of the amino acid sequence on thermal conduction through β-sheet crystals of natural silk protein. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 29007–29013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malay, A.D.; Sato, R.; Yazawa, K.; Watanabe, H.; Ifuku, N.; Masunaga, H.; Hikima, T.; Guan, J.; Mandal, B.B.; Damrongsakkul, S. Relationships between physical properties and sequence in silkworm silks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taddei, P.; Asakura, T.; Yao, J.; Monti, P. Raman study of poly (alanine-glycine)-based peptides containing tyrosine, valine, and serine as model for the semicrystalline domains of Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Biopolymers 2004, 75, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, T.; Ohgo, K.; Ishida, T.; Taddei, P.; Monti, P.; Kishore, R. Possible implications of serine and tyrosine residues and intermolecular interactions on the appearance of silk I structure of Bombyx mori silk fibroin-derived synthetic peptides: High-resolution 13C cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning NMR study. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keten, S.; Xu, Z.; Ihle, B.; Buehler, M.J. Nanoconfinement controls stiffness, strength and mechanical toughness of [beta]-sheet crystals in silk. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Knight, D.P. Effect of metallic ions on silk formation in the mulberry silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 16937–16945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicko, C.; Kenney, J.M.; Knight, D.; Vollrath, F. Transition to a β-sheet-rich structure in spidroin in vitro: The effects of pH and cations. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 14080–14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xie, X.; Knight, D.P.; Zong, X.H.; Deng, F.; Yao, W.H. Effects of pH and calcium ions on the conformational transitions in silk fibroin using 2D Raman correlation spectroscopy and 13C solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11302–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.W.P.; Bini, E.; Hensman, J.; Knight, D.; Lewis, R.; Kaplan, D. Role of pH and charge on silk protein assembly in insects and spiders. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2006, 82, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarieh, G.; Nordling, K.; Saenz, A.; Casals, C.; Rising, A.; Johansson, J.; Knight, S.D. Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay. Nature 2010, 465, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, P.; Murab, S.; Karmakar, S.; Chowdhury, P.K.; Ghosh, S. Modulation of self-assembly process of fibroin: An insight for regulating the conformation of silk biomaterials. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3936–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P. In vivo effects of metal ions on conformation and mechanical performance of silkworm silks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebe, P.; Partlow, B.P.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wurm, A.; Zhuravlev, E.; Schick, C. Silk I and Silk II studied by fast scanning calorimetry. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Qi, Z.; Knight, D.P.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Synchrotron FTIR microspectroscopy of single natural silk fibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Knight, D.P.; Vollrath, F. Copper in the silk formation process of Bombyx mori silkworm. FEBS Lett. 2003, 554, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.X.; Zhou, P.; Hu, B.W.; Ji, D. An investigation into the effect of potassium ions on the folding of silk fibroin studied by generalized two-dimensional NMR–NMR correlation and Raman spectroscopy. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, P. Interference of EGCG on the Zn (II)-induced conformational transition of silk fibroin as a model protein related to neurodegenerative diseases. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5543–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Terry, A.E.; Huang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Metal element contents in silk gland and silk fiber of Bombyx mori silkworm. Acta Chim. Sin. Chin. Ed. 2005, 63, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Paquet-Mercier, F.; Lefèvre, T.; Auger, M.; Pézolet, M. Evidence by infrared spectroscopy of the presence of two types of β-sheets in major ampullate spider silk and silkworm silk. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Biospinning by silkworms: Silk fiber matrices for tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.W.; Gracz, H.S.; Tonelli, A.E.; Hudson, S.M. Structural study of irregular amino acid sequences in the heavy chain of Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackledge, T.A.; Swindeman, J.E.; Hayashi, C.Y. Quasistatic and continuous dynamic characterization of the mechanical properties of silk from the cobweb of the black widow spider Latrodectus hesperus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S. Tensile Deformation of Fibers Used in Textile Industry: Agilent Technologies Application Note; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Hay, J.; Swindeman, J.; Oliver, W. Continuous dynamic analysis: Evolution of elastic properties with strain. MRS Commun. 2014, 4, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.G.; Casartelli, M.; Fiandra, L.; Parenti, P.; Giordana, B. Role of specific activators of intestinal amino acid transport in Bombyx mori larval growth and nutrition. Arch. Insect. Biochem. 2001, 48, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Ji, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. Direct in vivo functionalizing silkworm fibroin via molecular recognition. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Materials | Characteristics | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Nano Cu | Diameter: 20 nm, particles | Beijing DK Nano Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China |
| Nano CaCO3 | Diameter: 20 nm, particles | |
| Copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) | Purity: ≥99.00% | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Calcium chloride anhydrous (CaCl2) | Purity: ≥99.00% | |
| Serine (Ser) | L-Serine, food-grade | Huzhou Xintiansi Bio-tech Co., Ltd., Zhejiang province, China |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) | L-Tyrosine, food-grade | |
| Sericin amino acid (SAA) | Molecular weight: 500 Da | |
| Fibroin amino acid (FAA) | Molecular weight: 90 Da |
| Samples | Ts (°C) a | Tmax (°C) b | Residue at 800 °C (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 292.7 | 323.0 | 12.27 |
| Cu NPs group | 293.3 | 323.7 | 18.15 |
| CuCl2 group | 295.3 | 322.4 | 16.51 |
| CaCO3 group | 294.0 | 320.8 | 3.58 |
| CaCl2 group | 293.1 | 320.0 | 10.19 |
| Serine (Ser) group | 293.9 | 323.7 | 20.63 |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) group | 292.1 | 320.3 | 3.18 |
| Sericin amino acid (SAA) group | 297.1 | 323.8 | 18.65 |
| Fibroin amino acid (FAA) group | 290.8 | 320.8 | 15.14 |
| Samples | Dynamic Strength (MPa) | Dynamic Modulus (GPa) | Storage Modulus (GPa) | Loss Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 283 ± 31 | 10.6 ± 2.4 | 15.2 ± 2.2 | 1.32 ± 0.22 |
| Cu NPs group | 346 ± 50 * | 13.5 ± 1.8 * | 18.0 ± 2.2 * | 1.69 ± 0.35 * |
| CuCl2 group | 299 ± 61 | 11.8 ± 3.2 | 15.4 ± 2.1 | 1.48 ± 0.25 |
| CaCO3 group | 333 ± 57 | 12.7 ± 1.6 | 15.8 ± 2.1 | 1.45 ± 0.23 |
| CaCl2 group | 280 ± 46 | 11.3 ± 1.8 | 15.1 ± 2.6 | 1.42 ± 0.17 |
| Serine (Ser) group | 377 ± 49 * | 13.1 ± 1.4 * | 18.6 ± 2.1 * | 1.69 ± 0.27 * |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) group | 400 ± 41 * | 13.5 ± 1.6 * | 20.1 ± 2.2 * | 1.69 ± 0.21 * |
| Sericin amino acid (SAA) group | 386 ± 56 * | 13.3 ± 1.7 * | 19.4 ± 2.3 * | 1.77 ± 0.24 * |
| Fibroin amino acid (FAA) group | 459 ± 52 * | 15.7 ± 1.9 * | 23.3 ± 3.0 * | 1.96 ± 0.27 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Z.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Dai, F. Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk. Materials 2019, 12, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010014
Cheng L, Huang H, Zeng J, Liu Z, Tong X, Li Z, Zhao H, Dai F. Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk. Materials. 2019; 12(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Lan, Huiming Huang, Jingyou Zeng, Zulan Liu, Xiaoling Tong, Zhi Li, Hongping Zhao, and Fangyin Dai. 2019. "Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk" Materials 12, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010014
APA StyleCheng, L., Huang, H., Zeng, J., Liu, Z., Tong, X., Li, Z., Zhao, H., & Dai, F. (2019). Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk. Materials, 12(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010014