Mesoporous Palladium N,N’-Bis(3-Allylsalicylidene)o-Phenylenediamine-Methyl Acrylate Resins as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Heck Coupling Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of the Schiff Base Ligands and Pd(II) Complexes
2.3. Synthesis of the PdAS(x)-MA, (x = 1, 2, 5 or 10 wt.%) Resins
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Catalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Coupled with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.3. Nitrogen Adsorption-Desorption Isotherms at −196 °C
3.4. CP/MAS 13C NMR Spectroscopy
3.5. DRS UV–Vis Measurements
3.6. ICP-OES
3.7. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
3.8. Catalytic Activity
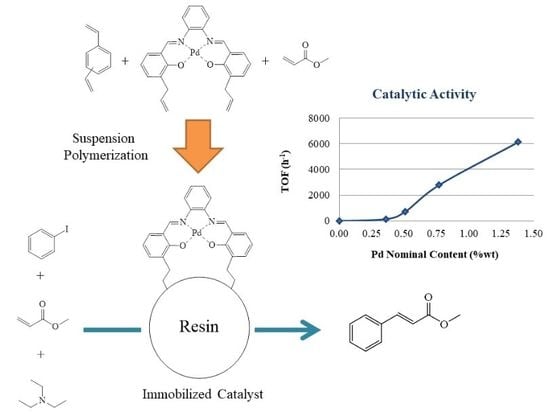
3.8.1. Effect of PdAS Loading


3.8.2. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magano, J.; Dunetz, J.R. Large-Scale Applications of Transition Metal-Catalyzed Couplings for the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2177–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, H.-U.; Indolese, A.; Schnyder, A. Applied homogeneous catalysis by organometallic complexes. Curr. Sci. 2000, 78, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Zapf, A.; Beller, M. Fine Chemical Synthesis with Homogeneous Palladium Catalysts: Examples, Status and Trends. Top. Catal. 2002, 19, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S. Heck Reaction—State of the Art. Catalysts 2017, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Cheprakov, A.V. The Heck Reaction as a Sharpening Stone of Palladium Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, E.-I. A genealogy of Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 653, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.F. Palladium-catalyzed reactions of organic halides with olefins. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979, 12, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Kinney, E.P.; Yang, Z. Ligand-Free Heck Reaction: Pd(OAc)2 as an Active Catalyst Revisited. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7528–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson Seechurn, C.C.C.; Kitching, M.O.; Colacot, T.J.; Snieckus, V. Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling: A Historical Contextual Perspective to the 2010 Nobel Prize. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5062–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Hamilton, D.J.; Tooze, R.P. Homogeneous Catalysis—Advantages and Problems. In Catalyst Separation, Recovery and Recycling: Chemistry and Process Design; Cole-Hamilton, D.J., Tooze, R.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Kirchhoff, M.M.; Williamson, T.C. Catalysis as a foundational pillar of green chemistry. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 221, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heveling, J. Heterogeneous Catalytic Chemistry by Example of Industrial Applications. J. Chem. Educ. 2012, 89, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinner, M.J.; Grosche, M.; Herdtweck, E.; Thiel, W.R. A Merrifield Resin Functionalized with Molybdenum Peroxo Complexes: Synthesis and Catalytic Properties. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2003, 629, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; Kulkarni, G.M.; Ramesh, C. Mizoroki–Heck reaction, catalysis by nitrogen ligand Pd complexes and activation of aryl bromides. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, T.M.; Hong, F.-E. Palladium(II)-catalyzed Heck reaction of aryl halides and arylboronic acids with olefins under mild conditions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamboulis, A.; Moitra, N.; Moreau, J.J.E.; Cattoen, X.; Man, M.W.C. Hybrid materials: Versatile matrices for supporting homogeneous catalysts. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9322–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, F. Catalyst Immobilization Strategy: Some General Considerations and a Comparison of the Main Features of Different Supports. In Recoverable and Recyclable Catalysts; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 427–461. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.S.; Bao, X.Y.; Guo, W.; Lee, F.Y. Immobilizing catalysts on porous materials. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Garcia, H. Metal-organic frameworks catalyzed C-C and C-heteroatom coupling reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1922–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Toy, P.H. Organic Polymer Supports for Synthesis and for Reagent and Catalyst Immobilization. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 815–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Sun, Q.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Strategies for the design of porous polymers as efficient heterogeneous catalysts: From co-polymerization to self-polymerization. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.; Santora, B.P.; Gagné, M.R. A Polymer-Supported Rhodium Catalyst that Functions in Polar Protic Solvents. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1781–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbeater, N.E.; Marco, M. Preparation of Polymer-Supported Ligands and Metal Complexes for Use in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3217–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boruah, J.J.; Das, S.P.; Ankireddy, S.R.; Gogoi, S.R.; Islam, N.S. Merrifield resin supported peroxomolybdenum(vi) compounds: Recoverable heterogeneous catalysts for the efficient, selective and mild oxidation of organic sulfides with H2O2. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2944–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Uflyand, I.E. Metal Chelate Monomers as Precursors of Polymeric Materials. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2016, 26, 1112–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Uflyand, I.E. Review: Recent advances in the chemistry of metal chelate monomers. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 1468–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Riduan, S.N. Functional porous organic polymers for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulko, I.; Wall, J.; Krajnc, P.; Cameron, N.R. Ultra-High Surface Area Functional Porous Polymers by Emulsion Templating and Hypercrosslinking: Efficient Nucleophilic Catalyst Supports. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Zou, W.; Du, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. Fabrication of micro-mesopores in macroporous poly (formaldehyde-melamine) monoliths via reaction-induced phase separation in high internal phase emulsion template. Polymer 2019, 167, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, T.; Ren, H.; Ma, S.; Cao, D.; Lan, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, F.; Simmons, J.M.; et al. Targeted Synthesis of a Porous Aromatic Framework with High Stability and Exceptionally High Surface Area. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9457–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Dong, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhu, D.; Li, T. The study and application of three highly porous hyper-crosslinked catalysts possessing similar catalytic centers. Polymer 2019, 164, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J. Pore structure of water-wettable hydrophobic resins based on divinylbenzene and methyl acrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.H.; Wilson, L.D. Porous Copolymer Resins: Tuning Pore Structure and Surface Area with Non Reactive Porogens. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh Dastidar, D.; Saha, S.; Chowdhury, M. Porous microspheres: Synthesis, characterisation and applications in pharmaceutical & medical fields. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Russell, T.P. Nanoparticle Assembly at Liquid–Liquid Interfaces: From the Nanoscale to Mesoscale. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alacid, E.; Alonso, D.A.; Botella, L.; Nájera, C.; Pacheco, M.C. Oxime palladacycles revisited: Stone-stable complexes nonetheless very active catalysts. Chem. Rec. 2006, 6, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, D.A.; Nájera, C.; Pacheco, M.C. Oxime Palladacycles: Stable and Efficient Catalysts for Carbon−Carbon Coupling Reactions. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1823–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodja, W.; Leclair, A.; Rull-Barrull, J.; Zammattio, F.; Kutonova, K.V.; Trusova, M.E.; Felpin, F.-X.; Rodriguez-Zubiri, M. The promoting effect of pyridine ligands in the Pd-catalysed Heck–Matsuda reaction. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8855–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnaz, N.; Banik, B.; Das, P. A highly efficient Schiff-base derived palladium catalyst for the Suzuki–Miyaura reactions of aryl chlorides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 2886–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Linert, W. Schiff base-derived homogeneous and heterogeneous palladium catalysts for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 311, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.P.S.; Arantes, L.M.; Kadooca, J.Y.; Carvalho, R.L.; de Fátima, Â.; Sabino, A.A. Palladium Complexes with Tetradentate Schiff Bases or their Corresponding Amines: Synthesis and Application in Heck Reactions. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhade, S.R.; Waghmode, S.B. Phosphine-free Pd–salen complexes as efficient and inexpensive catalysts for Heck and Suzuki reactions under aerobic conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 3423–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, Y. A water-soluble palladium-salen catalyst modified by pyridinium salt showing higher reactivity and recoverability for Heck coupling reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabdian, M.; Nasseri, M.A.; Allahresani, A.; Motavallizadehkakhky, A. Pd salen complex@CPGO as a convenient, effective heterogeneous catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck–Mizoroki cross-coupling reactions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, K.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, R. Magnetite nanoparticles immobilized Salen Pd (II) as a green catalyst for Suzuki reaction. Catal. Comm. 2012, 26, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, X.-J.; He, R. Salen and half-salen palladium(II) complexes: Synthesis, characteriztion and catalytic activity toward Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassagh, B.; Parvis, F.S.; Navidi, M. Pd(II) salen complex covalently anchored to multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a heterogeneous and reusable precatalyst for Mizoroki–Heck and Hiyama cross-coupling reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 29, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoorazm, M.; Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Jabbari, A. A facile preparation of palladium Schiff base complex supported into MCM-41 mesoporous and its catalytic application in Suzuki and Heck reactions. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Soh, S.K.; Shamsuddin, M. Tetradentate N2O2 Chelated Palladium(II) Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Activity towards Mizoroki-Heck Reaction of Aryl Bromides. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiasz, A.; Walas, S.; Trzewik, B.; Grzybek, P.; Zaitz, M.M.; Gawin, M.; Mrowiec, H. Cu(II)-imprinted styrene–divinylbenzene beads as a new sorbent for flow injection-flame atomic absorption determination of copper. Microchem. J. 2009, 93, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J. Thermal, physical and chemical stability of porous polystyrene-type beads with different degrees of crosslinking. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 73, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.-X.; Gong, F.-L.; Wei, W.; Hu, G.-H.; Ma, G.-H.; Su, Z.-G. Porogen effects in synthesis of uniform micrometer-sized poly(divinylbenzene) microspheres with high surface areas. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.H.; Belmar, J.B.; Jeria, S.E.; Urbano, B.F.; Torres, C.C.; Alderete, J.B. Rhodium(I) diphenylphosphine complexes supported on porous organic polymers as efficient and recyclable catalysts for alkene hydrogenation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3398–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, S.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, L.; Liao, B.; Ou, B.; Ding, Y. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked polymer beads with tunable pore morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.V.; Sherrington, D.C.; Snape, C.E. Quantitative Solid State 13C NMR Studies of Highly Cross-Linked Poly(divinylbenzene) Resins. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Banana, K.; Liu, H.Y.; Krause, M.; Yang, M. Cross-Linked Porous Polymer Resins with Reverse Micellar Imprints: Factors Affecting the Porosity of the Polymers. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Kumari, S.; Ray, S. Tuning of Catalytic Property Controlled by the Molecular Dimension of Palladium–Schiff Base Complexes Encapsulated in Zeolite Y. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6636–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.; Tedim, J.; Biernacki, K.; Magalhães, A.L.; Gurman, S.J.; Freire, C.; Hillman, A.R. Structural and electrochemical characterisation of [Pd(salen)]-type conducting polymer films. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7726–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, S.; Falatooni, Z.M.; Asadi, S.; Honarmand, M. Palladium-Schiff Base Complex Immobilized Covalently on Magnetic Nanoparticles as an Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Heck and Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reactions. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, S.; Ghasemzadeh, M.S.; Honarmand, M.; Zarifi, F. Acetamidine–palladium complex immobilized on γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: A novel magnetically separable catalyst for Heck and Suzuki coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44166–44174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgholiloo, H.; Rostamnia, S.; Hassankhani, A.; Khalafy, J.; Baradarani, M.M.; Mahmoudi, G.; Liu, X. Stepwise post-modification immobilization of palladium Schiff-base complex on to the OMS-Cu (BDC) metal–organic framework for Mizoroki-Heck cross-coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtaka, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Teratani, T.; Shimomura, O.; Nomura, R. Linear polystyrene-stabilized PdO nanoparticle-catalyzed Mizoroki-Heck reactions in water. Molecules 2011, 16, 9067–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.; Rivero-Crespo, M.A.; Domínguez, I.; Rubio-Marqués, P.; Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Liu, L.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C.; Boronat, M.; et al. Base-Controlled Heck, Suzuki, and Sonogashira Reactions Catalyzed by Ligand-Free Platinum or Palladium Single Atom and Sub-Nanometer Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajender Reddy, K.; Kumar, N.S.; Surendra Reddy, P.; Sreedhar, B.; Lakshmi Kantam, M. Cellulose supported palladium(0) catalyst for Heck and Sonogashira coupling reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 252, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiviaho, J.; Hanaoka, T.; Kubota, Y.; Sugi, Y. Heterogeneous palladium catalysts for the Heck reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1995, 101, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.G. A unifying mechanism for all high-temperature Heck reactions. The role of palladium colloids and anionic species. Dalton Trans. 2006, 21, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Maddipoti, K.; Das, B.; Ray, S. Palladium–Schiff Base Complexes Encapsulated in Zeolite-Y Host: Functionality Controlled by the Structure of a Guest Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layek, S.; Anuradha; Agrahari, B.; Pathak, D.D. Synthesis and characterization of a new Pd(II)-Schiff base complex [Pd(APD)2]: An efficient and recyclable catalyst for Heck-Mizoroki and Suzuki-Miyaura reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 846, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortea-Pérez, F.R.; Julve, M.; Dikarev, E.V.; Filatov, A.S.; Stiriba, S.-E. Synthesis and structural characterization of well-defined bis(oxamato)palladate(II) precatalysts for Suzuki and Heck reactions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, K.; Salami, R.; Rastegar, S.F.; Roe, S.M. Dithiophosphorus-Palladium Complexes as a Catalyst in the Heck Reaction via Pd(II)/Pd(IV) Catalytic Cycle: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 7822–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.U.; Lakshmidevi, J.; Appa, R.M.; Prasad, S.S.; Narasimhulu, M.; Vijitha, R.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Venkateswarlu, K. Palladium(II)-Porphyrin Complexes as Efficient and Eco-Friendly Catalysts for Mizoroki-Heck Coupling. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 7394–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Label | wt.% | Grain Diameter 1 µm | SBET m2g−1 | Pore Size nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DVB | MA | AIBN | PdAS | ||||
| PdAS(1)-MA | 60 | 38 | 1 | 1 | 184 ± 20 | 586 | 17.0 |
| PdAS(2)-MA | 60 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 196 ± 28 | 665 | 19.7 |
| PdAS(5)-MA | 60 | 34 | 1 | 5 | 227 ± 32 | 671 | 17.3 |
| PdAS(10)-MA | 60 | 29 | 1 | 10 | 272 ± 41 | 754 | 22.3 |
| Label | Pd wt.% | Pd exp/Pd nom | Immobilized PdAS mmol gcat−1 | Binding Energy eV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd 3d5/2 | N 1s | ||||
| PdAS | - | - | - | 338.4 | 400.0 |
| PdAS(1)-MA | 0.36 | 1.3 | 0.034 | 338.0 | 400.4 |
| PdAS(2)-MA | 0.51 | 0.8 | 0.050 | 338.5 | 400.0 |
| PdAS(5)-MA | 0.77 | 0.6 | 0.074 | 338.5 | 400.0 |
| PdAS(10)-MA | 1.38 | 0.5 | 0.132 | 338.3 | 400.4 |
| Catalyst | Conversion % | Selectivity MCIN 1 % | t5% conversion 2 min | ro ×104 mol·L−1min−1 | TOF h−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd(CH3CO2)2 | 100 | 100 | 0.2 | 1280 | 29554 |
| PdAS | 100 | 100 | 6.4 | 40 | 929 |
| PdAS(1)-MA | 58 | 100 | 43.7 | 2 | 137 |
| PdAS(2)-MA | 99 | 100 | 8.3 | 9 | 720 |
| PdAS(5)-MA | 99 | 100 | 2.2 | 67 | 2782 |
| PdAS(10)-MA | 100 | 100 | 1.0 | 265 | 6122 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mella, C.; Torres, C.C.; Pecchi, G.; Campos, C.H. Mesoporous Palladium N,N’-Bis(3-Allylsalicylidene)o-Phenylenediamine-Methyl Acrylate Resins as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Heck Coupling Reaction. Materials 2019, 12, 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162612
Mella C, Torres CC, Pecchi G, Campos CH. Mesoporous Palladium N,N’-Bis(3-Allylsalicylidene)o-Phenylenediamine-Methyl Acrylate Resins as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Heck Coupling Reaction. Materials. 2019; 12(16):2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162612
Chicago/Turabian StyleMella, Claudio, Cecilia C. Torres, Gina Pecchi, and Cristian H. Campos. 2019. "Mesoporous Palladium N,N’-Bis(3-Allylsalicylidene)o-Phenylenediamine-Methyl Acrylate Resins as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Heck Coupling Reaction" Materials 12, no. 16: 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162612
APA StyleMella, C., Torres, C. C., Pecchi, G., & Campos, C. H. (2019). Mesoporous Palladium N,N’-Bis(3-Allylsalicylidene)o-Phenylenediamine-Methyl Acrylate Resins as Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Heck Coupling Reaction. Materials, 12(16), 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162612