Assessing the Damage Tolerance of Out of Autoclave Manufactured Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
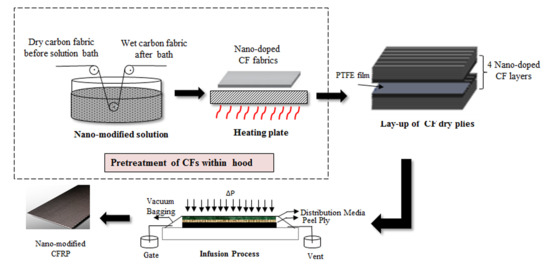
2.2. Work methods
2.2.1. Low Velocity Impact Test
2.2.2. Compression after Impact Test
2.2.3. Non Destructive Inspection (C-Scan)
2.2.4. Optical Microscopy and SEM
3. Results
3.1. Low Velocity Impact Test
3.2. Compression after Impact Test
3.3. Optical Microscopy and SEM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenhalgh, E.; Hiley, M. The assessment of novel materials and processes for the impact tolerant design of stiffened composite aerospace structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.O.W.; Wisheart, M.J. Review of low-velocity impact properties of composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarras, S.; Ghajari, M.; Robinson, P.; Iannucci, L. Performance of composite plates after multi-site impacts. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Composite Materials, Seville, Spain, 23 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Psarras, S.; Munoz, R.; Ghajari, M.; Robinson, P.; Furfari, D. Compression After Multiple Impacts: Modelling and Experimental Validation on Composite Coupon specimens. In Smart Intelligent Aircraft Structures; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Chapter 31; pp. 667–679. ISBN 978-3-319-22412-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mouritz, A.P. Review of z-pinned composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hounslow, L.; Grassi, M. Improvement of low-velocity impact and compression-after-impact performance by z-fibre pinning. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, F. Damage tolerance of a stitched carbon/epoxy laminate. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 28, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daelemans, L.; Cohades, A.; Meireman, T.; Beckx, J.; Spronk, S.; Kersemans, M. Electrospun nanofibrous interleaves for improved low velocity impact resistance of glass fibre reinforced composite laminates. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantzalis, S.; Karapappas, P.; Vavouliotis, A.; Tsotra, P.; Kostopoulos, V.; Tanimoto, T. On the improvement of toughness of CFRPs with resin doped with CNF and PZT particles. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Khan, S.U.; Munir, A.; Kim, J.K. Impact damage resistance of CFRP with nanoclay-filled epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, B.; Guan, J.; Mirjalili, V.; Zhang, Y.; Chun, L.; Hubert, P.; Johnston, A. Enhancement of mechanical performance of epoxy/carbon fibre laminate composites using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, V.; Baltopoulos, A.; Karapappas, P.; Vavouliotis, A.; Paipetis, A. Impact and after-impact properties of carbon fibre reinforced composites enhanced with multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 70, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosur, M.V.; Chowodhury, F.H.; Jeelani, S. Low-velocity impact response and ultrasonic NDE of woven carbon/epoxy_nanoclay nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 2195–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, M.; Tola, C.; Claes, M.; Lomov, S.V.; Verpoest, I.; Gorbatikh, L. Impact and residual after impact properties of carbon fibre/epoxy composites modified with carbon nanotubes. Compos. Struct. 2014, 111, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelakis, S.G.; Katsiropoulos, C.V.; Polydoropoulou, P.V. Assessing the compression after impact behaviour of innovative multifunctional composites. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, R.; Rao, S.; Zhou, J.; Guan, Z.; Cantwell, W.J. The low velocity impact response of nano modified composites manufactured using automated dry fibre placement. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2016, 24, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, R.; Gangireddy, S.; Minaie, B.; Hsiao, K.T. Manufacturing carbon nanofibers toughened polyester/glass fibre composites using vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding for enhancing the mode-I delamination resistance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, Y. Interfacially reinforced methylphenylsilicone resin composites by chemically grafting multiwall carbon nanotubes onto carbon fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 82, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapappas, P.; Tsantzalis, S. Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Chemically Grafted and Physically Adsorpted on Reinforcing Carbon Fibres. Adv. Compos. 2008, 17, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Greef, N.; Zhang, L.; Magrez, A.; Forró, L.; Locquet, J.P.; Verpoest, I.; Seo, J.W. Direct growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fibers: Effect of the CVD parameters on the degradation of mechanical properties of carbon fibers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 51, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resoltech Advanced Technology Resins. Available online: https://www.resoltech.com/en/ (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- RESOLTECH Resin Resolcoat 1400 Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.resoltech.com/en/products/epoxy/1400-detail.html (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- FIBERMAX COMPOSITES. Available online: http://www.fibermaxcomposites.com/shop/?language=gr (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Pyrofil Carbon Fiber Datasheet. Available online: http://mccfc.com/pan-fiber/ (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Nanocyl. Available online: https://www.nanocyl.com (accessed on 9 March 2017).
- Nanocyl Sizing Agent Data Sheet. Available online: http://www.nanocyl.com/product/ (accessed on 9 March 2017).
- ASTM D 5528-01. ASTM International Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 7905/D7905M-14. ASTM International Standard Test Method for Determination of the Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dimoka, P.; Kostagiannakopoulou, C.; Masouras, A.; Kostopoulos, V. Improvement of interlaminar fracture properties of Out of Autoclave manufactured carbon fibre reinforced polymers using multi walled carbon nanotubes. World J. Mech. 2019. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 7136. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D7137. Standard Test Method for Compressive Residual Strength Properties of Damaged Polymer Matrix Composite Plates; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Image J Software. Available online: https://imagej.net/Welcome (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Yokozeki, T.; Iwahori, Y.; Ishiwata, S.; Enomoto, K. Mechanical properties of CFRP laminates manufactured from unidirectional prepregs using CSCNT-dispersed epoxy. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Laminate | MWCNTs Content (wt.%) | Thickness (mm) | Fibre Volume Fraction Vf (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plate 1-Ref. | 0 | 3.93 ± 0.04 | 57 |
| Plate 2-Ref. | 0 | 3.94 ± 0.02 | 57 |
| Plate 3-P15 | 1.5 | 4.05 ± 0.03 | 56 |
| Plate 4-P15 | 1.5 | 4.08 ± 0.03 | 56 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimoka, P.; Psarras, S.; Kostagiannakopoulou, C.; Kostopoulos, V. Assessing the Damage Tolerance of Out of Autoclave Manufactured Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Materials 2019, 12, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071080
Dimoka P, Psarras S, Kostagiannakopoulou C, Kostopoulos V. Assessing the Damage Tolerance of Out of Autoclave Manufactured Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimoka, Polyxeni, Spyridon Psarras, Christine Kostagiannakopoulou, and Vassilis Kostopoulos. 2019. "Assessing the Damage Tolerance of Out of Autoclave Manufactured Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes" Materials 12, no. 7: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071080
APA StyleDimoka, P., Psarras, S., Kostagiannakopoulou, C., & Kostopoulos, V. (2019). Assessing the Damage Tolerance of Out of Autoclave Manufactured Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers Modified with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Materials, 12(7), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071080