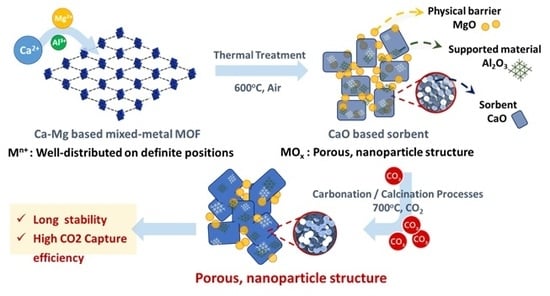
Multi-Metals CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework as CaO-based Sorbent to Achieve Highly CO2 Capture Capacity and Cyclic Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrothermal Synthesis of CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework Nanocrystals
2.3. Characterization
2.4. CO2 Capture Capacity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Character of MOF with Different Ca/Mg Ratios
3.2. Phase and Microstructure of Multi-Metals CaMgAl-MOFs
3.3. Long-term CO2 Carbonation-Calcination Cyclic Performances of Al-Substitution Ca-Mg-MOF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metz, B.; Davidson, O.; de Coninck, H.; Loos, M.; Meyer, L. IPCC Special Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; p. 442. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier Jos, G.J.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Muntean, M.; Peters, J.A.H.W. Trends in Global CO2 Emissions: 2014 Report; PBL Publishers: Hague, Netherland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, R.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.W.; Gao, Y.S.; Wang, Q.; O’Hare, D.; Zhong, Z.Y. Recent advances in solid sorbents for CO2 capture and new development trends. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3478–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramaratne, N.P.; Jaroniec, M. Activated carbon spheres for CO2 adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iruretagoyena, D.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Chadwick, D. Layered double oxides supported on graphene oxide for CO2 adsorption: Effect of support and residual sodium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 26, 6781–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.P.; Zhu, X.M.; Liu, H.L.; Hu, J. Interfacial growth of metal-organic framework/graphite oxide composites through pickering emulsion and their CO2 capture performance in the presence of humidity. Langmuir 2015, 26, 7410–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Seredych, M.; Zhong, Q.; Bandosz, T.J. Superior performance of copper based MOF and aminated graphite oxide composites as CO2 adsorbents at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 11, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.H.; Hudson, M.R.; Mason, J.A.; Queen, W.L.; Dutton, J.J.; Sumida, K.; Micklash, K.J.; Kaye, S.S.; Brown, C.M.; Long, J.R. Evaluation of cation-exchanged zeolite adsorbents for post-combustion carbon dioxide capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckert, N.R.; Yang, R.T. CO2 Capture from the atmosphere and simultaneous concentration using Zeolites and amine-grafted SBA-15. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 23, 10257–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-A.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.-T.; Ahn, W.-S. CO2 capture and conversion using Mg-MOF-74 prepared by a sonochemical method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 4, 6465–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, P.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Burd, S.D.; Cairns, A.J.; Luebke, R.; Forrest, K.; Pham, T.; Ma, S.Q.; Space, B.; Wojtas, L.; et al. Porous materials with optimal adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics for CO2 separation. Nature 2013, 7439, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.B. Hydrothermal synthesis of K2CO3-promoted hydrotalcite from hydroxide-form precursors for novel high-temperature CO2 sorbent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 9, 6914–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Nanoti, A. High temperature CO2 adsorption by mesoporous silica supported magnesium aluminum mixed oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierzkowska, A.M.; Pacciani, R.; Müller, C.R. CaO-based CO2 sorbents: From fundamentals to the development of new, highly effective materials. ChemSusChem 2013, 7, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.P.; Fan, S.S.; Fan, L.J.; Zhao, Y.J.; Ma, X.B. Effect of cerium oxide doping on the performance of CaO-based sorbents during calcium looping cycles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 5021–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sachdeva, S.; Lee, A.K.; Jeong, H.K. Current status of metal–organic framework membranes for gas separations: Promises and challenges. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 5, 2179–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic frameworks as platforms for clean energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1656–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic methods for the functionalization of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 2, 970–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Dai, F.N.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, C.G. The structure-directed effect of Al-based metal–organic frameworks on fabrication of alumina by thermal treatment. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 65, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaj, M.; Mali, G.; Rangus, M.; Zunkovic, E.; Kaucic, V.; Logar, N.Z. Spectroscopic studies of structural dynamics induced by heating and hydration: A case of calcium-terephthalate metal–organic framework. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 15, 7552–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Wu, U.-T.; Lin, H.-P. Cyclic performance of CaCO3@mSiO2 for CO2 capture in a calcium looping cycle. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 22, 8252–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Feng, B.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, G.X.; Barry, J.; da Costa, J.C.D. Synthesis of sintering-resistant sorbents for CO2 capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Z.; Zhang, X.; Jaegers, N.R.; Wan, C.; Graham, T.R.; Hu, M.; Pearce, C.I.; Felmy, A.R.; Clark, S.B.; Rosso, K.M. Transitions in Al coordination during gibbsite crystallization using high-field 27Al and 23Na MAS NMR spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 27555–27562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.H.; Chang, Y.P.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Yu, C.T.; Chyou, Y.P. Synthesis, characterization and high temperature CO2 capture capacity of nanoscale Ca-based layered double hydroxides via reverse microemulsion. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S498–S505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.H.; Huang, W.C.; Lee, T.J.; Chang, Y.P.; Chen, S.Y. Self-reactivated mesostructured Ca–Al–O composite for enhanced high-temperature CO2 capture and carbonation/calcination cycles performance. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Composition (Mole %) | Ca | Mg | Al |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Code | |||
| Ca0.85Mg0.15-MOF | 85 | 15 | 0 |
| Ca0.85Mg0.125Al0.025-MOF | 85 | 12.5 | 2.5 |
| Ca0.85Mg0.075Al0.075-MOF | 85 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Ca0.85Al0.15-MOF | 85 | 0 | 15 |
| Ca0.97Mg0.03-MOF | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| Ca0.97Mg0.025Al0.005-MOF | 97 | 2.5 | 0.5 |
| Ca0.97Mg0.02Al0.01-MOF | 97 | 2 | 1 |
| Ca0.97Mg0.015Al0.015-MOF | 97 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.-C.; Chang, P.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Peng, C.-H. Multi-Metals CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework as CaO-based Sorbent to Achieve Highly CO2 Capture Capacity and Cyclic Performance. Materials 2020, 13, 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102220
Wu S-C, Chang P-H, Lin C-Y, Peng C-H. Multi-Metals CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework as CaO-based Sorbent to Achieve Highly CO2 Capture Capacity and Cyclic Performance. Materials. 2020; 13(10):2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102220
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Szu-Chen, Po-Hsueh Chang, Chieh-Yen Lin, and Cheng-Hsiung Peng. 2020. "Multi-Metals CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework as CaO-based Sorbent to Achieve Highly CO2 Capture Capacity and Cyclic Performance" Materials 13, no. 10: 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102220
APA StyleWu, S. -C., Chang, P. -H., Lin, C. -Y., & Peng, C. -H. (2020). Multi-Metals CaMgAl Metal-Organic Framework as CaO-based Sorbent to Achieve Highly CO2 Capture Capacity and Cyclic Performance. Materials, 13(10), 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102220