Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Samples Preparation
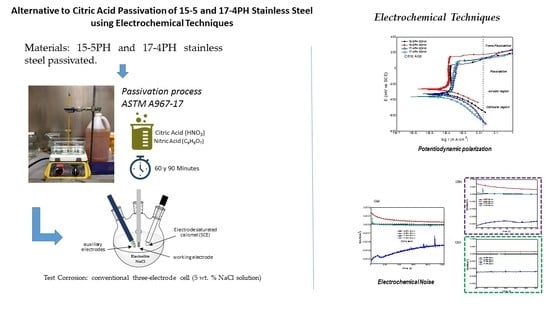
2.2. Passivation Process
2.3. Electrochemical Techniques
2.3.1. Electrochemical Noise (EN)
2.3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization Curves (PPC)
3. Results
3.1. Electrochemical Noise
3.2. Potenciodynamic Polarization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddiqui, T. Aircraft Materials and Analysis; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- ASM International. ASM Handbook; Corrosion Environments and Industries; Cramer, S.D., Covino, B.S., Jr., Eds.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2006; Volume 13, p. 27, Corrosion Environments and Industries. [Google Scholar]
- Schorr, M.; Valdez, B.; Salinas, R.; Ramos, R.; Nedey, N.; Curiel, M. Corrosion control in military assets. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2016, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Banda, M.; Ortiz, D.; Gaoan-Tiburcio, C.; Zambrano, P.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.C.; Almeraya-Calderon, F. Citric Acid Passivation of 15-5PH and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Used in the Aeronautical Industry. In International Materials Research Congress; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, J.C. Material selection for aeronautical structural application. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 2008, 20, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.; Kolody, M. Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of Stainless Steel Alloys. In Technology Evaluation for Environmental Risk Mitigation Compendium, Proceedings of the NASA Technology Evaluation for Environmental Risk Mitigation Principal Center (TEERM); Department od Defense (DoD) and NASA: Merritt Island, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Calle, L.M. Coatings on Earth and Beyond. In Proceedings of the Coatings Summit 2015, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 21–23 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- O’Laoire, C.; Tmmins, B.; Kremer, L.; Holmes, J.D.; Morris, M.A. Analysis of the acid passivation of stainless steel. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 2255–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.O.; Landolt, D. Passive films on stainless steels-chemistry, structure and growth. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasensky, D.; Reali, J.; Larson, C.; Carl, C. Citric acid passivation of stainless steel. In Proceedings of the Aircraft Airworthiness and Sustainment Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, K.H.; Shek, C.H.; Lai, J.K.L. Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2009, 65, 39–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, H.M. The History of Stainless Steel; ASM International: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2010; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.H.; Won, C.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, J.; Lee, C.G. Investigation of the localized corrosion and passive behavior of type 304 stainless steels with 0.2–1.8 wt% B. Materials 2018, 11, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmuki, P. From bacon to barriers: A review on the passivity of metal and alloys. J. Solid State Electr. 2002, 6, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelshehid, M.; Mahmodieh, K.; Mori, K.; Chen, L.; Stoyanov, P.; Davlantes, D.; Foyos, J.; Ogren, J.; Clark, R., Jr.; Es-Said, O.S. On the correlation between fracture toughness and precipitation hardening heat treatments in 15-5PH stainless steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, M.; Dong, H. The corrosion and corrosion–wear behaviour of plasma nitrided 17-4PH precipitation hardening stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Esfandiari, M.; Li, X.Y. On the microstructure and phase identification of plasma nitrided 17-4PH precipitation hardening stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2969–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.N.; Chiou, C.S.; Yang, J.R. Aging reactions in a 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 74, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. Precipitation hardening in metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, C.; Stears, P.; Lawley, A.; Doherty, R. Precipitation Hardening PM Stainless Steels. Adv. Powder Part. 2006, 1, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gaydos, S.P. Passivation of aerospace stainless parts with citric acid solutions. Plat. Surf. Finish. 2003, 90, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, T. Stochastic studies of passivity breakdown. Corros. Sci. 1990, 31, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashassi-Sorkhabi, H.; Seifzadeh, D.; Raghibi-Boroujeni, M. Analysis of electrochemical noise data in both time and frequency domains to evaluate the effect of ZnO nanopowder addition on the corrosion protection performance of epoxy coatings. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1320–S1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isselin, J.; Kasada, R.; Kimura, A. Effects of aluminum on the corrosion behavior of 16% Cr ODS ferritic steels in a nitric acid solution. J. Nucl. Sci. Techmol. 2011, 48, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán, F.H.; Almeraya, F.; Margulis, R.B.; Zamora, M.B.; Martínez, A.; Gaona, C. Transient analysis of electrochemical noise for 316 and duplex 2205 stainless steels under pitting corrosion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, N.; Pujar, M.G.; Sekhar, S.S.; Gopala, K.N.; Mallika, C.; Kamachi, M.U. Evaluation of the Effect of Molybdenum on the Pitting Corrosion Behavior of Austenitic Stainless Steels Using Electrochemical Noise Technique. Corrosion 2017, 73, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragaglia, M.; Cherubini, V.; Cacciotti, I.; Rinaldi, M.; Mori, S.; Soltani, P.; Nanni, F.; Kaciulis, S.; Montesperelli, G. Citric Acid Aerospace Stainless Steel Passivation: A Green Approach. In Proceedings of the CEAS Aerospace Europe Conference 2015, Delft, The Netherlands, 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huet, F. Electrochemical Noise Technique. In Analytical Methods in Corrosion Science and Engineering; Marcus, P., Florian, B., Eds.; Mansfeld CRC Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Chapter 14; pp. 507–570. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, G.U.; Kamachi, M.S. Electrochemical Noise Analysis of Pitting Corrosion of Type 304L Stainless Steel. Corrosion 2014, 70, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homborg, A.M.; Cottis, R.A.; Mol, J.M.C. An integrated approach in the time, frequency and time-frequency domain for the identification of corrosion using electrochemical noise. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarnezhad, B.M.; Neshati, J.; Hossein, S.M. Development of Time-Frequency Analysis in Electrochemical Noise for Detection of Pitting Corrosion. Corrosion 2019, 75, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, A.C.J.; Lucio–Garcia, M.A.; Hermoso-Diaz, I.A.; Chacon-Nava, J.G.; Martínez-Villafañe, A.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J.G. Detection of Sulfide Stress Cracking in a Supermartensitic Stainless Steel by Using Electrochemical Noise. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 6717–6733. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zanki, I.A.; Gill, J.S.; Dawson, J.L. Electrochemical Noise Measurements on Mild Steel in 0.5 M Sulphuric Acid. Mater. Sci. Forum 1986, 8, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Arteaga, C.; Porcayo-Calderón, J. Electrochemical noise analysis in the frequency domain and determination of corrosion rates for SS-304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435–436, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Practice for Cleaning, Descaling and Passivation of Stainless-Steel Parts, Equipment, and Systems; ASTM A380-17; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Standard Specification for Chemical Passivation Treatments for Stainless Steel Parts; ASTM A967-17; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Standard Guide for Electrochemical Noise Measurement; ASTM G199-09; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Mansfeld, F.; Sun, Z. Localization index obtained from electrochemical noise analysis. Corrosion 1999, 55, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Cottis, R.A.; Botana, F.J. Shot noise and statistical parameters for the estimation of corrosion mechanisms. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 3280–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.G.; Inman, M.E.; Hudson, J.L. Analysis of electrochemical noise for type 410 stainless steel in chloride solutions. In Electrochemical Noise Measurement for Corrosion Applications; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Reference Test Method for Making Potentiostaticc and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements; ASTM-G5-13E2; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates from Electrochemical Measurements; ASTM-G102-89; ASTM International: West Conshohoken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Ha, H.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. Limitations in the use of the potentiodynamic polarisation curves to investigate the effect of Zn on the corrosion behaviour of as-extruded Mg–Zn binary alloy. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, R.S. NACE Corrosion Engineers Reference Book, 2nd ed.; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bertocci, U.; Yang-Xiang, Y. An examination of current fluctuations during pit initiation in Fe-Cr alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1984, 131, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Koike, M.; Leigh, S.; Qiu, F.; Yang, G. A statistical analysis of the fluctuations of the passive current. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Handa, T.; Takazawa, H. An analysis of current fluctuations during passive film breakdown and repassivation in stainless alloys. Corros. Sci. 1990, 31, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, T.P.; Wang, A.Y.L.; Earthman, J.C. The effect of heat treatment on the corrosion resistance of 440C stainless steel in 20% HNO3 + 2.5% Na2Cr2O7 solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyn, A.; Goellner, J.; Bierwirth, M.; Klapper, H. Recent applications of electrochemical noise for corrosion testing-Benefits and restrictions. In CORROSION 2007, Proceedings of the Corrosion NACE Expo2007, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 March 2007; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, A.D.; John, G.D.; Dawson, J.L. Corrosion Monitoring. International Patent WO1987007022A1, 19 November 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Brennenstuhl, A.M.; Palumbo, G.; Gonzalez, F.S.; Quirk, P.G. The Use of Electrochemical Noise to Investigate the Corrosion Resistance of UNS Alloy N04400 Nuclear Heat Exchanger Tubes. In Electrochemical Noise Measurement for Corrosion Applications; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Viveros, A.; Garcia-Ochoa, E.; Alazard, D. Comparative electrochemical noise study of the corrosion process of carbon steel by the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio alaskensis under nutritionally rich and oligotrophic culture conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3841–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.; Nathanson, L.; Green, A.G.; Johnson, B.V. The Use of Electrochemical Noise to Assess Inhibitor Film Stability. In UK Corrosion 1992; Institute of Corrosion: Manchester, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell, A.N.; Edgemon, G.L.; Bell, G.E.C. Data Processing for Current and Potential Logging Field Monitoring Systems; CORROSION/1999, paper no. 192; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Girija, U.; Mudali, K.; Khatak, H.S.; Raj, B. The application of electrochemical noise resistance to evaluate the corrosion resistance of AISI type 304 SS in nitric acid. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4051–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homborg, A.M.; Tinga, T.; Van Westing, P.M.; Zhang, X.; Ferrari, G.M.; de Wit, J.H.W.; Mol, J.M.C. A Critical Appraisal of the Interpretation of Electrochemical Noise for Corrosion Studies. Corrosion 2014, 70, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottis, R.A.; Al-Awadhi, M.A.A.; Al-Mazeedi, H.; Turgoose, S. Measures for the detection of localized corrosion with electrochemical noise. Electrochim. Acta. 2001, 46, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurak, T.; Jamali, S.S.; Yue Zhao, Y. Theoretical analysis of electrochemical noise measurement with single substrate electrode configuration and examination of the effect of reference electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 3011, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottis, R.A. Interpretation of Electrochemical Noise Data. Corrosion 2001, 57, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betova, I.; Bojinov, M.; Laitinen, T.; Mäkelä, K.; Pohjanne, P.; Saario, T. The transpassive dissolution mechanism of highly alloyed stainless steels: I. Experimental results and modelling procedure. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 2675–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. The improvement of the corrosion resistance of 309stainless steel in the transpassive region by nano-crystallization. Electrochem. Acta 2009, 54, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.; Dong, C.; Cui, Z.; Xiao, K.; Yu, Q.; Li, X. A comparative study of primary and secondary passive films formed on AM355 stainless steel in 0.1 M NaOH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, M.; Betova, I.; Fabricius, G.; Laitinen, T.; Saario, T. The stability of the passive state of iron–chromium alloys in sulphuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 1999, 41, 1557–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, M.; Fabricius, G.; Kinnunen, P.; Laitinen, T.; Mäkelä, K.; Saario, T.; Sundholm, G. The mechanism of transpassive dissolution of Ni–Cr alloys in sulphate solutions. Electrochem. Acta 2000, 45, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara Banda, M.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Zambrano-Robledo, P.; Cabral, M.J.A.; Estupinan, F.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Almeraya-Calderon, F. Corrosion Behaviour of 304 Austenitic, 15-5PH and 17-4PH Passive Stainless Steels in acid solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 10314–10324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Han, E.H. Electrochemical properties and growth mechanism of passive films on Alloy 690 in high-temperature alkaline environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3444–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calinski, C.; Strehblow, H.H. ISS depth profiles of the passive layer on Fe/Cr alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 36, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnamurty, P.; Adaikkalam, P. pH-potential diagrams at elevated temperatures for the chromium/water systems. Corros. Sci. 1982, 22, 753–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Stainless Steel | Elements | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Nb | Cu | Fe | |
| 15-5PH | 0.024 | 0.817 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 1.569 | 14.410 | 3.937 | 0.383 | 0.308 | 3.558 | Bal. |
| 17-4PH | 0.022 | 0.827 | 0.023 | 0.029 | 1.637 | 15.204 | 3.050 | 0.340 | 0.144 | 3.908 | Bal. |
| Stainless Steel | Citric Acid (C6H8O7) | Nitric Acid (HNO3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passivated Time (min) | ||||
| 60 | 90 | 60 | 90 | |
| 15-5PH | X | X | X | X |
| 17-4PH | X | X | X | X |
| Passivated Agent | Stainless Steel | Time (min) | Rn (Ω/cm2) | icorr (mA/cm2) | LI | Corrosion Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid | 15-5PH | 60 | 8.01 × 10−4 | 6.49 × 10−4 | 0.0862 | Mixed |
| 90 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 1.04 × 10−4 | 0.0308 | Mixed | ||
| 17-4PH | 60 | 5.76 × 10−4 | 4.51 × 10−4 | 0.2492 | Localized | |
| 90 | 3.27 × 10−5 | 1.59 × 10−4 | 0.0900 | Mixed | ||
| Nitric acid | 15-5PH | 60 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 0.1871 | Localized |
| 90 | 1.51 × 10−6 | 1.72 × 10−5 | 0.1077 | Localized | ||
| 17-4PH | 60 | 1.03 × 10−6 | 2.52 × 10−5 | 0.1485 | Localized | |
| 90 | 1.34 × 10−6 | 1.94 × 10−4 | 0.1727 | Localized |
| Passivated Agent | Stainless Steel | Time (Min) | Ecorr (mV) | Epit (mV) | icorr (mA/cm2) | C. R. (mm/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citric Acid | 15-5PH | 60 | −323 | 42 | 5.26 × 10−5 | 5.54 × 10−7 |
| 90 | −266 | 147 | 4.50 × 10−5 | 4.75 × 10−7 | ||
| 17-4PH | 60 | −335 | 91 | 9.22 × 10−5 | 9.64 × 10−7 | |
| 90 | −360 | 97 | 5.38 × 10−5 | 5.63 × 10−7 | ||
| Nitric Acid | 15-5PH | 60 | −228 | 467 | 2.16 × 10−5 | 2.28 × 10−7 |
| 90 | −228 | 765 | 2.27 × 10−5 | 2.39 × 10−7 | ||
| 17-4PH | 60 | −271 | 439 | 3.51 × 10−5 | 3.67 × 10−7 | |
| 90 | −279 | 323 | 4.41 × 10−5 | 4.61 × 10−7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara-Banda, M.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Zambrano-Robledo, P.; Delgado-E, M.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.A.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Estupiñan-López, F.; G. Chacón-Nava, J.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques. Materials 2020, 13, 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122836
Lara-Banda M, Gaona-Tiburcio C, Zambrano-Robledo P, Delgado-E M, Cabral-Miramontes JA, Nieves-Mendoza D, Maldonado-Bandala E, Estupiñan-López F, G. Chacón-Nava J, Almeraya-Calderón F. Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques. Materials. 2020; 13(12):2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122836
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara-Banda, María, Citlalli Gaona-Tiburcio, Patricia Zambrano-Robledo, Marisol Delgado-E, José A. Cabral-Miramontes, Demetrio Nieves-Mendoza, Erick Maldonado-Bandala, Francisco Estupiñan-López, José G. Chacón-Nava, and Facundo Almeraya-Calderón. 2020. "Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques" Materials 13, no. 12: 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122836
APA StyleLara-Banda, M., Gaona-Tiburcio, C., Zambrano-Robledo, P., Delgado-E, M., Cabral-Miramontes, J. A., Nieves-Mendoza, D., Maldonado-Bandala, E., Estupiñan-López, F., G. Chacón-Nava, J., & Almeraya-Calderón, F. (2020). Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques. Materials, 13(12), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122836