Investigation of Phase Transformation of Fe65Ni35 Alloy by the Modified Pulse Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Short Description of Method and Test Bench

3. Sample and Its Investigation Preparation
- during the measuring cycle, the sample face was not shielded from the direct interaction of laser-radiation quanta (without oxides or another coating);
- the interaction of the photons of the laser pulse with atoms and free electrons in the surface layer of the examined sample caused heat fluxes below the surface, which were created separately by these two carriers;
- each time the laser pulse impacted on the material of the tested sample, it positively influenced the ordering of the sample’s structure.
4. Results
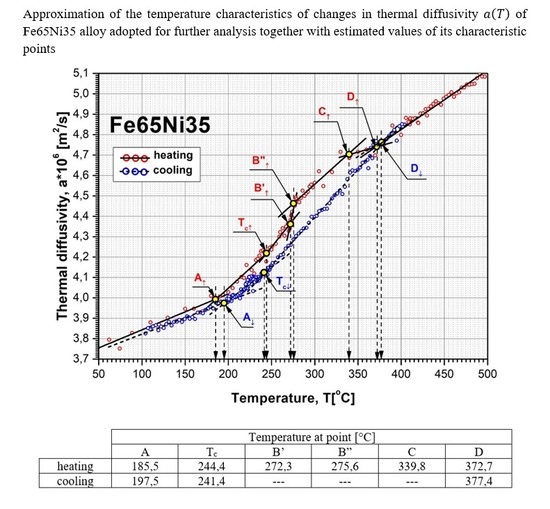
 paramagnetic). The test was carried out on an identical stand as that in [39] during one cycle, including the heating and cooling of the tested sample. Test-bench testing was carried out on a Ni999 sample with a diameter of 12 mm and a thickness of 1.85 mm. The layout of the test bench and the results of these tests are shown in Figure 8.
paramagnetic). The test was carried out on an identical stand as that in [39] during one cycle, including the heating and cooling of the tested sample. Test-bench testing was carried out on a Ni999 sample with a diameter of 12 mm and a thickness of 1.85 mm. The layout of the test bench and the results of these tests are shown in Figure 8.5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, B.; Hu, W. Grain growth and grain size effects on the thermal expansion properties of an electrodeposited Fe–Ni invar alloy. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chong, X.Y.; Zhou, R.; Feng, J. Microstructure and thermal properties of RETaO4 (RE= Nd, Eu, Gd, Dy, Er, Yb, Lu) as promising thermal barrier coating materials. Scr. Mater. 2017, 126, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.; Zayachuk, Y.; Yu, H.; Hofmann, F. Transient grating spectroscopy of thermal diffusivity degradation in deuterium implanted tungsten. Scr. Mater. 2020, 174, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, S.; Bovesecchi, G.; Cataldo, A.; Coppa, P.; Corasaniti, S.; Potenza, M. Transmittance and Reflectance Effects during Thermal Diffusivity Measurements of GNP Samples with the Flash Method. Materials 2019, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, W.J.; Jenkins, R.J.; Butler, C.P.; Abbot, G.L. Flash Method of Determining Thermal Diffusivity, Heat Capacity, and Thermal Conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, J.A.; Lehman, G.W. Temperature and Finite Pulse-Time Effects in the Flash Method for Measuring Thermal Diffusivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.E.; Magliĉ, K.D. Compendium of Thermophysical Property Measurement Methods; Magliĉ, K.D., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 299–454. [Google Scholar]
- Maglic, K.D.; Cezairliyan, A.; Peletsky, V.E. Compendium of Thermophysical Property Measurement Methods—Vol. 2: Recommended Measurement Techniques and Practices; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, T.; Ono, A. Improvement of the laser flash method to reduce uncertainty in thermal diffusivity measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernuschi, F.; Bison, P.G.; Marinetti, S.; Figari, A.; Lorenzoni, L.; Grinzato, E. Comparison of thermal diffusivity measurement techniques. In Proceedings of the QIRT 6th International Conference on Quantitative InfraRed Thermography, Švaić Dubrovnik, Croatia, 24–27 September 2002; Volume 6, pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Vozár, L.; Hohenauer, W. Flash method of measuring the thermal diffusivity, a review. High Temp. High Press. 2003/2004, 35/36, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, H.; Pinto, C.S.C.; Couto, P.; Orlande, H.R.B.; Cotta, R.M. Analysis of flash method physical models for the measurement of thermal diffusivity of solid materials. In Proceedings of the 10th Brazilian Congress of Thermal Sciences and Engineering—ENCIT 2004, ABCM, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 29 November–3 December 2004. Paper CIT04-0537. [Google Scholar]
- Hemberger, F.; Ebert, H.P.; Fricke, J. Determination of the Local Thermal Diffusivity of Inhomogeneous Samples by a Modified Laser-Flash Method. Int. J. Thermophys. 2007, 28, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfield, P.L.; Monde, M.; Mitsutake, Y. On estimating thermal diffusivity using analytical inverse solution for unsteady one-dimensional heat conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2007, 50, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, J.M.; Bagavathiappan, S.; Sardar, M.; Jayakumar, T.; Philip, J.; Raj, B. Measurement of thermal diffusivity of solids using infrared thermography. Mater. Lett. 2008, 63, 2740–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukrainczyk, N. Thermal diffusivity estimation using numerical inverse solution for 1D heat conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2009, 52, 5674–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vălu, O.S.; Staicu, D.; Beneš, O.; Konings, R.J.M.; Lajarge, P. Heat capacity, thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of uranium–americium mixed oxides. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 614, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martin, C.; Torres, C.; Esparza, D.; Bonilla, D. Thermal diffusivity measurements of spherical samples using active infrared thermography. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, K.; Marín, E.; Glorieux, C.; Lara-Bernal, A.; Calderón, A.; Peña Rodríguez, G.; Ivanov, R. Thermal diffusivity measurements in solids by photothermal infrared radiometry: Influence of convection–radiation heat losses. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 98, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Anderko, K. Constitution of Binary Alloys; Graw-Hill Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.A.; Schmid, R.; Lin, J.C. Magnetic Contributions to the Thermodynamic Functions of Alloys and the Phase Equilibria of Fe–Ni System below 1200K. Metall. Trans. A 1986, 17, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.B.; Williams, D.B.; Goldstein, J.I. Determination of the Fe−Ni phase diagram below 400°C. Metall. Trans. A 1989, 20, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.B.; Williams, D.B.; Goldstein, J.I. Ordering in the Fe−Ni system under electron irradiation. Metall. Trans. A 1989, 20, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, L.J.; Itkin, V.P.; Alcock, C.B. The Fe–Ni (Iron–Nickel) System. J. Phase Equilib. 1991, 12, 288–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Williams, D.B.; Goldstein, J.I. A revision of the Fe–Ni phase diagram at low temperatures (<400 °C). J. Phase Equilib. 1996, 17, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.; Dinsdale, A.; Palumbo, M.; Pasturel, A. The Fe–Ni system: Thermodynamic modelling assisted by atomistic calculations. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhang, H.; Vitos, L.; Selleby, M. Magnetic phase diagram of the Fe–Ni system. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silman, G.I. Compilative Fe-Ni phase diagram with author’s correction. Met Sci. Heat Treat. 2012, 54, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, N.Y.; Mevada, A.D.; Gajjar, P.N. Lattice dynamical and thermodynamic properties of FeNi3, FeNi and Fe3Ni invar materials. Comp. Mater Sci. 2016, 123, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zemtsova, N.D. Some discussion topics on the representation of the equilibrium Fe–Ni phase diagram and on the nature of Invar effect. Phys. Uspekhi 2018, 61, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberod, A.; Laugier, J.; Penisson, J.M. Electron Irradiation Effects on Iron Nickel Invar. In Proceedings of the INVAR Symposium, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 September 1978. CEA-COMF-4510. [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann, E. The Invar problem. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 100, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas, M.R.; da Jornada, J.A.H. Effects of annealing processes on the Curie temperature of Fe–Ni Invar alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1991, 3, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorzelli, R.B. A study of phase stability in invar Fe–Ni alloys obtained by non-conventional methods. Hyperfine Interact. 1997, 110, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schilfgaarde, M.; Abrikosov, I.A.; Johansson, B. Origin of the Invar effect in iron–nickel alloys. Nature 1999, 400, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorria, P.; Martnez-Blanco, D.; Blanco, J.A.; Smith, R.I. Neutron powder thermo-diffraction in mechanically alloyed Fe64Ni36 invar alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Uruga, T.; Ishigami, R.; Iwase, A. Effect of 50 keV proton irradiation on the magnetism of a Fe66Ni34 Invar alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2013, 333, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 42Tirsatine, K.; Azzeddine, H.; Huang, Y.; Baudin, T.; Helbert, A.L.; Brisset, F.; Bradai, D.; Langdon, T.G. An EBSD analysis of Fe–36%Ni alloy processed by HPT at ambient and a warm temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 753, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terpiłowski, J.; Rudzki, R.; Szczepaniak, R.; Woroniak, G. Thermal diffusivity investigation of Fe61Ni39, Fe52Ni48 and Fe40Ni60 binary iron–nickel alloys using the modified pulse method. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 657, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpiłowski, J.; Rudzki, R.; Szczepaniak, R.; Woroniak, G. Investigation of thermal diffusivity of Fe80Ni20 alloy by means of modified pulse method. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 560–568. [Google Scholar]
- Terpiłowski, J. A modified flash method for determination of thermal diffusivity in solids. Arch. Thermodyn. 2003, 24, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Terpiłowski, J.; Szczepaniak, R.; Woroniak, G.; Rudzki, R. Adaptation of the modified pulse method for determination of thermal diffusivity of solids in the vicinity of the second-order phase transition points. Arch. Thermodyn. 2013, 34, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Omega Engineering. The Temperature. Handbook and Encyclopedia; Omega Engineering: Stamford, CT, USA, 2000; Available online: www.omega.com (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Material Property Database. MPDB; v. 7.49; JAHM Software 1 nc; JAHM Software: North Reading, UK, 2012; Available online: www.jahm.com (accessed on 30 April 2020).







 paramagnetic).
paramagnetic).
 paramagnetic).
paramagnetic).



| Alloy | Density (kg/m3) | Content, (wt %) | Sample Phase Structure before Experiment (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Fe | Co | Cu | Cr | Al | Zn | Si | Ca | α | γ | |||
| Fe65Ni35 | 12.0/1.89 | 8030 ± 130 | 35.45 | bal. | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 5.69 | 94.31 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terpiłowski, J.; Jóźwiak, S.; Rudzki, R.; Szczepaniak, R.; Woroniak, G. Investigation of Phase Transformation of Fe65Ni35 Alloy by the Modified Pulse Method. Materials 2020, 13, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153425
Terpiłowski J, Jóźwiak S, Rudzki R, Szczepaniak R, Woroniak G. Investigation of Phase Transformation of Fe65Ni35 Alloy by the Modified Pulse Method. Materials. 2020; 13(15):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153425
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerpiłowski, Janusz, Stanisław Jóźwiak, Rafał Rudzki, Robert Szczepaniak, and Grzegorz Woroniak. 2020. "Investigation of Phase Transformation of Fe65Ni35 Alloy by the Modified Pulse Method" Materials 13, no. 15: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153425
APA StyleTerpiłowski, J., Jóźwiak, S., Rudzki, R., Szczepaniak, R., & Woroniak, G. (2020). Investigation of Phase Transformation of Fe65Ni35 Alloy by the Modified Pulse Method. Materials, 13(15), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153425