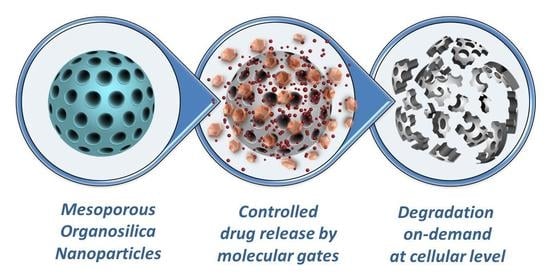
Trends in Degradable Mesoporous Organosilica-Based Nanomaterials for Controlling Drug Delivery: A Mini Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Degradable Non-Porous Organosilica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
2.1. Non-Porous Nanoparticles Containing Sulphide or Oxamide-Based Organosilane Bridges
2.2. Non-Porous Silica Nanoparticles Containing Other Degradable Organo-Bridged Alkoxysilanes
3. Degradable Mesoporous Organo-Bridged Silica Nanoparticles (MONs) for Drug Delivery
3.1. MONs Containing Biocleavable Oxamide or Sulphide-Based Organosilane Bridges
3.2. MONs Containing Other Interesting Biobreakable Organosilane Bridges
3.3. Degradable MONs Grafted with Stimuli-Responsive Molecular Gates
4. Degradable Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas (PMOs) for Drug Delivery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancenõn, F.; Pascual, L.; Oroval, M.; Aznar, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Gated Silica Mesoporous Materials in Sensing Applications. ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine-Recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popplewell, J.F.; King, S.J.; Day, J.P.; Ackrill, P.; Fifield, L.K.; Cresswell, R.G.; Di Tada, M.L.; Liu, K. Kinetics of uptake and elimination of silicic acid by a human subject: A novel application of 32Si and accelerator mass spectrometry. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1998, 69, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Hurley, K.R.; Haynes, C.L. Critical considerations in the biomedical use of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovsky, E.; Baabur-Cohen, H.; Eldar-Boock, A.; Omer, L.; Tiram, G.; Ferber, S.; Ofek, P.; Polyak, D.; Scomparin, A.; Satchi-Fainaro, R. Administration, distribution, metabolism and elimination of polymer therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, R.; Duncan, R. Polymeric carriers: Preclinical safety and the regulatory implications for design and development of polymer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug-delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; MacLachlan, M.J.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G.A. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas with organic groups inside the channel walls. Nature 1999, 402, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Guan, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasaki, O. Novel mesoporous materials with a uniform distribution of organic groups and inorganic oxide in their frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9611–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Mesoporous silica/organosilica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biological effect and biomedical application. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2019, 137, 66–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Voort, P.; Esquivel, D.; De Canck, E.; Goethals, F.; Van Driessche, I.; Romero-Salguero, F. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas: From simple to complex bridges; A comprehensive overview of functions, morphologies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3913–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles: Physical Chemistry, Biosafety, Delivery Strategies, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric sufactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S.Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 90–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatieiev, Y.; Croissant, J.G.; Julfakyan, K.; Deng, L.; Anjum, D.H.; Gurinov, A.; Khashab, N.M. Enzymatically degradable hybrid organic-inorganic bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles for in vitro imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15046–15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleige, E.; Quadir, M.A.; Haag, R. Stimuli-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for the controlled transport of active compounds: Concepts and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 866–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpferich, A. Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, E.; Oroval, M.; Pascual, L.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Gated Materials for On-Command Release of Guest Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 561–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.A.; Padavettan, V. Synthesis of Silica nanoparticles by Sol-Gel: Size-dependent properties, surface modification, and applications in silica-polymer nanocomposites—A Review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 132424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Blaaderen, A.; Van Geest, J.; Vrij, A. Particle Formation and Growth Mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 154, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesche, H. Synthesis of monodispersed silica powders II. Controlled growth reaction and continuous production process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.L.; Mena, S.; Estrela, J.M. Glutathione in cancer cell death. Cancers 2011, 3, 1285–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mekaru, H.; Yoshigoe, A.; Nakamura, M.; Doura, T.; Tamanoi, F. Biodegradability of Disulfide-Organosilica Nanoparticles Evaluated by Soft X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: Cancer Therapy Implications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doura, T.; Nishio, T.; Tamanoi, F.; Nakamura, M. Relationship between the glutathione-responsive degradability of thiol-organosilica nanoparticles and the chemical structures. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.P.H.; Saikia, J.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Ghandehari, H. Redox-Responsive Polysulfide-Based Biodegradable Organosilica Nanoparticles for Delivery of Bioactive Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21133–21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Julfakyan, K.; Lu, J.; Emwas, A.-H.; Anjum, D.H.; Omar, H.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I.; Kashab, N.M. Biodegradable Oxamide-Phenylene-Based Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles with Unprecedented Drug Payloads for Delivery in Cells. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14806–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Gil, M.H.; Simões, P.N. Biodegradable poly(ester amide)s—A remarkable opportunity for the biomedical area: Review on the synthesis, characterization and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1291–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, S.; Teasdale, I. Preparation of polyphosphazenes: A tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5200–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teasdale, I.; Brüggemann, O. Polyphosphazenes: Multifunctional, Biodegradable Vehicles for Drug and Gene Delivery. Polymers 2014, 5, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, M.C. Sol-gel silica nanoparticles in medicine: A natural choice. design, synthesis and products. Molecules 2018, 23, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, I.A.; Vejayakumaran, P.; Sipaut, C.S.; Ismail, J.; Chee, C.K. Size-dependent physicochemical and optical properties of silica nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Y.; Zou, M.-Z.; Zhang, C.-X.; Ma, J.-B.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, W. Fabrication of rapid-biodegradable nano-vectors for endosomal-triggered drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Moghaddam, S.P.H.; Ghandehari, H.; Zharov, I. Synthesis of water-degradable silica nanoparticles from carbamate-containing bridged silsesquioxane precursor. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4914–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggini, L.; Cabrera, I.; Ruiz-Carretero, A.; Prasetyanto, E.A.; Robinat, E.; De Cola, L. Breakable mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7240–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Mauriello-Jimenez, C.; Maynadier, M.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Raehm, L.; Mangin, O.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; Garcia, M.; Gary-Bobo, M.; et al. Synthesis of disulfide-based biodegradable bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles for two-photon imaging and therapy of cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12324–12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Large-pore ultrasmall mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: Micelle/precursor co-templating assembly and nuclear-targeted gene delivery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wan, J.; Niu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Structure-Dependent and Glutathione-Responsive Biodegradable Dendritic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for Safe Protein Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 9008–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Du, W.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Ultrasmall mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: Morphology modulations and redox-responsive biodegradability for tumor-specific drug delivery. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; Luo, S.-Z.; Lu, M.-M.; Shao, D.; Wang, Z.; Dang, W.-F. A comparison of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles as drug vehicles for cancer therapy. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 92, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.L.; Meng, J.; Zhang, D.-D.; Chen, M.-L.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J.-H. Functionalization of mesoporous organosilica nanocarrier for pH/glutathione dual-responsive drug delivery and imaging of cancer therapy process. Talanta 2018, 177, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; He, J.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Qin, X.; Niu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. Gradient Redox-Responsive and Two-Stage Rocket-Mimetic Drug Delivery System for Improved Tumor Accumulation and Safe Chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 8690–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Lao, Y.-H.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Lu, M.; Yue, J.; Hu, H.; et al. Bioinspired Diselenide-Bridged Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Responsive Protein Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratirotjanakul, W.; Suteewong, T.; Polpanich, D.; Tangboriboonrat, P. Amino acid as a biodegradation accelerator of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 282, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchetti, P.; Di Marco, B.N.; Travagline, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ortega-Liebana, M.C.; De Cola, L. Breaking with Light: Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Organosilica Particles. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, G.; Chen, C.S.; Pagano, R.E. Elevated lysosomal pH in mucolipidosis type IV cells. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 280, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Fabrication of biodegradable auto-fluorescent organosilica nanoparticles with dendritic mesoporous structures for pH/redox-responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Kong, C.; Huo, M.; Liu, C.; Peng, L.; Zhao, T.; Wie, Y.; Qian, F.; Yuan, J. Schiff base interaction tuned mesoporous organosilica nanoplatforms with pH-responsive degradability for efficient anti-cancer drug delivery: In Vivo. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9190–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Kim, J.; Yongoh, J.; Choi, H.; Park, M.-H.; Kim, C.; Ryu, J.-H. Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Polymeric Gatekeepers on Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datz, S.; Engelke, H.; Schirnding, C.V.; Nguyen, L.; Bein, T. Lipid bilayer-coated curcumin-based mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for cellular delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 225, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Ha, C.S. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas for advanced applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ding, X.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.-S.; Sun, S. BSA modified, disulfide-bridged mesoporous silica with low biotoxicity for dual-responsive drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 278, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.; Moosa, B.; Alamoudi, K.; Anjum, D.M.; Emwas, A.-H.; El Tall, O.; Vu, B.; Tamanoi, F.; AlMalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Impact of Pore-Walls Ligand Assembly on the Biodegradation of Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5195–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.; Khan, A. Hypersensitive azobenzenes: Facile synthesis of clickable and cleavable azo linkers with tunable and high reducibility. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahikkala, A.; Pereira, S.A.P.; Figueiredo, P.; Passos, M.L.C.; Araújo, A.R.T.S.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S.; Santos, H.A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted and Stimuli-Responsive Delivery of Chemotherapeutics: A Review. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1800020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daurat, M.; Rahmani, S.; Bouchal, R.; Akrout, A.; Budimir, J.; Nguyen, C.; Charnay, C.; Guari, Y.; Richeter, S.; Raehm, L.; et al. Organosilica Nanoparticles for Gemcitabine Monophosphate Delivery in Cancer Cells. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.X.D.; Birault, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Ta, H.K.T.; Intasa-ard, S.G.; Morrison, K.; Thang, P.B.; Doan, T.L.H.; Tamano, F. Biodegradable Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica (BPMO) Loaded with Daunorubicin: A Promising Nanoparticle-Based Anticancer Drug. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poscher, V.; Salinas, Y. Trends in Degradable Mesoporous Organosilica-Based Nanomaterials for Controlling Drug Delivery: A Mini Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173668
Poscher V, Salinas Y. Trends in Degradable Mesoporous Organosilica-Based Nanomaterials for Controlling Drug Delivery: A Mini Review. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173668
Chicago/Turabian StylePoscher, Vanessa, and Yolanda Salinas. 2020. "Trends in Degradable Mesoporous Organosilica-Based Nanomaterials for Controlling Drug Delivery: A Mini Review" Materials 13, no. 17: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173668
APA StylePoscher, V., & Salinas, Y. (2020). Trends in Degradable Mesoporous Organosilica-Based Nanomaterials for Controlling Drug Delivery: A Mini Review. Materials, 13(17), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173668