Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Mimosa albida (Mimosoideae): Characterization and Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
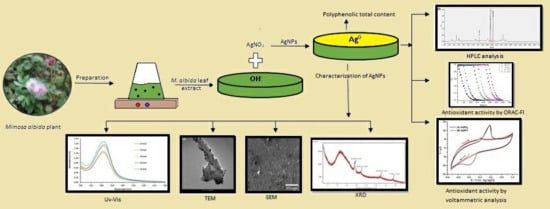
2.1. Preparation of Mimosa Albida Leaf Extract
2.2. Synthesis of M. Albida Silver Nanoparticles (MaAgNPs)
2.3. Characterization of MaAgNPs
2.4. Polyphenolic Total Content
2.5. Phenolic Profile
2.6. Antioxidant Activity by Oxygen radical absorbance capacity-Fluorescein assay ORAC-FL
2.7. Antioxidant Activity by Voltamperommetric Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MaAgNPs
3.2. Polyphenolic Total Content
3.3. Phenolic Profile
3.4. Antioxidant Activity by ORAC-FL
3.5. Antioxidant Activity by Voltammetric Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MaAgNPs
4.2. Polyphenolic Total Content
4.3. Phenolic Profile
4.4. Antioxidant Activity by ORAC-FL
4.5. Antioxidant Activity by Voltammetric Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evanoff, D.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.; Saad, O.; Rashed, H.; Hessen, O.; Elgamal, K.; Aboelfetouh, M. Alternative green chemistry methods of silver nanoparticles synthesis: Review and comparison. J. Bionanoscience 2017, 11, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haqq, S.; Chattree, A. A review: A green approach for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial applications. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Mohanta, B.; Pandey, P.; Singha, M.; Nasiri, F. Optical and antibacterial properties of synthesised silver nanoparticles. Micro Nano Lett. 2017, 12, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhler, J.S.; Sim, W.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Cooper, M.A.; Ziora, Z.M. Silver bullets: A new lustre on an old antimicrobial agent. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sim, W.; Barnard, R.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Ziora, Z. Antimicrobial silver in medicinal and consumer applications: A patent review of the past decade (2007–2017). Antibiotics 2018, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Güzel, R.; Erdal, G. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. In Silver Nanoparticles-Fabrication, Characterization and Applications; Intech Open: Rajasthan, India, 2018; ISBN 9789537619992. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, H.; Patel, A.; Chen, Z.S.; Chen, G. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and therapeutic applications. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, A.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasiri, J.; Rahimi, M.; Hamezadeh, Z.; Motamedi, E.; Naghavi, M.R. Fulfillment of green chemistry for synthesis of silver nanoparticles using root and leaf extracts of Ferula persica: Solid-state route vs. solution-phase method. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitesh; Lata, S. Green Chemistry Based Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Floral Extract of Nelumbo Nucifera. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 6227–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, S.; Tahir, B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwel, P.; Küünal, S.; Ferdov, S.; Rauwel, E. A Review on the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Morphologies Studied via TEM. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaraj, P.; Kumari, P.; Aarti, C.; Renganathan, A. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using cannonball leaves and their cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 cell line. J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 2013, 598328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Das, T.K. Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles-A Review. Int. J. Plant Biol. Res. 2015, 3, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, M. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorescu, A.; Ion, R.; Nuţă, A.; Bunghez, I. A review on the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 4th Global Virtual Conference, Žilina, Slovakia, 6–10 June 2016; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S. Antioxidants and their role in biological functions: An overview. Indian Drugs 2003, 40, 501–516. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, R.; Cao, G.; Martin, A.; Sofic, E.; McEwen, J.; O’Brien, C.; Lischner, N.; Ehlenfeldt, M.; Kalt, W.; Krewer, G.; et al. Antioxidant Capacity As Influenced by Total Phenolic and Anthocyanin Content, Maturity, and Variety of Vaccinium Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirwaikar, A.; Rajendran, K.; Kumar, C. In vitro antioxidant studies of Annona squamosa Linn. leaves. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 42, 803–807. [Google Scholar]
- Mantena, S.K.; Jagadish; Badduri, S.R.; Siripurapu, K.B.; Unnikrishnan, M.K. In vitro evaluation of antioxidant properties of Cocos nucifera Linn. water. Nahr. Food 2003, 47, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, M.; Chávez, J.; Plaza, N.; Wessel, M. Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity in organically and conventionally grown eggplant (Solanum melongena) fruits following thermal processing. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lizcano, L.; Bakkali, F.; Begoña, M.; Ignacio, J. Antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of aqueous extracts from Colombian Amazonian plants with medicinal use. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, R. Phenolic Antioxidant Capacity: A Review of the State of the Art. In Phenolic Compounds-Biological Activity; InTech: Texcoco, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kähkönen, M.; Hopia, A.; Vuorela, H.; Rauha, J.; Pihlaja, K.; Kujala, T.; Heinonen, M. Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, D. Compuestos fenólicos en los alimentos y sus efectos sobre la salud II. In Antioxidantes Y Prevención Del Cáncer; InTech: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1992; pp. 54–71. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, S.; Shivprasad, H.; Kshama, D. In vitro antioxidant screening models: A review. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2004, 38, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, H.; Hussain, G.; Mustafa, I. Antioxidants from Natural Sources. In Antioxidants in Foods and Its Applications; InTech: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scroccarello, A.; Della Pelle, F.; Neri, L.; Pittia, P.; Compagnone, D. Silver and gold nanoparticles based colorimetric assays for the determination of sugars and polyphenols in apples. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyürek, M.; Güngör, N.; Baki, S.; Güçlü, K.; Apak, R. Development of a silver nanoparticle-based method for the antioxidant capacity measurement of polyphenols. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8052–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, D.; González, M.; Escarpa, A. Nanoparticles as analytical tools for in-vitro antioxidant-capacity assessment and beyond. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scampicchio, M.; Wang, J.; Blasco, A.; Sanchez, A.; Mannino, S.; Escarpa, A. Nanoparticle-based assays of antioxidant activity. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Moreira, E.; Andrade, P.; Valentão, P.; Romano, A. Effect of in vitro gastrointestinal digestion on the total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of wild Mediterranean edible plant extracts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoc, Y.; Lyubenova, L.; Grausgruber, H.; Janovská, D.; Yazici, A.; Cakmak, I.; Gozuacik, D. Minor cereals exhibit superior antioxidant effects on human epithelial cells compared to common wheat cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 85, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, O.; Samaras, Y.; Gatidou, G.; Thomaidis, N.; Stasinakis, A. Review on fresh and dried figs: Chemical analysis and occurrence of phytochemical compounds, antioxidant capacity and health effects. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 244–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.; Ba, G.; Mathe, G. Polyphenols: Do they play a role in the prevention of human pathologies? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Chavarria, D.; Borges, F.; Wojtczak, L.; Wieckowski, M.; Karkucińska-Wieckowska, A.; Oliveira, P. Dietary polyphenols and mitochondrial function: Role in health and disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 24, 3376–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oreopoulou, A.; Tsimogiannis, D.; Oreopoulou, V. Extraction of polyphenols from aromatic and medicinal plants: An overview of the methods and the effect of extraction parameters. In Polyphenols in Plants; Academic Press: Athens, Greece, 2019; pp. 243–259. ISBN 9780128137680. [Google Scholar]
- El Gharras, H. Polyphenols: Food sources, properties and applications—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Pelle, F.; Scroccarello, A.; Sergi, M.; Mascini, M.; Del Carlo, M.; Compagnone, D. Simple and rapid silver nanoparticles based antioxidant capacity assays: Reactivity study for phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilaquinga, F.; Morejón, B.; Ganchala, D.; Morey, J.; Piña, N.; Debut, A.; Neira, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum Mammosum L. (Solanaceae) fruit extract and their larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borase, H.; Salunke, B.; Salunkhe, R.; Patil, C.; Hallsworth, J.; Kim, B.; Patil, S. Plant extract: A promising biomatrix for ecofriendly, controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Kaur, A. Phytochemical analysis of crude plant extracts and laboratory synthesized green nanoparticles from Acacia auriculiformis A Cunn. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Nano Sci. 2016, 5, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Thangam, Y.; Govindasamy, C.; Shiranjivi, C. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesis froma acacia nilotica plant leaf. World J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 7, 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Saratale, R.; Saratale, G.; Cho, S.; Ghodake, G.; Kadam, A.; Kumar, S.; Mulla, S.; Kim, D.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Chang, J.S.; et al. Phyto-fabrication of silver nanoparticles by Acacia nilotica leaves: Investigating their antineoplastic, free radical scavenging potential and application in H2O2 sensing. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 99, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, K.; Moncada, M.; Morales, J.; Barriga, G.; Navarrete, P.; Núñez, L.; Squella, J.; Olea, C. Synthesis and antioxidant study of new polyphenolic hybrid-coumarins. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaguaña, D. Síntesis Y Caracterización de Nanopartículas de Plata Usando Como Reductor Químico El Extracto Acuoso de las Hojas d e Sensitiva (Mimosa Albida); PUCE: Quito, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marimuthu, S.; Rahuman, A.; Rajakumar, G.; Santhoshkumar, T.; Kirthi, A.; Jayaseelan, C.; Bagavan, A.; Zahir, A.; Elango, G.; Kamaraj, C. Evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, V.; Kumar, N.; Suguna, M.; Asif, M.; Al-Ghurabi, E.; Huang, Z.; Zhen, Z. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Mimosa pudica plant root extract: Characterization, antibacterial activity and electrochemical detection of dopamine. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 9959–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, P.; León, S. Catalogue of the Vascular Plants of Ecuador; Missouri Botanical Garden: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1999; pp. 1–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kadhemy, M.F.H.; Nawaf, S.H. Investigations the effect of eosin b dye on x- ray diffraction pattern of silver nitrate doped pvp films. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 2017, 27, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theivasanthi, T.; Alagar, M. Electrolytic synthesis and characterization of silver nanopowder. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2012, 4, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.; Anwar, F.; Janjua, M.R.S.A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Rashid, U. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through reduction with Solanum xanthocarpum L. berry extract: Characterization, antimicrobial and urease inhibitory activities against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9923–9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Williamson, G. Methods in Polyphenol Analysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: Oeiras, Portugal, 2003; ISBN 0854045805. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, U.; Abdullah, N.; Bakar, B.; Itam, K.; Abdullah, F.; Sukari, M. Flavonoid glycosides in the leaves of Mimosa species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 4, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, S.; Shoaib Khan, H.; Anwar, Z.; Talbot, B.; Walsh, J. HPLC profiling of Mimosa pudica polyphenols and their non-invasive biophysical investigations for anti-dermatoheliotic and skin reinstating potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nery, N.; Quirino, B.; As Graças, A. Exploring the Chemistry of Natural Products and Biological Properties of Mimosa Linnaeus Genus (FABACEAE-MIMOSOIDADE). Rev. Virtual Química 2019, 11, 970–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, W.L.; Zhou, J.; Yang, P. Studies on the active components and antioxidant activities of the extracts of Mimosa pudica Linn. from southern China. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, J.; Johnson, E.; DiLabio, G. Predicting the activity of phenolic antioxidants: Theoretical method, analysis of substituent effects, and application to major families of antioxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głód, B.; Czapski, G.; Haddad, P. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography to the investigation of free radical reactions in biological systems. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech, A.; Gavara, R.; Hernández, P.; Domínguez, I. Contact probe voltammetry for in situ monitoring of the reactivity of phenolic tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.) compounds with ROS. Talanta 2015, 144, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.; Faulkner, L.; Leddy, J.; Zoski, C. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]











| Element | C | O | Na | Mg | S | K | Ca | Ag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norm. wt% | 68.22 | 25.50 | 3.50 | 0.44 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 0.44 | 0.44 |
| σ | 7.34 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.08 |
| Sample | Total Polyphenol (Mg GAE 100 g−1 Dry Mass) |
|---|---|
| M. albida extract | 1320.4 ± 17.6 |
| MaAgNPs | 257.3 ± 5.1 |
| Sample | ORAC-FL (µmol TE/g of Extract) |
|---|---|
| M. albida extract | 86,917 ± 6287 |
| MaAgNPs | 7563 ± 967 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilaquinga, F.; Amaguaña, D.; Morey, J.; Moncada-Basualto, M.; Pozo-Martínez, J.; Olea-Azar, C.; Fernández, L.; Espinoza-Montero, P.; Jara-Negrete, E.; Meneses, L.; et al. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Mimosa albida (Mimosoideae): Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Materials 2020, 13, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030503
Pilaquinga F, Amaguaña D, Morey J, Moncada-Basualto M, Pozo-Martínez J, Olea-Azar C, Fernández L, Espinoza-Montero P, Jara-Negrete E, Meneses L, et al. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Mimosa albida (Mimosoideae): Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Materials. 2020; 13(3):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030503
Chicago/Turabian StylePilaquinga, Fernanda, Dennis Amaguaña, Jeroni Morey, Mauricio Moncada-Basualto, Josué Pozo-Martínez, Claudio Olea-Azar, Lenys Fernández, Patricio Espinoza-Montero, Eliza Jara-Negrete, Lorena Meneses, and et al. 2020. "Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Mimosa albida (Mimosoideae): Characterization and Antioxidant Activity" Materials 13, no. 3: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030503
APA StylePilaquinga, F., Amaguaña, D., Morey, J., Moncada-Basualto, M., Pozo-Martínez, J., Olea-Azar, C., Fernández, L., Espinoza-Montero, P., Jara-Negrete, E., Meneses, L., López, F., Debut, A., & Piña, N. (2020). Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Mimosa albida (Mimosoideae): Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Materials, 13(3), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030503