Effective Elimination of Contaminant Antibiotics Using High-Surface-Area Magnetic-Functionalized Graphene Nanocomposites Developed from Plastic Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Preparation of Graphenic Materials
2.3. Characterization of Graphenic Materials
2.4. Adsorption Tests
2.5. Efficiency of Garamycin and Ampicillin Adsorption
2.6. Adsorption Optimization
2.7. Kinetics and Isotherm Modeling
2.8. Adsorption–Desorption Test for MSG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Graphenic-Based Materials
3.2. Effect of Solution pH on the Surface Chemistry
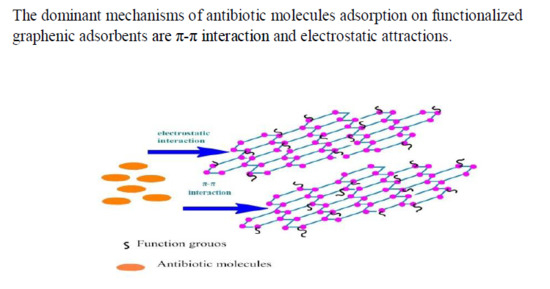
3.3. Speculations on the Adsorption Mechanism
3.4. Efficiency of Garamycin and Ampicillin Adsorption
3.5. Optimization of Adsorption
3.6. Adsorption Kinetic Models
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
3.8. Adsorption–Desorption Test for MSG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, X.; Cai, W.; Lan, R.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous removal of amoxicillin, ampicillin and penicillin by clay supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, S.M.; Quinn, D.J.; Ingram, R.J.; Gilmore, B.F.; Donnelly, R.F.; Taggart, C.C.; Scott, C.J. Gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles show improved antimicrobial effects towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4053–4063. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D. Gentamicin removal in submerged fermentation using the novel fungal strain Aspergillus terreus FZC3. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamma, P.D.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Maragakis, L.L. Combination therapy for treatment of infections with gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 450–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R. Removal of ampicillin sodium in solution using activated carbon adsorption integrated with H2O2 oxidation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Behzadi, S.; Sekhavatjou, M.S. Optimizing Fenton process for the removal of amoxicillin from the aqueous phase using Taguchi method. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 6604–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Sodhi, K.K.; Shree, P.; Singh, D.K.; Agrawal, P.K.; Shukla, P. Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, H.; Li, Z.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D.; Xue, J. Biodegradation of gentamicin by bacterial consortia AMQD4 in synthetic medium and raw gentamicin sewage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcelino, R.B.P.; Andrade, L.N.; Starling, M.C.V.M.; Amorim, C.C.; Barbosa, M.L.T.; Lopes, R.P.; Reis, B.G.; Leão, M.M.D. Evaluation of aerobic and anaerobic biodegradability and toxicity assessment of real pharmaceutical wastewater from industrial production of antibiotics, Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Benab, Y.; Caixia, F.C.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Wong, M.H.; Zheng, C. Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, A.; Haghighat, F.; Chen, Z.; Yerushalmi, L. Sonocatalytic removal of ampicillin by Zn(OH)F: Effect of operating parameters, toxicological evaluation and by-products identification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Dai, J.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wan, J.; Xu, P.; et al. Co-occurrence and interactions of pollutants, and their impacts on soil remediation-A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1528–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Dai, J.; Liang, J.; Yu, J.; Ren, X.; Yi, H.; Cheng, M.; et al. Biological technologies for the remediation of co-contaminated soil. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Shan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Adsorption of antibiotics from aqueous solution by different aerogels. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 505, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bao, D.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Qu, L.; Li, H. Removal of Antibiotics From Water with an All-Carbon 3D Nanofiltration Membrane. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorsandi, H.; Teymori, M.; Aghapour, A.A.; Jafari, S.J.; Taghipour, S.; Bargeshadi, R. Photodegradation of ceftriaxone in aqueous solution by using UVC and UVC/H2O2 oxidation processes. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Gouda, M.H.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; El-Shazly, Y.M.S.; Farag, H.A. Development of grafted cotton fabrics ions exchanger for dye removal applications: Methylene blue model. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 1, 22049–22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liu, N.; Liu, S. Graphene and graphene-based nanocomposites used for antibiotics removal in water treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, N.; Lin, Y.F.; Labrugere, C.; Le Grognec, E.; Rataboul, F.; Felpin, F. Practical and scalable synthesis of sulfonated grapheme. Carbon 2016, 96, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, B. Sulfonated Graphene Nanosheets as a Superb Adsorbent for Various Environmental Pollutants in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7364–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upare, P.P.; Yoon, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Kang, H.; Hwang, D.W.; Hwang, Y.K.; Kung, H.H.; Chang, J. Chemical conversion of biomass-derived hexose sugars to levulinic acid over sulfonic acid-functionalized graphene oxide catalysts. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2935–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Deng, S. A new approach towards acid catalysts with high reactivity based on graphene nanosheets. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.M.; Russo, P.A.; Wiper, P.V.; Veiga, J.M.; Pillinger, M.; Mafra, L.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Pinna, N.; Valente, A.A. Sulfonated graphene oxide as effective catalyst for conversion of 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furfural into biofuels. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L.; Meng, X.; Qi, C.; Xiao, F.S. Sulfated graphene as an efficient solid catalyst for acid-catalyzed liquid reactions. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5495–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Sulfonated graphene as water-tolerant solid acid catalyst. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; He, L.; Yang, H.Y. Large scale synthesized sulphonated reduced graphene oxide: A high performance material for electrochemical capacitors. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14954–14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. Etherification of glycerol with isobutene on sulfonated graphene: Reaction and separation. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4669–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Sun, D.D.; Ng, W.J. Multifunctional nanostructured membrane for clean water reclamation from wastewater with various Ph conditions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15202–15210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Jiang, L.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Sulfonated Graphene for Persistent Aromatic Pollutant Management. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3959–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of 1-naphthol adsorption from aqueous solution to sulfonated graphene nanosheets. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, J.; Shi, Z.; Lian, M.; Tian, M.; Yin, J. Preparation and characterization of sulfonated graphene-enhanced poly (vinyl alcohol) composite hydrogel and its application as dye absorbent. Polymer 2015, 60, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Abdi, G.; Khodaei, M.M. Graphene oxide/Fe3O4/SO3H nanohybrid: A new adsorbent for adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, A.; Zeng, G.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution using sulfonated magnetic graphene oxide composite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Lv, S.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, F. Removal of Organic Dyes in Environmental Water onto Magnetic-Sulfonic Graphene Nanocomposite. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Hu, X.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M. Adsorption behavior of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution onto magnetic graphene oxide functionalized with 1,2-diaminocyclohexanetetraacetic acid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Essawy, N.A.; Konsowa, A.H.; Elnouby, M.; Farag, H.A. A novel one-step synthesis for carbon-based nanomaterials from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles waste. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Essawy, N.A.; Ali, S.M.; Farag, H.A.; Konsowa, A.H.; Elnouby, M.; Hamad, H.A. Green synthesis of graphene from recycled PET bottle wastes for use in the adsorption of dyes in aqueous solution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, H.; Golestanzadeh, M. Highly sulfonated graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets as heterogeneous nanocatalysts in green synthesis of bisphenolic antioxidants under solvent free conditions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56475–56488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jin, P.; Lei, W.; La, P.; Du, X.; Zhang, D. One-pot method fabrication of superparamagnetic sulfonated polystyrene/Fe3O4/graphene oxide micro-nano composites. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Gouda, M.H.; Youssef, M.E.; El-Shazly, Y.M.S.; Farag, H.A. Removal of Methylene Blue by Amidoxime Polyacrylonitrile-Grafted Cotton Fabrics: Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Simulation Studies. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamud, H.; Ivanov, P.; Russell, B.C.; Regan, P.H.; Ward, N.I. Selective sorption of uranium from aqueous solution by graphene oxide-modified materials. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 316, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naeem, H.; Ajmal, M.; Muntha, S.; Ambreen, J.; Siddiq, M. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide sheets integrated with gold nanoparticles and their applications to adsorptive removal and catalytic reduction of water contaminants. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 3599–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Box, G.; Behnken, D.W. Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 1960, 2, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajootan, E.; Arami, M.; Rahimdokht, M. Application of carbon nanotubes coated electrodes and immobilized TiO2 for dye degradation in a continuous photocatalyticelectro-fenton process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 16261–16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; Tong, L.; Su, R.; He, Z. Hydrolysis of cellulose by sulfonated magnetic reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Li, W.; Ju, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q. One-pot synthesis of sulfonated graphene oxide for efficient conversion of fructose into HMF. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104016–104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghi, H.; Javanbakht, M.; Bagheri, A.; Salarizadeh, P.; Ghafarian-Zahmatkesh, H.; Kashefic, S.; Kowsaria, E. Novel nanocomposite membranes based on blended sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/poly(vinyl alcohol) containing sulfonated graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanosheets for DMFC applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74054–74064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Kong, L.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H. Magnetic ferrous-doped graphene for improving Cr (VI) removal. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wuc, Y.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Wanga, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole decorated reduced graphene oxide–Fe3O4 magnetic composites and its application for the Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Basko, D.M. Raman spectroscopy as a versatile tool for studying the properties of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A.; Memon, F.A.; Gomez, D.E.; Horsell, D.W.; Zhang, S. A facile synthesis of porous graphene for efficient water and wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Feng, C.; Gao, Y.J.; Ma, X.X.; Wu, Q.H.; Wang, Z. Preparation of a Graphene-Based Magnetic Nanocomposite for the Removal of an Organic Dye from Aqueous Solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T.M.; Fachikov, L.; Hristov, J. The Magnetite as Adsorbent for Some Hazardous Species from Aqueous Solutions: A Review. Int. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2011, 3, 134–152. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. The role of graphene oxide and graphene oxide-based nanomaterials in the removal of pharmaceuticals from aqueous media: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7938–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.L.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.R.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zhu, D.Q. Adsorption of Sulfonamide Antibiotics to Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11608–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Chen, L.; Que, C.; Yang, K.; Deng, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, G.; Wu, M. Adsorption of Antibiotics on Graphene and Biochar in Aqueous Solutions Induced by π-π Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Carbon-based nanomaterials for removal of chemical and biological contaminants from water: A review of mechanisms and applications. Carbon 2015, 91, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairi, V.; Medda, L.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Adsorption and release of ampicillin antibiotic from ordered mesoporous silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, E.C.; Correa, G.G.; Brambilla, R.; dos Santos, J.H.Z.; Fisch, A.G. Selective silica-based sorbent materials synthesized by molecular imprinting for adsorption of pharmaceuticals in aqueous matrices. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola Del Vecchio, A.; Haro, N.K.; Souza, F.S.; Marcílio, N.R.; Féris, L.A. Ampicillin removal by adsorption onto activated carbon: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; He, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced Removal of Antibiotic in Wastewater Using Liquid Nitrogen-Treated Carbon Material: Material Properties and Removal Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Kinetic Models Parameters | Garamycin Starting Concentration (mg L−1) Adsorbed on MSG | Ampicillin Starting Concentration (mg L−1) Adsorbed on SG | ||||
| 100 | 500 | 900 | 100 | 500 | 900 | |
| qe,exp (mg/g) * | 50 | 242 | 411 | 50 | 226 | 378 |
| Pseudo-1st-order | ||||||
| qe’cal(mg/g) | 6.6 | 51.9 | 139.7 | 3.4 | 28.6 | 224.8 |
| k1(min−1) | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| R2 | 0.991 | 0.984 | 0.982 | 0.993 | 0.961 | 0.984 |
| Pseudo-2nd-order | ||||||
| qe,cal(mg/g) | 50 | 245 | 414 | 50.2 | 235 | 383 |
| k2(min−1) | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.993 |
| Garamycin Adsorption on MSG | Ampicillin Adsorption on SG | |||||
| Temperature (°C) | 25 °C | 35 °C | 25 °C | 35 °C | ||
| Langmuir isotherm | ||||||
| qm (mg/g) | 456.6 | 473.9 | 500 | 384.6 | ||
| kL(L/mg) | 0. 113 | 0.547 | 0.04 | 0.65 | ||
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.995 | ||
| RL | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.002 | ||
| Freundlich isotherm | ||||||
| KF(mg/g) | 61.6 | 88.6 | 79.04 | 123.3 | ||
| 1/nF | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.3 | 0.2 | ||
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.996 | ||
| Adsorbent Nanomaterials | Adsorbate | Optimum Adsorption Condition (Temperature °C, pH) | Adsorbate Initial Concentration (mg L−1) | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicas (SILs) | Garamycin | ------ | 478 | 49.42 | [60] |
| silica matrices (SBA-15-NH2) | Ampicillin | 25, 7.4 | ------ | 333 | [59] |
| Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) | Ampicillin | 25, 6 | 750 | 12.7 | [61] |
| Carbon Materials (CM2) Nitrogen Treated Carbon Materials (CM1) | Ampicillin | 25, 7 | 1048 1048 | 206 178 | [62] |
| HRGO | Garamycin | 25, 6 | 500 | 232.5 | This work |
| Ampicillin | 25, 6 | 500 | 235 | This work | |
| SG | Garamycin | 25, 5.5 | 500 | 170 | This work |
| Ampicillin | 25, 5.5 | 500 | 233.75 | This work | |
| MSG | Garamycin | 25, 5.5 | 500 | 240 | This work |
| Ampicillin | 25, 5.5 | 500 | 183.5 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elessawy, N.A.; Gouda, M.H.; M. Ali, S.; Salerno, M.; Eldin, M.S.M. Effective Elimination of Contaminant Antibiotics Using High-Surface-Area Magnetic-Functionalized Graphene Nanocomposites Developed from Plastic Waste. Materials 2020, 13, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071517
Elessawy NA, Gouda MH, M. Ali S, Salerno M, Eldin MSM. Effective Elimination of Contaminant Antibiotics Using High-Surface-Area Magnetic-Functionalized Graphene Nanocomposites Developed from Plastic Waste. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071517
Chicago/Turabian StyleElessawy, Noha A., M. H. Gouda, Safaa M. Ali, M. Salerno, and M. S. Mohy Eldin. 2020. "Effective Elimination of Contaminant Antibiotics Using High-Surface-Area Magnetic-Functionalized Graphene Nanocomposites Developed from Plastic Waste" Materials 13, no. 7: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071517
APA StyleElessawy, N. A., Gouda, M. H., M. Ali, S., Salerno, M., & Eldin, M. S. M. (2020). Effective Elimination of Contaminant Antibiotics Using High-Surface-Area Magnetic-Functionalized Graphene Nanocomposites Developed from Plastic Waste. Materials, 13(7), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071517