The Mould War: Developing an Armamentarium against Fungal Pathogens Utilising Thymoquinone, Ocimene, and Miramistin within Bacterial Cellulose Matrices
Abstract
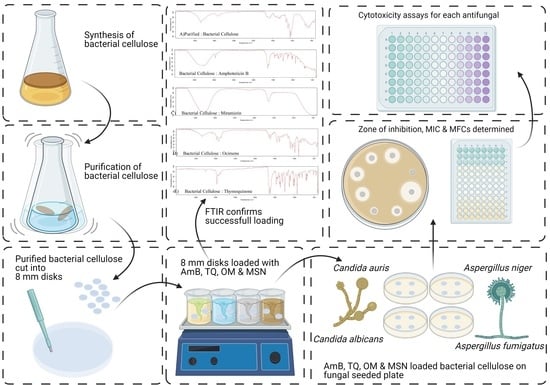
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Media and Reagents
2.2. Microorganisms
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Fungal Starter Cultures
2.5. Production and Purification of Bacterial Cellulose
2.6. Preparation of Working Solutions and Loading of Antifungal Agents
2.7. Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC)
2.8. Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC)
2.9. Quantification of Loaded Compound in BC
2.10. Zone of Inhibition (ZOI)
2.11. Cytotoxicity
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.13. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of BC Hydrogels and Characterisation
3.2. Antifungal Studies
3.3. Cytotoxicity Studies
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swingler, S.; Gupta, A.; Gibson, H.; Kowalczuk, M.; Heaselgrave, W.; Radecka, I. Recent Advances and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose in Biomedicine. Polymers 2021, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Briffa, S.M.; Swingler, S.; Gibson, H.; Kannappan, V.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M.M.; Martin, C.; Radecka, I. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrington, M.; Sharma, S.K. Chapter 14—Chemotherapy of bacterial infections. In Clinical Pharmacology, 11th ed.; Bennett, P.N., Brown, M.J., Sharma, P., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 1996; pp. 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Maurel, V.; Denis, B.; Camby, M.; Jeanne, M.; Cornesse, A.; Glavnik, B.; Alanio, A.; Rousseau, A.-F.; Lefloch, R.; Lagrange-Xelot, M.; et al. Outcome and characteristics of invasive fungal infections in critically ill burn patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Mycoses 2020, 63, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janbon, G.; Quintin, J.; Lanternier, F.; D’Enfert, C. Studying fungal pathogens of humans and fungal infections: Fungal diversity and diversity of approaches. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. First Meeting of the WHO Antifungal Expert Group on Identifying Priority Fungal Pathogens: Meeting Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Enoch, D.A.; Yang, H.; Aliyu, S.H.; Micallef, C. The Changing Epidemiology of Invasive Fungal Infections. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 1508, pp. 17–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jenks, J.D.; Cornely, O.A.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Thompson, G.R.; Hoenigl, M. Breakthrough invasive fungal infections: Who is at risk? Mycoses 2020, 63, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Dadwal, R.; Singh, S.; Shaw, D.; Chakrabarti, A.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Ghosh, A.K. Rapid detection of ERG11 polymorphism associated azole resistance in Candida tropicalis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Mechanism of Candida pathogenesis: Revisiting the vital drivers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1797–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A. Antimicrobial Action of Thymoquinone. In Molecular and Therapeutic actions of Thymoquinone; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, E.B.; Marcu, J. Cannabis Pharmacology: The Usual Suspects and a Few Promising Leads. DNA Topoisomerases Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 80, 67–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.A.; Sahoo, D.; Singh, T.B.; Rajashekar, Y. Antifungal activity and volatile organic compounds analysis of essential oils from Cymbopogon species using solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thobity, A.M.; Al-Khalifa, K.S.; Gad, M.M.; Al-Hariri, M.; Ali, A.A.; Alnassar, T. In Vitro Evaluation of the Inhibitory Activity of Thymoquinone in Combatting Candida albicans in Denture Stomatitis Prevention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaterzadeh-Yazdi, H.; Noorbakhsh, M.-F.; Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T. An Overview on Renoprotective Effects of Thymoquinone. Kidney Dis. 2018, 4, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osmanov, A.; Wise, A.; Denning, D.W. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of miramistin against drug-resistant fungi. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavassin, F.B.; Baú-Carneiro, J.L.; Vilas-Boas, R.R.; Queiroz-Telles, F. Sixty years of Amphotericin B: An Over-view of the Main Antifungal Agent Used to Treat Invasive Fungal Infections. Infect. Dis. 2021, 10, 115–147. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, A.; Pantet, O.; Laurent, L.; Hirt-Burri, N.; de Buys Roessingh, A.; Raffoul, W.; Laurent, P.; Monod, M.; Applegate, L. Potency and stability of liposomal Amphotericin B formulated for topical management of Aspergillus species. infections in burn patients. Burns Open 2019, 4, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, K.M. Development of an Oral Amphotericin B Formulation as an Alternative Approach to Parenteral Amphotericin B Administration in the Treatment of Blood-Borne Fungal Infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1521–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almshawit, H.; Macreadie, I. Fungicidal effect of thymoquinone involves generation of oxidative stress in Candida glabrata. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 195, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gintjee, T.J.; Donnelley, M.A.; Thompson, G.R. Aspiring Antifungals: Review of Current Antifungal Pipeline Developments. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, J.; Gong, Y.; Li, N.; Luo, G. Candidemia in major burn patients and its possible risk factors: A 6-year period retrospective study at a burn ICU. Burns 2019, 45, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, A.T.; Nguyen, N.M.T.; Do, N.A.; Nguyen, N.-L.; Tran, N.D.; Le, T.A. Infection of burn wound by Aspergillus fumigatus with gross appearance of fungal colonies. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2019, 24, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Ford, B.; Brown-Joel, Z.; Shields, B.; Rosenbach, M.; Wanat, K. Angioinvasive fungal infections impacting the skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 883–898.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, S.; Rautji, R.; Radhakrishna, K.; Baghel, J.; Shivakumar, D.; Aziz, N. Disseminated invasive Aspergillosis in a case of fatal antemortem flame burns. J. Indian Acad. Forensic Med. 2019, 41, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphotericin Bekar, R.; Kandasubramanian, B. Advancements in nanofibers for wound dressing: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 304–336. [Google Scholar]
- Alexis, O.D.P.; Guang, Y.; Guiaro, M.N. New Approach for Skin Repair by Using Bacterial Cellulose Altered with Paraffin and Porous Bacterial Cellulose based Scaffold with Alginate. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2017, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khalili, S.; Khorasani, S.N.; Neisiany, R.E.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portela, R.; Leal, C.R.; Almeida, P.L.; Sobral, R.G. Bacterial cellulose: A versatile biopolymer for wound dressing applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 586–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Gultekinoglu, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Bacterial cellulose micro-nano fibres for wound healing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, A.P.; Henderson, K.; Spencer, A.; Sligar, A.D.; Baker, A.B. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, V.; Vitta, S. Bacterial cellulose based flexible multifunctional nanocomposite sheets. Cellul. 2017, 24, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosvirnikov, D.B.; Safin, R.G.; Zakirov, S. Microcrystalline Cellulose Based on Cellulose Containing Raw Material Modified by Steam Explosion Treatment. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 284, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Prudnikova, S.; Sukovatyi, A.G.; Shishatskaya, E.I. Production and properties of bacterial cellulose by the strain Komagataeibacter xylinus B-12068. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7417–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Low, W.; Radecka, I.; Britland, S.; Mohd Amin, M.; Martin, C. Characterisation And In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity Of Biosynthetic Silver-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogels. J Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Low, W.-L.; Britland, S.; Radecka, I.; Martin, C. Physicochemical characterisation of biosynthetic bacterial cellulose as a potential wound dressing material. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 2, S37–S38. [Google Scholar]
- Revin, V.; Pestov, N.; Shchankin, M.; Mishkin, V.; Platonov, V.; Uglanov, D. A Study of The Physical And Mechanical Prop-erties Of Aerogels Obtained From Bacterial Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wan, Y.; Yang, C.; Dai, K.; Tang, T.; Luo, H.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose sponge with hierarchical pore structure as tissue engineering scaffold. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 18, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, A.; Oddershede, J.; Lilholt, H.; Thomsen, A.; Ståhl, K. On the Determination of Crystallinity And Cellulose Content In Plant Fibres. Cellulose 2005, 12, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Abidi, N.; Hu, Y.; Catchmark, J. Effect of Cellulose Crystallinity On Bacterial Cellulose Assembly. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Gama, M.; Dourado, F.; Souto, A. Development of novel bacterial cellulose composites for the textile and shoe industry. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Qiao, X.; Song, Q.; Li, S.; Kim, R.-C.; Pan, L.; Han, Y.; Xiao, H.; et al. Production, Optimization and Partial Characterization of Bacterial Cellulose from Gluconacetobacter xylinus TJU-D2. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, J.; Nie, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Recent advances in bacterial cellulose. Cellul. 2014, 21, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaremera, L.; Lee, K.K.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Gow, N.A.R. Candida albicans Yeast, Pseudohyphal, and Hyphal Morphogenesis Differentially Affects Immune Recognition. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO. ISO/TC 212 Clinical Laboratory Testing and In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems, Clinical Laboratory Testing and In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Reference Method for Testing the In Vitro Activity of Antimicrobial Agents against Yeast Fungi Involved in Infectious Diseases; ISO 16256:2012; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; ISO 16256:2012. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Standard-Third Edition M27-A3; Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi, 3rd ed.; CLSI Guideline M38; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Method for Antifungal Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 3rd ed.; CLSI Guideline M44; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Method for Antifungal Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Non-Dermatophyte Filamentous Fungi, 1st ed.; CLSI Guideline M51-A; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2010; CLSI Guideline M51-A. [Google Scholar]
- Frone, A.N.; Panaitescu, D.M.; Nicolae, C.A.; Gabor, A.R.; Trusca, R.; Casarica, A.; Stanescu, P.O.; Baciu, D.D.; Salageanu, A. Bacterial cellulose sponges obtained with green cross-linkers for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abral, H.; Chairani, M.K.; Rizki, M.D.; Mahardika, M.; Handayani, D.; Sugiarti, E.; Muslimin, A.N.; Sapuan, S.; Ilyas, R. Characterization of compressed bacterial cellulose nanopaper film after exposure to dry and humid conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Yadagiri, G.; Parvez, S.; Singh, O.P.; Verma, A.; Sundar, S.; Mudavath, S.L. Formulation, characteriza-tion and in vitro anti-leishmanial evaluation of amphotericin B loaded solid lipid nanoparticles coated with vitamin B12-stearic acid conjugate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agafonova, M.N.; Kazakova, R.R.; Lubina, A.P.; Zeldi, M.I.; Nikitina, E.V.; Balakin, K.V. and Shtyrlin, Y.G. Antibacterial activity profile of miramistin in in vitro and in vivo models. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañuelos-Valenzuela, R.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, L.; Echavarría-Cháirez, F.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, O.; Meza-López, C.; Bañue-los-Valenzuela, R.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, L.; Echavarría-Cháirez, F.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, O.; Meza-López, C. Chemical composition and FTIR of ethane extracts of Larrea tridentata, Origanum vulgare, Artemisa ludoviciana and Ruta graveolens. Agrociencia 2018, 52, 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Pagola, S.; Benavente, A.; Raschi, A.; Romano, E.; Molina, M.A.A.; Stephens, P.W. Crystal structure determination of thymoquinone by high-resolution X-ray powder diffraction. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 2nd ed.; CLSI Guideline M60; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; CLSI Guideline M60. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi, 2nd ed.; CLSI Guideline M61; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; CLSI Guideline M61. [Google Scholar]
- AbuKhader, M. Thymoquinone in the clinical treatment of cancer: Fact or fiction? Pharm. Rev. 2013, 7, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel Azeiz, A.Z.; Saad, A.H.; Darweesh, M.F. Efficacy of Thymoquinone against Vaginal Candidiasis in Predni-solone-induced Immunosuppressed Mice. J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa, M.A.; Gondal, M.A.; Al-Zahrani, A.-H.J.; Rashid, S.G.; Ali, A. Synthesis, morphology and antifungal activity of nano-particulated amphotericin-B, ketoconazole and thymoquinone against Candida albicans yeasts and Candida biofilm. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Aldebasi, Y.H.; Alsuhaibani, S.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Khan, A.; Younus, H. Therapeutic potential of thymoquinone liposomes against the systemic infection of Candida albicans in diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Gonçalves, M.-J.; Hrimpeng, K.; Pinto, J.; Pinto, E. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Angelica major against Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, M.; Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P. In vitro toxicological properties of thymoquinone. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanov, A.; Farooq, Z.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. The antiseptic Miramistin: A review of its comparative in vitro and clinical activity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, C.; Oliveira, F.D.S.D.; Grossmann, B.; Kretzmann, N.; Da Silveira, T.R.; Giugliani, R.; Matte, U. Cytotoxic effect of Amphotericin B in a myofibroblast cell line. Toxicol. Vitro 2013, 27, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.N.; Prajapati, C.P.; Gore, P.R.; Patil, C.R.; Mahajan, U.B.; Sharma, C.; Talla, S.P.; Ojha, S.K. Therapeutic Potential and Pharmaceutical Development of Thymoquinone: A Multitargeted Molecule of Natural Origin. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-S.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wei, H.; Yin, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Yan, L.-H.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yang, L.-X. Chemical compositions, yield variations and antimicrobial activities of essential oils from three species of Euodiae Fructus in China. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 138, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, R.; Tabassum, B.; Idrees, N.; Hussain, M. Bio-active Compounds Isolated from Neem Tree and Their Applications. Nat. Bio-Act. Compd. 2019, 509–528. [Google Scholar]
- Heard, S.C.; Wu, G.; Winter, J.M. Antifungal natural products. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Bradley, D.T.; Tunney, M.M.; Hughes, C.M. Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials aimed at improving antimicrobial stewardship in care homes. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelfrene, E.; Botgros, R.; Cavaleri, M. Antimicrobial multidrug resistance in the era of COVID-19: A forgotten plight? Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2021, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlet, K.J.; Spadafora, K.; Walia, R.; Nailor, M.D. Updates in the Treatment of Breakthrough Mold Infections. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2020, 14, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Venkataraman, M.; Renaud, H.J.; Summerbell, R.; Shear, N.H.; Piguet, V. The increasing problem of treatment-resistant fungal infections: A call for antifungal stewardship programs. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Cantón, E.; Pemán, J. Antifungal Resistance among Less Prevalent Candida Non-albicans and Other Yeasts versus Established and under Development Agents: A Literature Review. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esson, M.M.; Mecozzi, S. Preparation, Characterization, and Formulation Optimization of Ionic-Liquid-in-Water Nanoemulsions toward Systemic Delivery of Amphotericin B. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolus, H.; Pierson, S.; Lagrou, K.; Van Dijck, P. Amphotericin B and Other Polyenes—Discovery, Clinical Use, Mode of Action and Drug Resistance. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Step | Concentration (mg/L) | Source | Volume of Antifungal (μL) | Volume of Solvent (μL) | Intermediate Concentration (mg/L) | Concentration (mg/L) after 1:100 Dilution with Double Strength RPMI 2% (w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3200 | Stock | 200 | 0 | 3200 | 32 |
| 2 | 3200 | Stock | 100 | 100 | 1600 | 16 |
| 3 | 3200 | Stock | 50 | 150 | 800 | 8 |
| 4 | 3200 | Stock | 50 | 350 | 400 | 4 |
| 5 | 400 | Step 4 | 100 | 100 | 200 | 2 |
| 6 | 400 | Step 4 | 50 | 150 | 10 | 1 |
| 7 | 400 | Step 4 | 50 | 350 | 50 | 0.5 |
| 8 | 50 | Step 7 | 100 | 100 | 25 | 0.25 |
| 9 | 50 | Step 7 | 50 | 150 | 12.5 | 0.125 |
| 10 | 50 | Step 7 | 25 | 175 | 6.25 | 0.06 |
| Step | Concentration (mg/L) | Source | Volume of Antifungal (μL) | Volume of Solvent (μL) | Intermediate Concentration (mg/L) | Concentration (mg/L) after 1:100 Dilution with Double Strength RPMI 2% (w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12,800 | Stock | 200 | 0 | 12,800 | 128 |
| 2 | 12,800 | Stock | 100 | 100 | 6400 | 64 |
| 3 | 12,800 | Stock | 50 | 150 | 3200 | 32 |
| 4 | 12,800 | Stock | 50 | 350 | 1600 | 16 |
| 5 | 1600 | Step 4 | 100 | 100 | 800 | 8 |
| 6 | 1600 | Step 4 | 50 | 150 | 400 | 4 |
| 7 | 1600 | Step 4 | 50 | 350 | 200 | 2 |
| 8 | 200 | Step 7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1 |
| 9 | 200 | Step 7 | 50 | 150 | 50 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 200 | Step 7 | 25 | 175 | 25 | 0.26 |
| Fungi | Amphotericin B | Thymoquinone | Ocimene | Miramistin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC90 (mg/L) | MFC (mg/L) | MIC90 (mg/L)) | MFC (mg/L) | MIC90 (mg/L) | MFC (mg/L) | MIC90 (mg/L) | MFC (mg/L) | |
| A. fumigatus | 0.06–1 | 0.07–1 | 1.3–2 | 1.5–2 | 0.7–1 | 1.6–2 | 21 | 27 |
| A. niger | 0.06–1 | 0.09–1 | 0.9–2 | 1–2 | 0.4–0.9 | 1–2 | 18-20 | 25 |
| C. albicans | 0.03 | 0.06–1 | 4.9–5.2 | 6.2–7 | 0.3–0.9 | 0.3–0.9 | 1.3–3 | 2.6–4 |
| C. auris | 0.05 | 0.08–1 | 7.9–8.2 | 8.4–9.7 | 1.2–1.9 | 2–2.5 | 1.4–2.8 | 3–5 |
| Drug | Unloaded BC (mg) | Loaded BC (mg) | Average Compound Loaded (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thymoquinone | 1.6375 ± 0.364 | 1.678 ± 0.357 | 42.0 ± 8 |
| Ocimene | 1.5500 ± 0.208 | 1.588 ± 0.207 | 37.4 ± 9 |
| Miramistin | 1.5750 ± 0.175 | 1.615 ± 0.183 | 46.0 ± 8 |
| Amphotericin B | 1.7000 ± 0.221 | 1.733 ± 0.220 | 32.5 ± 10 |
| Control | 1.6200 ± 0.125 | 1.627 ± 0.120 | 7.00 ± 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swingler, S.; Gupta, A.; Gibson, H.; Heaselgrave, W.; Kowalczuk, M.; Adamus, G.; Radecka, I. The Mould War: Developing an Armamentarium against Fungal Pathogens Utilising Thymoquinone, Ocimene, and Miramistin within Bacterial Cellulose Matrices. Materials 2021, 14, 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102654
Swingler S, Gupta A, Gibson H, Heaselgrave W, Kowalczuk M, Adamus G, Radecka I. The Mould War: Developing an Armamentarium against Fungal Pathogens Utilising Thymoquinone, Ocimene, and Miramistin within Bacterial Cellulose Matrices. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102654
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwingler, Sam, Abhishek Gupta, Hazel Gibson, Wayne Heaselgrave, Marek Kowalczuk, Grazyna Adamus, and Iza Radecka. 2021. "The Mould War: Developing an Armamentarium against Fungal Pathogens Utilising Thymoquinone, Ocimene, and Miramistin within Bacterial Cellulose Matrices" Materials 14, no. 10: 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102654
APA StyleSwingler, S., Gupta, A., Gibson, H., Heaselgrave, W., Kowalczuk, M., Adamus, G., & Radecka, I. (2021). The Mould War: Developing an Armamentarium against Fungal Pathogens Utilising Thymoquinone, Ocimene, and Miramistin within Bacterial Cellulose Matrices. Materials, 14(10), 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102654