Estrogen Modulates Epithelial Breast Cancer Cell Mechanics and Cell-to-Cell Contacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and AFM Sample Preparation
2.2. Cell Fixation, Permeabilization and Immunostaining
2.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4. Atomic Force Microscopy—Imaging
2.5. Surface Roughness Determination
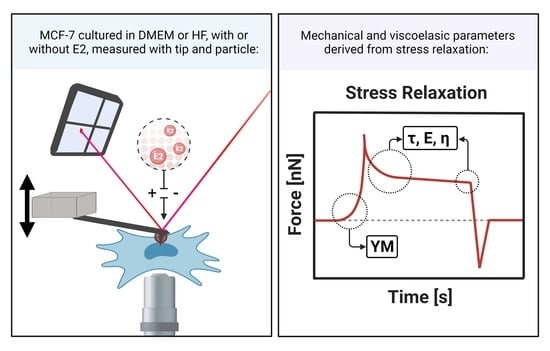
2.6. Atomic Force Microscopy—Force Spectroscopy
2.7. Data Analysis of Force Spectroscopy Curves
2.7.1. Elastic Properties
2.7.2. Viscoelastic Properties
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estrogen Leads to Softening of Breast Cancer Cells
3.1.1. Elastic Properties from Indentation Curves
3.1.2. Viscoelastic Properties from Stress Relaxation Experiments
3.2. Surface Roughness and Cell Height Increases Due to Estrogen Treatment
3.3. Estrogen Changes E-Cadherin Distribution
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardoso, F.; Harbeck, N.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Cortés, J.; El Saghir, N.; Francis, P.A.; Hudis, C.A.; Ohno, S.; Partridge, A.H.; et al. Research needs in breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, B.M.; Vivanco, M.D. Cancer stem cells in the human mammary gland and regulation of their differentiation by estrogen. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, M.; Domenici, G.; Iriondo, O.; Rabano, M.; Simoes, B.M.; Comaills, V.; Barredo, I.; Lopez-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; Kypta, R.; et al. Sox2 promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.W.; Weinberg, R.A. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas-Silva, M.D.; Waltz, P.K. Estrogen promotes reversible epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transition and collective motility in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 104, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouris, P.; Skandalis, S.S.; Piperigkou, Z.; Afratis, N.; Karamanou, K.; Aletras, A.J.; Moustakas, A.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen receptor alpha mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition, expression of specific matrix effectors and functional properties of breast cancer cells. Matrix Biol. 2015, 43, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, P.; Kornhuber, M.; Dunst, S.; Zell, J.; Fauler, B.; Mielke, T.; Taubenberger, A.V.; Guck, J.; Oelgeschläger, M.; Schönfelder, G. Estrogens Determine Adherens Junction Organization and E-Cadherin Clustering in Breast Cancer Cells via Amphiregulin. iScience 2020, 23, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseervatham, J. Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Cancer. Biology 2020, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, D.A.; Mullins, R.D. Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton. Nature 2010, 463, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Weaver, V.M. Mechanics, malignancy, and metastasis: The force journey of a tumor cell. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieg, M.; Fläschner, G.; Alsteens, D.; Gaub, B.M.; Roos, W.H.; Wuite, G.J.L.; Gaub, H.E.; Gerber, C.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Müller, D.J. Atomic force microscopy-based mechanobiology. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vining, K.H.; Mooney, D.J. Mechanical forces direct stem cell behaviour in development and regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.A.; Donato, D.M.; Balcioglu, H.E.; Schmidt, T.; Danen, E.H.J.; Koenderink, G.H. A guide to mechanobiology: Where biology and physics meet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paluch, E.K.; Nelson, C.M.; Biais, N.; Fabry, B.; Moeller, J.; Pruitt, B.L.; Wollnik, C.; Kudryasheva, G.; Rehfeldt, F.; Federle, W. Mechanotransduction: Use the force(s). BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roca-Cusachs, P.; Conte, V.; Trepat, X. Quantifying forces in cell biology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, P.; Valcarcel-Jimenez, L.; Frezza, C.; Dupont, S. Crosstalk between mechanotransduction and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskratsch, T.; Wolfenson, H.; Sheetz, M.P. Appreciating force and shape—The rise of mechanotransduction in cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moeendarbary, E.; Harris, A.R. Cell mechanics: Principles, practices, and prospects. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2014, 6, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-H.; Aroush, D.R.-B.; Asnacios, A.; Chen, W.-C.; Dokukin, M.E.; Doss, B.L.; Durand-Smet, P.; Ekpenyong, A.; Guck, J.; Guz, N.V.; et al. A comparison of methods to assess cell mechanical properties. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.W.; Fodor, É.; Betz, T. Active cell mechanics: Measurement and theory. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavara, N. A beginner’s guide to atomic force microscopy probing for cell mechanics. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S. Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 413–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, C.M.; Puech, P.-H. Atomic Force Microscopy: A Versatile Tool for Studying Cell Morphology, Adhesion and Mechanics. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2008, 1, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotsch, C.; Radmacher, M. Drug-induced changes of cytoskeletal structure and mechanics in fibroblasts: An atomic force microscopy study. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, A.; Iturri, J.; Benitez, R.; Zemljic-Jokhadar, S.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Microtubule disruption changes endothelial cell mechanics and adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Cencerrado, A.; Iturri, J.; Pecorari, I.; Vivanco, D.M.M.; Sbaizero, O.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Investigating cell-substrate and cell-cell interactions by means of single-cell-probe force spectroscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.L.; Goldmann, W.H. Feeling the forces: Atomic force microscopy in cell biology. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Flores, S.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. The new future of scanning probe microscopy: Combining atomic force microscopy with other surface-sensitive techniques, optical microscopy and fluorescence techniques. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.-J.; Cappella, B.; Kappl, M. Force measurements with the atomic force microscope: Technique, interpretation and applications. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2005, 59, 1–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Flores, S.; Benitez, R.; Vivanco, M.d.M.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Stress relaxation and creep on living cells with the atomic force microscope: A means to calculate elastic moduli and viscosities of cell components. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 445101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcaraz, J.; Buscemi, L.; Grabulosa, M.; Trepat, X.; Fabry, B.; Farré, R.; Navajas, D. Microrheology of human lung epithelial cells measured by atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, E.M.; Zauscher, S.; Guilak, F. Viscoelastic properties of zonal articular chondrocytes measured by atomic force microscopy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Mizutani, Y.; Toda, A.; Fukushima, N.; Kawahara, K.; Tokumoto, H.; Okajima, T. Power-law stress and creep relaxations of single cells measured by colloidal probe atomic force microscopy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 08JB17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigato, A.; Miyagi, A.; Scheuring, S.; Rico, F. High-frequency microrheology reveals cytoskeleton dynamics in living cells. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butt, H.-J.; Jaschke, M. Calculation of thermal noise in atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 1995, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Zbiral, B.; Iturri, J.; Benitez, R.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Measuring (biological) materials mechanics with atomic force microscopy. 2. Influence of the loading rate and applied force (colloidal particles). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Iturri, J.; Benitez, R.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Measuring biomaterials mechanics with atomic force microscopy. 1. Influence of the loading rate and applied force (pyramidal tips). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benítez, R.; Bolós, V.J.; Herrera, J.-L.T. AfmToolkit: An R Package for Automated AFM Force-Distance Curves Analysis. R J. 2017, 9, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, R.; Moreno-flores, S.; Bolós, V.J.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. A new automatic contact point detection algorithm for AFM force curves. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2013, 76, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, E.K.; Horkay, F.; Maresca, J.; Kachar, B.; Chadwick, R.S. Determination of Elastic Moduli of Thin Layers of Soft Material Using the Atomic Force Microscope. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.T.; Zhou, E.H.; Quek, S.T. Mechanical models for living cells—A review. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Nanobiomechanics of living cells: A review. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Efremov, Y.M.; Okajima, T.; Raman, A. Measuring viscoelasticity of soft biological samples using atomic force microscopy. Soft Matter 2019, 16, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, L.D.; Lev, D. Theory of Elasticity/by L.D. Landau and E.M. Lifshitz; Translated from the Russian by J.B. Sykes and W.H. Reid; Lifshitz, E.M., Evgenii, M., Eds.; Course of Theoretical Physics; Pergamon: London, UK, 1959; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Zemła, J.; Danilkiewicz, J.; Orzechowska, B.; Pabijan, J.; Seweryn, S.; Lekka, M. Atomic force microscopy as a tool for assessing the cellular elasticity and adhesiveness to identify cancer cells and tissues. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhune, M.; Belge, G.; Dotzauer, A.; Bullerdiek, J.; Radmacher, M. Comparison of mechanical properties of normal and malignant thyroid cells. Micron 2012, 43, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterreich, S.; Deng, W.; Jiang, S.; Cui, X.; Ivanova, M.; Schiff, R.; Kang, K.; Hadsell, D.L.; Behrens, J.; Lee, A. V Estrogen-mediated Down-Regulation of E-cadherin in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5203–5208. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, T.; Rizvi, A.; Batta, S.P.R.; Kataria, S.; Jamora, C. Signaling and Mechanical Roles of E-cadherin. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2013, 20, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omidvar, R.; Tafazzoli-shadpour, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Rostami, M. Atomic force microscope-based single cell force spectroscopy of breast cancer cell lines: An approach for evaluating cellular invasion. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 3373–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolyakov, G.; Thiebot, B.; Campillo, C.; Labdi, S.; Severac, C.; Pelta, J.; Dague, É. Elasticity, Adhesion, and Tether Extrusion on Breast Cancer Cells Provide a Signature of Their Invasive Potential. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27426–27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mekhdjian, A.H.; Kai, F.; Rubashkin, M.G.; Prahl, L.S.; Przybyla, L.M.; McGregor, A.L.; Bell, E.S.; Barnes, J.M.; DuFort, C.C.; Ou, G.; et al. Integrin-mediated traction force enhances paxillin molecular associations and adhesion dynamics that increase the invasiveness of tumor cells into a three-dimensional extracellular matrix. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 1467–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullkopf, L.; West, A.-K.V.; Leijnse, N.; Cox, T.R.; Madsen, C.D.; Oddershede, L.B.; Erler, J.T. Cancer cells’ ability to mechanically adjust to extracellular matrix stiffness correlates with their invasive potential. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 2378–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acerbi, I.; Cassereau, L.; Dean, I.; Shi, Q.; Au, A.; Park, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liphardt, J.; Hwang, E.S.; Weaver, V.M. Human breast cancer invasion and aggression correlates with ECM stiffening and immune cell infiltration. Integr. Biol. (Camb.) 2015, 7, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domenici, G.; Aurrekoetxea-Rodriguez, I.; Simoes, B.M.; Rabano, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Millan, J.S.; Comaills, V.; Oliemuller, E.; Lopez-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; et al. A Sox2-Sox9 signalling axis maintains human breast luminal progenitor and breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3151–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Dong, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. Matrix stiffness-mediated effects on stemness characteristics occurring in HCC cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32221–32231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joyce, M.H.; Lu, C.; James, E.R.; Hegab, R.; Allen, S.C.; Suggs, L.J.; Brock, A. Phenotypic Basis for Matrix Stiffness-Dependent Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Doxorubicin. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Tip | Particle | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL DMEM | DMEM E2 | CTL HF | HF E2 | CTL DMEM | DMEM E2 | CTL HF | HF E2 | |
| Eelastic (Pa) | 3058.9 | 2410.5 | 2933.1 | 2046.8 | 308.7 | 275.9 | 436.7 | 316.6 |
| E∞ (Pa) | 507.9 | 347.9 | 508.8 | 312.7 | 94.5 | 68.4 | 107.5 | 89.3 |
| E1 (Pa) | 416.2 | 364.7 | 501.0 | 347.8 | 68.0 | 57.3 | 75.9 | 69.9 |
| E2 (Pa) | 374.9 | 321.6 | 449.3 | 277.2 | 53.7 | 45.3 | 59.6 | 55.0 |
| Einst (Pa) | 1299.1 | 1085.3 | 1492.3 | 952.3 | 214.0 | 170.2 | 247.5 | 214.1 |
| η1 (Pa s) | 71.2 | 69.05 | 81.8 | 65.8 | 12.0 | 10.2 | 14.1 | 11.8 |
| η2 (Pa s) | 1067.7 | 912.5 | 1205.9 | 791.3 | 180.7 | 141.2 | 191.6 | 159.9 |
| Cell Height (µm) | Ra (nm) | Rq (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTL DMEM | 5.25 ± 0.16 | 128 ± 3 | 166 ± 3 |
| DMEM E2 | 5.98 ± 0.23 | 182 ± 6 | 220 ± 8 |
| CTL HF | 5.62 ± 0.19 | 139 ± 5 | 178 ± 5 |
| HF E2 | 5.96 ± 0.20 | 147 ± 5 | 180 ± 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zbiral, B.; Weber, A.; Iturri, J.; Vivanco, M.d.M.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Estrogen Modulates Epithelial Breast Cancer Cell Mechanics and Cell-to-Cell Contacts. Materials 2021, 14, 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112897
Zbiral B, Weber A, Iturri J, Vivanco MdM, Toca-Herrera JL. Estrogen Modulates Epithelial Breast Cancer Cell Mechanics and Cell-to-Cell Contacts. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112897
Chicago/Turabian StyleZbiral, Barbara, Andreas Weber, Jagoba Iturri, Maria d. M. Vivanco, and José L. Toca-Herrera. 2021. "Estrogen Modulates Epithelial Breast Cancer Cell Mechanics and Cell-to-Cell Contacts" Materials 14, no. 11: 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112897
APA StyleZbiral, B., Weber, A., Iturri, J., Vivanco, M. d. M., & Toca-Herrera, J. L. (2021). Estrogen Modulates Epithelial Breast Cancer Cell Mechanics and Cell-to-Cell Contacts. Materials, 14(11), 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112897