Effect of Hemp Fiber Surface Treatment on the Moisture/Water Resistance and Reaction to Fire of Reinforced PLA Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- i
- To produce composites with two fiber loadings (30 and 50 wt.%) using frost-retted hemp fibers from Estonia and polylactic acid (PLA). These locally obtained hemp fibers are commonly considered as waste. Using them as PLA reinforcement is a way to value these by-products from the cannabidiol industry [17] and to enhance the contribution to a carbon-neutral environment;
- ii
- To study the influence of a combination of fiber surface pretreatments and modification of hemp fibers on the hemp PLA properties of interest (moisture/water resistance and fire behaviour) to promote the development of biocomposites as building materials.
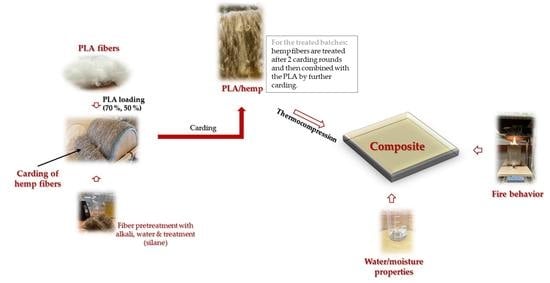
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hemp Fibers Treatments
2.2.2. Fabrication of the Hemp Reinforced Polylactide (HPLA) Composite
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Moisture Adsorption Properties
2.2.5. Long-Term Water Absorption (WA) and Thickness Swelling (TS)
2.2.6. Reaction to Fire of the Composites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Fiber Treatment on the Fiber Mass
3.2. Cross-Sectional SEM Observations of the Hemp Reinforced PLA Composites
3.3. Moisture Adsorption Properties
3.4. Water Absorption and Thickness Swelling Results
3.5. Reaction to Fire of Composite Materials
3.5.1. Temperature Response through Depth
3.5.2. Other Reaction to Fire Test Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hroudová, J.; Zach, J. The Possibilities of Modification of Crop-based Insulation Materials Applicable in Civil Engineering in Low-energy and Passive Houses. Procedia Eng. 2017, 180, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Calabria-Holley, J.; Lawrence, M.; Jiang, Y. Hygrothermal and mechanical characterisation of novel hemp shiv based thermal insulation composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevulova, N.; Estokova, A.; Cigasova, J.; Schwarzova, I.; Kacik, F.; Geffert, A. Thermal degradation of natural and treated hemp hurds under air and nitrogen atmosphere. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 128, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawpan, M.A.; Pickering, K.L.; Fernyhough, A. Improvement of mechanical performance of industrial hemp fibre reinforced polylactide biocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Swan, R.H.; Ferguson, I. Composition, structure, and mechanical properties of hemp fiber reinforced composite with recycled high-density polyethylene matrix. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.F. Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Pickering, K.L.; Foreman, N.J. Influence of alkali treatment on the interfacial and physico-mechanical properties of industrial hemp fibre reinforced polylactic acid composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, A.; Pickering, K.L.; Thakur, V.K. Manufacturing and characterization of sustainable hybrid composites using sisal and hemp fibres as reinforcement of poly (lactic acid) via injection moulding. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 137, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, P.F.; Marrot, L.; Burnard, M.D.; Lavrič, G.; Saarna, M.; Kers, J. Impact of Alkali and Silane Treatment on Hemp/PLA Composites’ Performance: From Micro to Macro Scale. Polymers 2021, 13, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Efendy, M.G.A.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Beckermann, G.W.; Alam, S.N.; Foreman, N.J. Optimising industrial hemp fibre for composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejic, B.M.; Kostic, M.M.; Skundric, P.D.; Praskalo, J.Z. The effects of hemicelluloses and lignin removal on water uptake behavior of hemp fibers. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7152–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlowski, R.M.; Muzyczek, M.; Walentowska, J. Chapter 23—Flame Retardancy and Protection against Biodeterioration of Natural Fibers: State-of-Art and Future Prospects. Polym. Green Flame Retard. 2014, 801–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, A.; Fan, M.; Bregulla, J. Fire resistance characterisation of hemp fibre reinforced polyester composites for use in the construction industry. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 60, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrot, L.; Alao, P.F.; Mikli, V.; Kers, J. Properties of Frost-Retted Hemp Fibers for the Reinforcement of Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Lacasta, A.M.; Holcroft, N.; Shea, A.; Walker, P. Determination of hygrothermal parameters of experimental and commercial bio-based insulation materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, D.; Svennerstedt, B.; Wretfors, C. Adsorption equilibrium moisture contents of flax straw, hemp stalks and reed canary grass. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 91, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantaridis, L.D.; Östman, B.A.L.; Köning, J. Short communication: Fire protected wood by different gypsum plasterboards. Fire Mater. 1999, 23, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallakas, H.; Liblik, J.; Alao, P.F.; Poltimaë, T.; Just, A.; Kers, J. Fire and Mechanical Properties of Hemp and Clay Boards for Timber Structures. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019; Volume 290, p. 012019. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/290/1/012019/pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Bourmaud, A.; Morvan, C.; Baley, C. Importance of fiber preparation to optimize the surface and mechanical properties of unitary flax fiber. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 32, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Lim, J.-K. Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Completely Biodegradable Hemp Fiber Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Sarkar, B.K.; Rana, A.K.; Bose, N.R. Mechanical properties of vinylester resin matrix composites reinforced with alkali-treated jute fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2001, 32, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix, S.; Philippe, E.; Bessadok, A.; Lebrun, L.; Morvan, C.; Marais, S. Effect of chemical treatments on water sorption and mechanical properties of flax fibres. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4742–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, N.; Toǧrul, H. The fitting of various models to water sorption isotherms of tea stored in a chamber under controlled temperature and humidity. J. Stored Prod. Resour. 2006, 42, 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, P.A.; Thomas, S.P.; Saiter, J.M.; Joseph, K.; Unnikrishnan, G.; Thomas, S. Effect of fiber surface modification on the mechanical and water absorption characteristics of sisal/polyester composites fabricated by resin transfer molding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väisänen, T.; Batello, P.; Lappalainen, R.; Tomppo, L. Modification of hemp fibers (Cannabis sativa L.) for composite applications. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 111, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaei, B.; Skrifvars, M.; Salehi, M.; Bashir, T.; Rissanen, M.; Nousiainen, P. Novel aligned hemp fibre reinforcement for structural biocomposites: Porosity, water absorption, mechanical performances and viscoelastic behaviour. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgriccia, N.; Hawley, M.C.; Misra, M. Characterization of natural fiber surfaces and natural fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.N.; Prabhakar, M.N.; Siddaramaiah, J.; Song, I.L. Influence of silane-modified Vinyl ester on the properties of Abaca fiber reinforced composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin | * Solubles | Inorganic Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77.4 ± 0.3 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 12.6 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| Treatment | Weight Change % |
|---|---|
| Water | −4.0 ± 0.3 |
| Alkali treatments | −14.2 ± 0.8 |
| Silane modification of water pre-treated fibers | −3.0 ± 0.6 |
| Silane modification of alkali pre-treated fibers | +0.9 ± 0.0 |
| Composites | 30 wt.% VP (%) | 50 wt.% VP (%) |
|---|---|---|
| UH | 10 | 13 |
| WH | 6 | 13 |
| WSH | 7 | 9 |
| AH | 4 | 7 |
| ASH | 4 | 8 |
| 30 wt.% HF | 50 wt.% HF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite Comparison | Difference at 95% RH | P-Value | Difference at 95% RH | P-Value |
| WH < UH | 6 | 0.144 | 5 | 0.5 |
| AH < UH | 18 | 0.012 | 14 | 0.012 |
| WSH < UH | 24 | 0.001 ** | 21 | 0.002 |
| ASH < UH | 16 | 0.001 | 25 | 0.001 ** |
| WSH < WH | 19 | 0.006 | 17 | 0.002 |
| AH < ASH/AH > ASH | 4 | 0.603 | 13 | 0.002 |
| WSH < AH | 7 | 0.369 | 4 | 0.034 |
| WSH < ASH | 10 | 0.051 | 5 | 0.144 |
| Constants | ROOT Mean Square (R2) | Standard Error of Estimate (Es) | Pd., % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||||
| 30 wt.% HF | ||||||
| UH | 1.48 | 0.02 | 2.22 | 0.997 | 0.17 | 7.2 |
| WH | 1.37 | 0.02 | 2.21 | 0.996 | 0.19 | 8.9 |
| WSH | 0.10 | 0.00 | 2.37 | 0.991 | 0.22 | 8.7 |
| AH | 0.95 | 0.01 | 1.97 | 0.998 | 0.12 | 8.0 |
| ASH | 1.30 | 0.02 | 2.33 | 0.995 | 0.19 | 8.8 |
| 50 wt.% HF | ||||||
| UM | 2.54 | 0.02 | 2.13 | 0.998 | 0.24 | 6.2 |
| WH | 2.29 | 0.02 | 2.06 | 0.987 | 0.57 | 5.7 |
| WSH | 2.13 | 0.02 | 2.25 | 0.997 | 0.22 | 6.6 |
| AH | 1.97 | 0.02 | 2.02 | 0.998 | 0.19 | 6.3 |
| ASH | 2.04 | 0.02 | 2.28 | 0.997 | 0.20 | 6.1 |
| Fiber Content | Samples | Weight of Board before Test (g) | Thickness (mm) | Density (gcm−3) | Average Ignition Time (s) | Ignition Temperature (°C) | Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30% | UH | 28 ± 1.8 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 1.01 ± 0.1 | 29 ± 10 | 112 ± 23 | 93 ± 2.0 |
| WH | 27 ± 1.4 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 1.10 ± 0.0 | 31 ± 10 | 117 ± 18 | 95 ± 0.1 | |
| WSH | 28 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 1.04 ± 0.1 | 30 ± 04 | 131 ± 28 | 94 ± 0.4 | |
| AH | 26 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 1.07 ± 0.1 | 44 ± 02 | 118 ± 08 | 94 ± 1.0 | |
| ASH | 28 ± 1.6 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 1.07 ± 0.0 | 33 ± 03 | 159 ± 18 | 94 ± 2.0 | |
| 50% | UH | 29 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 0.91 ± 0.1 | 32 ± 07 | 129 ± 15 | 90 ± 1.0 |
| WH | 29 ± 1.8 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 0.90 ± 0.1 | 49 ± 06 | 134 ± 17 | 91 ± 2.0 | |
| WSH | 30 ± 1.0 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 0.97 ± 0.0 | 46 ± 10 | 179 ± 29 | 90 ± 1.0 | |
| AH | 30 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 0.92 ± 0.0 | 51 ± 10 | 178 ± 18 | 90 ± 4.0 | |
| ASH | 30 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 0.98 ± 0.0 | 47 ± 09 | 181 ± 18 | 89 ± 1.0 | |
| 0% | Neat PLA | 26 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 37 ± 02 | 104 ± 04 | 100 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alao, P.F.; Marrot, L.; Kallakas, H.; Just, A.; Poltimäe, T.; Kers, J. Effect of Hemp Fiber Surface Treatment on the Moisture/Water Resistance and Reaction to Fire of Reinforced PLA Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154332
Alao PF, Marrot L, Kallakas H, Just A, Poltimäe T, Kers J. Effect of Hemp Fiber Surface Treatment on the Moisture/Water Resistance and Reaction to Fire of Reinforced PLA Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(15):4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154332
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlao, Percy Festus, Laetitia Marrot, Heikko Kallakas, Alar Just, Triinu Poltimäe, and Jaan Kers. 2021. "Effect of Hemp Fiber Surface Treatment on the Moisture/Water Resistance and Reaction to Fire of Reinforced PLA Composites" Materials 14, no. 15: 4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154332
APA StyleAlao, P. F., Marrot, L., Kallakas, H., Just, A., Poltimäe, T., & Kers, J. (2021). Effect of Hemp Fiber Surface Treatment on the Moisture/Water Resistance and Reaction to Fire of Reinforced PLA Composites. Materials, 14(15), 4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154332