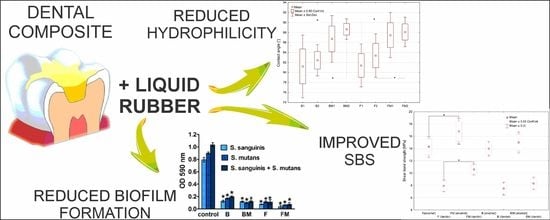
The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Dental Composites
2.2. Wettability Determination
2.3. Assessment of the Shear Bond Strength to the Tooth Tissues
2.4. Antibiofilm Activity
2.4.1. Bacterial Culture
2.4.2. Seeding of the Dental Composites with Bacteria
2.4.3. Quantitative Biofilm Determination
2.4.4. Qualitative Biofilm Determination by Confocal Microscopy
2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.5.1. Eukaryotic Cell Culture
2.5.2. Quantitative Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
2.5.3. Qualitative Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wettability Determination
3.2. Shear Bond Strength
3.3. Antibiofim Activity
3.4. Evaluation of Materials’ Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilie, N.; Hickel, R.; Valceanu, A.S.; Huth, K.C. Fracture toughness of dental restorative materials. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugolin, A.P.P.; Pfeifer, C.S. New resins for dental composites. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-H. Update on dental nanocomposites. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszner, N.; Salz, U. Composites for dental restoratives. In Polymers for Dental and Orthopedic Applications; Shalaby, W.S., Salz, U., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 13–68. ISBN 9781420003376. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, V.A.; Cardenas, H.L.; Rawls, H.R. Rubber-toughening of dimethacrylate dental composite resin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerby, R.E.; Tiba, A.; Knobloch, L.A.; Schricker, S.R.; Tiba, O. Fracture toughness of modified dental resin systems. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, K.; Kleczewska, J.; Sasimowski, E.; Belcarz, A.; Przekora, A. Improved fracture toughness and conversion degree of resin-based dental composites after modification with liquid rubber. Materials 2020, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mante, F.K.; Wadenya, R.O.; Bienstock, D.A.; Mendelsohn, J.; LaFleur, E.E. Effect of liquid rubber additions on physical properties of Bis-GMA based dental resins. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salz, U.; Bock, T. Testing adhesion of direct restoratives to dental hard tissue—A review. J. Adhes. Dent. 2010, 12, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausiello, P.; Cassese, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Di Jeso, B.; Ulianich, L. Cytotoxicity of dental resin composites: An in vitro evaluation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelka, M.; Distler, W.; Petschelt, A. Elution parameters and HPLC-detection of single components from resin composite. Clin. Oral Investig. 1999, 3, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelio, R.B.; Wikant, A.; Mjosund, H.; Kopperud, H.M.; Haasum, J.; Gedde, U.W.; Örtengren, U.T. The influence of bis-EMA vs bis GMA on the degree of conversion and water susceptibility of experimental composite materials. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.A. Miscibility and phase separation of epoxy/rubber blends. In Handbook of Epoxy Blends; Parameswaranpillai, J., Hameed, N., Pionteck, J., Woo, E.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 68–100. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, M.T.; Khan, A.S.; Muzzafar, D.; Faryal, R.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Ahmad, R.; Chauhdry, A.A.; Rehman, I.U. Structural, surface, in vitro bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation analysis of three dental restorative composites. Materials 2015, 8, 3221–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzaniga, G.; Ottobelli, M.; Ionescu, A.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Brambilla, E. Surface properties of resin-based composite materials and biofilm formation: A review of the current literature. Am. J. Dent. 2015, 28, 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Magno, A.F.F.; Enoki, C.; Ito, I.Y.; Matsumoto, M.A.N.; Faria, G.; Nelson-Filho, P. In-vivo evaluation of the contamination of super slick elastomeric rings by Streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, S104–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurnheer, T.; Belibasakis, G.N. Effect of sodium fluoride on oral biofilm microbiota and enamel demineralization. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 89, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Fiehn, N.E. Dental biofilm infections—An update. Apmis 2017, 125, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pałka, K.; Kleczewska, J.; Kalbarczyk, G. Light-curing dental composite modified with liquid rubber and the method for its production. Polish Patent Application P.427219, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dentistry-Polymer-Based Restorative Materials; ISO 4049:2019; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Przekora, A.; Benko, A.; Blazewicz, M.; Ginalska, G. Hybrid chitosan/β-1,3-glucan matrix of bone scaffold enhances osteoblast adhesion, spreading and proliferation via promotion of serum protein adsorption. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentistry—Adhesion—Notched-Edge Shear Bond Strength Test; ISO 29022:2013; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- De Munck, J.; Van Landuyt, K.; Peumans, M.; Poitevin, A.; Lambrechts, P.; Braem, M.; Van Meerbeek, B. A critical review of the durability of adhesion to tooth tissue: Methods and results. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Ling, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, H. Effect of S. Mutans and S. Sanguinis on growth and adhesion of P. Gingivalis and their ability to adhere to different dental materials. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 4539–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. In Current Protocols in Microbiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, Unit 1B.1. [Google Scholar]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajotia, S.S.; Smart, K.H.; Pilula, M.; Thompson, D.M. Concurrent quantification of cellular and extracellular components of biofilms. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, e50639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pączkowski, P.; Puszka, A.; Miazga-Karska, M.; Ginalska, G.; Gawdzik, B. Synthesis, characterization and testing of antimicrobial activity of composites of unsaturated polyester resins with wood flour and silver nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekora, A.; Palka, K.; Ginalska, G. Biomedical potential of chitosan/HA and chitosan/β-1,3-glucan/HA biomaterials as scaffolds for bone regeneration-A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przekora, A.; Ginalska, G. Addition of 1,3-β-d-glucan to chitosan-based composites enhances osteoblast adhesion, growth, and proliferation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekora, A.; Palka, K.; Ginalska, G. Chitosan/β-1,3-glucan/calcium phosphate ceramics composites-novel cell scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 182–183, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, E.; Ionescu, A.; Mazzoni, A.; Cadenaro, M.; Gagliani, M.; Ferraroni, M.; Tay, F.; Pashley, D.; Breschi, L. Hydrophilicity of dentin bonding systems influences in vitro Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wassmann, T.; Kreis, S.; Behr, M.; Buergers, R. The influence of surface texture and wettability on initial bacterial adhesion on titanium and zirconium oxide dental implants. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Rehbein, D.; Axmann, D.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, B.; Webster, T. Cell response to nanoscale features and its implications in tissue regeneration: An orthopedic perspective. In Nanotechnology and Tissue Engineering: The Scaffold; Laurencin, C., Nair, L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 151–155. ISBN 9781138076587. [Google Scholar]
- Rüttermann, S.; Trellenkamp, T.; Bergmann, N.; Raab, W.H.M.; Ritter, H.; Janda, R. A new approach to influence contact angle and surface free energy of resin-based dental restorative materials. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buergers, R.; Schneider-Brachert, W.; Hahnel, S.; Rosentritt, M.; Handel, G. Streptococcal adhesion to novel low-shrink silorane-based restorative. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kwon, T.-Y. In vitro study of Streptococcus mutans adhesion on composite resin coated with three surface sealants. Restor. Dent. Endodont. 2017, 42, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Brakel, R.; Cune, M.; Van Winkelhoff, A.; De Putter, C.; Verhoeven, J.; Van Der Reijden, W. Early bacterial colonization and soft tissue health around zirconia and titanium abutments: An in vivo study in man. Clin. Oral Implant. Res 2011, 22, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Wiedmann-Al-Ahmad, M.; Faust, J.; Bächle, M.; Follo, M.; Wolkewitz, M.; Hannig, C.; Hellwig, E.; Carvalho, C.; Kohal, R. Biofilm formation and composition on different implant materials in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, L. Decalcification during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances—An overview. Br. J. Orthod. 1992, 19, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-I.; Wang, Y. Cell response to surface and architecture of tissue engineering scaffolds. In Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering–Cells and Biomaterials; Eberli, D., Ed.; InTech Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Q. Cell-scaffold interaction within engineered tissue. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 323, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K.; Bigerelle, M. On the relation between surface roughness of metallic substrates and adhesion of human primary bone cells. Scanning 2014, 36, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pałka, K.; Miazga-Karska, M.; Pawłat, J.; Kleczewska, J.; Przekora, A. The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071704
Pałka K, Miazga-Karska M, Pawłat J, Kleczewska J, Przekora A. The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(7):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071704
Chicago/Turabian StylePałka, Krzysztof, Małgorzata Miazga-Karska, Joanna Pawłat, Joanna Kleczewska, and Agata Przekora. 2021. "The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites" Materials 14, no. 7: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071704
APA StylePałka, K., Miazga-Karska, M., Pawłat, J., Kleczewska, J., & Przekora, A. (2021). The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites. Materials, 14(7), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071704