Compression Properties and Fabrication of Closed-Cell Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams Al2O3hs/AZ91D
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D Syntactic Foams
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results
3.1. Optical Macrostructure and Microstructure of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D Syntactic Foam
3.2. Density of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D syntactic foam
3.3. Compressive Properties of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D Syntactic Foam
3.3.1. The Quasistatic Compressive Properties of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D Syntactic Foam
3.3.2. Dynamic Compact Properties of the Al2O3hs/AZ91D Foams
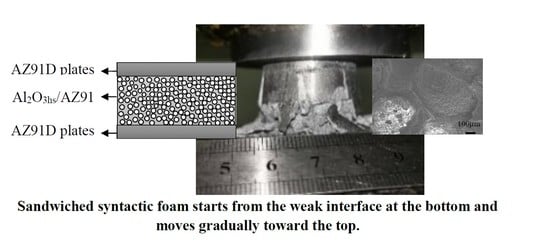
3.4. Research on the Preparation and Properties of Sandwiched Magnesium Matrix Syntactic Foams (Plates Added)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neville, B.P.; Rabiei, A. Composite metal foams processed through powder metallurgy. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenaiji, M.; Guan, Z.W.; Cantwell, W.J.; Zhao, Y.; Schleyer, G.K. Characterisation of aluminium matrix syntactic foams under drop weight impact. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlancsik, A.; Katona, B.; Karoly, D.; Orbulov, I.N. Notch (In)Sensitivity of Aluminum Matrix Syntactic Foams. Materials 2019, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogiatzis, C.A.; Tsouknidas, A.; Kountouras, D.T.; Skolianos, S. Aluminum–ceramic cenospheres syntactic foams produced by powder metallurgy route. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Zhao, Y.Y. Mechanical Response of Al Matrix Syntactic Foams Produced by Pressure Infiltration Casting. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 41, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Wang, H.; Hao, H. Compressive Properties of Aluminum Matrix Syntactic Foams Prepared by Stir Casting Method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.P.; Goel, M.D.; Upadhyay, V.; Das, S.; Singh, M.; Barnwal, A.K. Comparative Study on Microstructural Characteristics and Compression Deformation Behaviour of Alumina and Cenosphere Reinforced Aluminum Syntactic Foam Made Through Stir Casting Technique. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, T.P.D.; Pillai, R.M.; Pai, B.C.; Satyanarayana, K.G.; Rohatgi, P.K. Fabrication and characterisation of Al–7Si–0.35Mg/fly ash metal matrix composites processed by different stir casting routes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, B.; Hu, H.; Hu, G.; Miao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Sun, W. Melt flow and solidification during infiltration in making steel matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Kamieniak, J. AZ91 magnesium matrix foam composites with fly ash cenospheres fabricated by negative pressure infiltration technique. Mater. Charact. 2017, 128, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbulov, I.N. Metal matrix syntactic foams produced by pressure infiltration—The effect of infiltration parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 583, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.J.; Lee, T.S.; Lee, W.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, Y.H. Preparation and Characterization of Iron Matrix Syntactic Foams with Glass Microspheres via Powder Metallurgy. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 25, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, C.A.; Skolianos, S.M. On the sintering mechanisms and microstructure of aluminium–ceramic cenospheres syntactic foams produced by powder metallurgy route. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 82, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.P.; Datta Majumder, J.; Jha, N.; Badkul, A.; Das, S.; Patel, A.; Gupta, G. Titanium-cenosphere syntactic foam made through powder metallurgy route. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.D.; Peroni, M.; Solomos, G.; Mondal, D.P.; Matsagar, V.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Larcher, M.; Marburg, S. Dynamic compression behavior of cenosphere aluminum alloy syntactic foam. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.P.; Majumdar, D.D.; Bharti, R.K.; Majumdar, J. Microstructural characterisation and property evaluation of titanium cenosphere syntactic foam developed by powder metallurgy route. Powder Metall. 2015, 58, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Mondal, D.P.; Goel, M.D.; Majumdar, J.D.; Das, S.; Modi, O.P. Titanium cenosphere syntactic foam with coarser cenosphere fabricated by powder metallurgy at lower compaction load. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Q.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Nath, D. Preparation of aluminium-fly ash particulate composite by powder metallurgy technique. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 3971–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-yun, L.; Er-kuo, Y.; Lei, L.; Lei, X.; Guo-fa, M.; You-chao, W. Research progress of preparation of closed-cell metal matrix syntactic foam. Powder Metall. Technol. 2020, 38, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, Z.; Hu, S.; Shen, Z.; Ma, H. Mechanical response of the fly ash cenospheres/polyurethane syntactic foams fabricated through infiltration process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Kamieniak, J. Analysis of interface between components in AZ91 magnesium alloy foam composite with Ni-P coated fly ash cenospheres. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 720, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ Mg2Si/AZ91D composites through incorporating fly ash cenospheres. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.P.; Goel, M.D.; Das, S. Effect of strain rate and relative density on compressive deformation behaviour of closed cell aluminum–fly ash composite foam. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D.D.; Strbik, O.M.; Hammond, V.H.; Gupta, N.; Cho, K. Development of high performance lightweight aluminum alloy/SiC hollow sphere syntactic foams and compressive characterization at quasi-static and high strain rates. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 550, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemény, A.; Leveles, B.; Bubonyi, T.; Orbulov, I.N. Effect of particle size and volume ratio of ceramic hollow spheres on the mechanical properties of bimodal composite metal foams. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, B.; Szebényi, G.; Orbulov, I.N. Fatigue properties of ceramic hollow sphere filled aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Liao, B.; Hu, B. Compressive properties of closed-cell aluminum foams with different contents of ceramic microspheres. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.B.; Santa Maria, J.A.; Schultz, B.F.; Rohatgi, P.K. Al–Al2O3 syntactic foams—Part II: Predicting mechanical properties of metal matrix syntactic foams reinforced with ceramic spheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 582, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakari, V.; Parande, G.; Doddamani, M.; Gupta, M. Evaluation of wear resistance of magnesium/glass microballoon syntactic foams for engineering/biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9302–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, J. Microstructural characterization and compression mechanical response of glass hollow spheres/Al syntactic foams with different Mg additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chi, H.; Chang, J.; Wu, G. Quasi-static and dynamic compression behavior of glass cenospheres/5A03 syntactic foam and its sandwich structure. Compos. Struct. 2018, 183, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbuchezhiyan, G.; Mohan, B.; Sathianarayanan, D.; Muthuramalingam, T. Synthesis and characterization of hollow glass microspheres reinforced magnesium alloy matrix syntactic foam. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broxtermann, S.; Taherishargh, M.; Belova, I.V.; Murch, G.E.; Fiedler, T. On the compressive behaviour of high porosity expanded Perlite-Metal Syntactic Foam (P-MSF). J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherishargh, M.; Sulong, M.A.; Belova, I.V.; Murch, G.E.; Fiedler, T. On the particle size effect in expanded perlite aluminium syntactic foam. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, T.; Taherishargh, M.; Krstulović-Opara, L.; Vesenjak, M. Dynamic compressive loading of expanded perlite/aluminum syntactic foam. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 626, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherishargh, M.; Belova, I.V.; Murch, G.E.; Fiedler, T. Pumice/aluminium syntactic foam. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 635, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, M. Microstructures and compressive properties of AZ91D/fly-ash cenospheres composites. Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, D.B.; Schultz, B.F.; Ferguson, J.B.; Rohatgi, P.K. Synthesis and Quasi-Static Compressive Properties of Mg-AZ91D-Al2O3 Syntactic Foams. Materials 2015, 8, 6085–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Yang, Y.; Ahsan, M.U.; Luong, D.D.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Rohatgi, P.K. Zn-matrix syntactic foams: Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and compressive properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwekomi, A.D. Microstructural characterisation and corrosion behaviour of microwave-sintered magnesium alloy AZ61/fly ash microspheres syntactic foams. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinwekomi, A.D.; Adebisi, J.A.; Adediran, A.A. Compressive Characteristics of Aluminum-Fly Ash Syntactic Foams Processed by Microwave Sintering. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 4257–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Rao, D.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Sun, J.; Gupta, N.; Hu, Z. Gravity casting of aluminum-Al2O3 hollow sphere syntactic foams for improved compressive properties. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbulov, I.N.; Szlancsik, A.; Kemény, A.; Kincses, D. Compressive mechanical properties of low-cost, aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 135, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, T.; Al-Sahlani, K.; Linul, P.A.; Linul, E. Mechanical properties of A356 and ZA27 metallic syntactic foams at cryogenic temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 813, 152181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherishargh, M.; Linul, E.; Broxtermann, S.; Fiedler, T. The mechanical properties of expanded perlite-aluminium syntactic foam at elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 737, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Taherishargh, M.; Belova, I.V.; Murch, G.E.; Fiedler, T. Mechanical and Microstructural Characterization of an AZ91-Activated Carbon Syntactic Foam. Materials 2018, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha Rivero, G.A.; Schultz, B.F.; Ferguson, J.B.; Gupta, N.; Rohatgi, P.K. Compressive properties of Al-A206/SiC and Mg-AZ91/SiC syntactic foams. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Ricci, W. Comparison of compressive properties of layered syntactic foams having gradient in microballoon volume fraction and wall thickness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbulov, I.N.; Májlinger, K. Description of the compressive response of metal matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.F.; Zhao, Y.Y. Compressive failure of Al alloy matrix syntactic foams manufactured by melt infiltration. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Al | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.90 | 0.0006 | 0.0112 | 0.19 | 0.0030 |
| Si | Zn | Be | Impurities | Mg |
| 0.0030 | 0.0030 | 0.00098 | 0.001 | Bal. |
| Item | Category | DV (10)/μm | DV (50)/μm | DV (90)/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3hs | Volume fraction | 575 | 758 | 1010 |
| Temperature/°C | Yield Strength/MPa | Compressive Strength/MPa | Strain/% | Energy Absorption (ε = 2%)/MJ·mm−3 | Energy Absorption (ε = 6%)/MJ·mm−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 663 | 143.5 | 139.5 | 7 | 4.18 | --- |
| 693 | 167.87 | 156.10 | 15 | 8.54 | 10.07 |
| 723 | 135.6 | 132.5 | 12 | 5.35 | 8.83 |
| 753 | 112.5 | 98.85 | 9 | 3.28 | 5.53 |
| No. | Volume Fraction/% | Sintering Pressure/MPa | Sintering Temperature/°C | Thickness of the Mg Plates/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 70 | 15 | 573 K /1 h–693 K /1 h | 0.8 |
| #2 | 70 | 15 | 573 K /1 h–693 K /1 h | 2 |
| #3 | 70 | 15 | 573 K /1 h–693 K /1 h | 3 |
| #4 | 70 | 15 | 573 K /1 h–693 K /1 h | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Yang, E.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Compression Properties and Fabrication of Closed-Cell Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams Al2O3hs/AZ91D. Materials 2022, 15, 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196873
Li C, Yang E, Tang L, Li Y, Xu L. Compression Properties and Fabrication of Closed-Cell Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams Al2O3hs/AZ91D. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Changyun, Erkuo Yang, Ling Tang, Yang Li, and Lei Xu. 2022. "Compression Properties and Fabrication of Closed-Cell Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams Al2O3hs/AZ91D" Materials 15, no. 19: 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196873
APA StyleLi, C., Yang, E., Tang, L., Li, Y., & Xu, L. (2022). Compression Properties and Fabrication of Closed-Cell Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams Al2O3hs/AZ91D. Materials, 15(19), 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196873