Torrefaction of Napier Grass and Oil Palm Petiole Waste Using Drop-Type Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
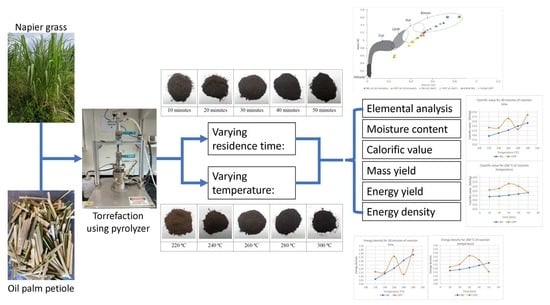
2.2. Torrefaction Process
2.3. Elemental Analysis
2.4. Moisture Content and Calorific Value
2.5. Mass Yield, Energy Yield, and Energy Density
3. Results
3.1. Elemental Analysis
3.2. Moisture Content and Calorific Value
3.3. Mass Yield, Energy Yield, and Energy Density
4. Discussion
4.1. Elemental Analysis
4.2. Moisture Content and Calorific Value
4.3. Mass Yield, Energy Yield, and Energy Density
4.4. Using Pyrolysis Reactor for Torrefaction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uemura, Y.; Omar, W.N.; Tsutsui, T.; Yusup, S.B. Torrefaction of Oil Palm Wastes. Fuel 2011, 90, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Peng, J.; Bi, X.T. A State-of-the-Art Review of Biomass Torrefaction, Densification and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 847–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, T.G.; Jones, J.M.; Shield, I.; Williams, P.T. Torrefaction of Reed Canary Grass, Wheat Straw and Willow to Enhance Solid Fuel Qualities and Combustion Properties. Fuel 2008, 87, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseltine, D.; Thanapal, S.S.; Annamalai, K.; Ranjan, D. Torrefaction of Woody Biomass (Juniper and Mesquite) Using Inert and Non-Inert Gases. Fuel 2013, 113, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, P.; Aguiar, C.; Labbé, N.; Commandré, J.M. Enhancing the Combustible Properties of Bamboo by Torrefaction. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8225–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S.K.; Tabil, L.G.; Meda, V.; Naik, S.N.; Prasad, R. Torrefaction of Wheat and Barley Straw after Microwave Heating. Fuel 2014, 124, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Cheng, W.Y.; Lu, K.M.; Huang, Y.P. An Evaluation on Improvement of Pulverized Biomass Property for Solid Fuel through Torrefaction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lin, B.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chu, Y.S.; Ubando, A.T.; Show, P.L.; Ong, H.C.; Chang, J.S.; Ho, S.H.; Culaba, A.B.; et al. Progress in Biomass Torrefaction: Principles, Applications and Challenges. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 82, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.Y.; Abakr, Y.A.; Kazi, F.K.; Yusup, S.; Alshareef, I.; Chin, S.A. Comprehensive Characterization of Napier Grass as a Feedstock for Thermochemical Conversion. Energies 2015, 8, 3403–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samson, R.; Mani, S.; Boddey, R.; Sokhansanj, S.; Quesada, D.; Urquiaga, S.; Reis, V.; Lem, C.H. The Potential of C4 Perennial Grasses for Developing a Global BIOHEAT Industry. CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 461–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukiran, M.A.; Abnisa, F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Abu Bakar, N.; Loh, S.K. A Review of Torrefaction of Oil Palm Solid Wastes for Biofuel Production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaim, T.; Abdul Rasid, R.; Wan Ismail, W.M.S. Torrefaction of Oil Palm Fronds (Opf) as a Potential Feedstock for Energy Production Processes. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2019, 27, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryani, H.; Norlindawati, A.P.; Norfadzrin, F.; Aswanimiyuni, A.; Azman, A. Yield and Nutritive Values of Six Napier (Pennisetum Purpureum) Cultivars at Different Cutting Age. Malaysian J. Vet. Res. 2018, 9, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 18134-1; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content—Oven Dry Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO E.N. 18125: 2017; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Calorific Value. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Grigiante, M.; Antolini, D. Experimental Results of Mass and Energy Yield Referred to Different Torrefaction Pathways. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, A.M.R.; Ahmad, M.; Mohd, K. Investigation of Oil Palm Frond Properties for Use as Biomaterials and Biofuels. Trop. Agric. Dev. 2014, 58, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, A.; Zwart, R.; Technology, S.R.; Kiel, J.H.A. Torrefaction for Biomass Co-Firing in Existing Coal-Fired Power Stations; Energy Research Centre of The Netherlands: Sint Maartensvlotbrug, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Cen, K.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H. Restudy on Torrefaction of Corn Stalk from the Point of View of Deoxygenation and Decarbonization. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 135, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Naz, M.Y. Thermochemical Characterization of Oil Palm Fronds, Coconut Shells, and Wood as A Fuel For Heat and Power Generation. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 225, 01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, M.; Petrovic, A.; Ban, I.; Goricanec, D.; Urbancl, D. Determination of the Kinetics and Thermodynamic Parameters of Lignocellulosic Biomass Subjected to the Torrefaction Process. Materials 2021, 14, 7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, D.A.; Basu, P.; Chejne, F.; Nhuchhen, D.R. Detailed Investigation into Torrefaction of Wood in a Two-Stage Inclined Rotary Torrefier. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, J.; Karki, S.; Oh, S.C. Valorization of Waste Wood as a Solid Fuel by Torrefaction. Energies 2018, 11, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskoti, N.; Dhital, H.C.; Aryal, A. Study of Effects of Temperature and Residence Time on Calorific Value of Torrefied Biomass. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacob, N.; Rahman, N.A.; Matali, S.; Idris, S.S.; Alias, A.B. An Overview of Oil Palm Biomass Torrefaction: Effects of Temperature and Residence Time. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pestaño, L.D.B.; Jose, W.I. Production of Solid Fuel by Torrefaction Using Coconut Leaves As Renewable Biomass. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2016, 5, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Świechowski, K.; Liszewski, M.; Babelewski, P.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. Oxytree Pruned Biomass Torrefaction: Mathematical Models of the Influence of Temperature and Residence Time on Fuel Properties Improvement. Materials 2019, 12, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z. Review of torrefaction reactor technology. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, B. Biomass Characterization and Its Use as Solid Fuel for Combustion. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2012, 3, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aytenew, G.; NIgus, G.; Bedewi, B. Improvement of the Energy Density of Rice Husk Using Dry and Chemical Treated Torrefaction. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kuo, P. Torrefaction and Co-Torrefaction Characterization of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin as Well as Torrefaction of Some Basic Constituents in Biomass. Energy 2011, 36, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, C.; Chen, S. A Novel On-Site Wheat Straw Pretreatment Method: Enclosed Torrefaction. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y.; Di Marcello, M.; De Jong, W. Torrefaction: Mechanistic Study of Constituent Transformations in Herbaceous Biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamvura, T.A.; Pahla, G.; Muzenda, E. Torrefaction of Waste Biomass for Application in Energy Production in South Africa. South African J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batidzirai, B.; Mignot, A.P.R.; Schakel, W.B.; Junginger, H.M.; Faaij, A.P.C. Biomass Torrefaction Technology: Techno-Economic Status and Future Prospects. Energy 2013, 62, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winjobi, O.; Shonnard, D.R.; Bar-Ziv, E.; Zhou, W. Techno-Economic Assessment of the Effect of Torrefaction on Fast Pyrolysis of Pine. Biofuels, Bioprod. Biorefining 2016, 10, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Biomass Sources | Percentage % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin | |
| Napier grass | 39–68 | 16–34 | 17–27 |
| Oil palm petiole | 35 | 18 | 22–25 |
| Solid Fuel | Torrefied NG 1 | Torrefied OPP 1 | Charcoal | Coal | Wood Pellets | Saw Dust | Rice Husk | Bamboo Leaves | Coconut Husk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content (%) | 1.59–5.57 | 1.13–5.05 | 1–5 | 10–15 | 7–10 | 13.8 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 13.4 |
| Calorific value (MJ/kg) | 18.7–24.3 | 21.6–26.2 | 30–32 | 23–28 | 15–16 | 16.9 | 15.6 | 15.7 | 15.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saadon, S.Z.A.H.; Osman, N.B.; Damodaran, M.; Liew, S.E. Torrefaction of Napier Grass and Oil Palm Petiole Waste Using Drop-Type Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis Reactor. Materials 2022, 15, 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082890
Saadon SZAH, Osman NB, Damodaran M, Liew SE. Torrefaction of Napier Grass and Oil Palm Petiole Waste Using Drop-Type Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis Reactor. Materials. 2022; 15(8):2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082890
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaadon, Syazmi Zul Arif Hakimi, Noridah Binti Osman, Moviin Damodaran, and Shan En Liew. 2022. "Torrefaction of Napier Grass and Oil Palm Petiole Waste Using Drop-Type Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis Reactor" Materials 15, no. 8: 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082890
APA StyleSaadon, S. Z. A. H., Osman, N. B., Damodaran, M., & Liew, S. E. (2022). Torrefaction of Napier Grass and Oil Palm Petiole Waste Using Drop-Type Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis Reactor. Materials, 15(8), 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082890