Particles–Matrix Bond in ZnCoO:H and ZnCoAlO:H Films: Issues of Magnetism and Spin Injection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
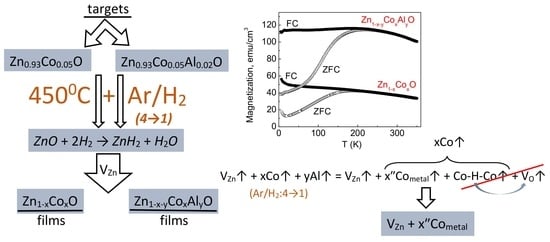
3.1. Magnetization
3.2. Magneto-Optic Spectroscopy
3.3. Electrical Resistance Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dietl, T.; Ohno, H. Dilute ferromagnetic semiconductors: Physics and spintronic structures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2014, 86, 187–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Yamada, K.; Nakatani, Y.; Prejbeanu, I.-L.; Diény, B.; Pirro, P.; Hillebrands, B. Review on spintronics: Principles and device applications. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2020, 509, 166711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, M.; Ilican, S.; Caglar, Y.; Yakuphanoglu, F. Electrical conductivity and optical properties of ZnO nanostructured thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4491–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Leem, J.Y. Crystallization of ZnO thin films via thermal dissipation annealing method for high-performance UV photodetector with ultrahigh response speed. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, M.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Lunney, J.G.; Coey, J.M.D. Anisotropic ferromagnetism in substituted zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 177206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Vijaya, A.R.; Khan, Z.A.; Tarafder, K.; Kumar, A.; Wadhwa, M.K.; Singh, B.; Ghosh, S. Ferromagnetism from non-magnetic ions: Ag-doped ZnO. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolio, A.D.; Testa, A.M.; Bonapasta, A.A. Ferromagnetic behavior and magneto-optical properties of semiconducting Co-doped ZnO. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, M.G.; Jang, H.M.; Ryu, S. Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, A.; Kovács, A.; Ney, V.; Ye, S.; Ollefs, K.; Kammermeier, T.; Wilhelm, F.; Rogalev, A.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E. Structural, chemical and magnetic properties of secondary phases in Co-doped ZnO. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, B.-S.; Cho, Y.C.; Shin, J.-M.; Seo, S.-W.; Cho, C.R.; Takeuchi, I.; Jeong, S.-Y. Origin of the ferromagnetism in ZnCoO from chemical reaction of Co3O4. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Dizayee, W.; Li, X.; Score, D.S.; Neal, J.R.; Behan, A.J.; Mokhtari, A.; Alshammari, M.S.; Al-Qahtani, M.S.; Blythe, H.J.; et al. Enhanced magnetic properties in ZnCoAlO caused by exchange coupling to Co nanoparticles. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 113040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, M.; Hübner, J.; Hägele, D.; Klar, P.J.; Heimbrodt, W.; Rühle, W.W.; Ashenford, D.E.; Lunn, B. Spin injection into semiconductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Addison, K.; Gehring, G.A.; Xu, X. Enhanced room temperature magnetoresistance and spin injection from metallic cobalt in Co/ZnO and Co/ZnAlO films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3607–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrecy, N.; Hamieh, M.; Hebert, C.; Perriere, J. High magnetoresistance at low magnetic fields in self-assembled ZnO-Co nanocomposite films. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Park, C.H.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Yee, K.-J.; Cho, C.R.; Jung, M.-H.; Chadi, D.J. Hydrogen-induced ferromagnetism in ZnCoO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 062504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.S.; Huang, J.C.A.; Chen, S.F.; Liu, C.P. Role of grain boundary and grain defects on ferromagnetism in Co:ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuma, Y.; Odawara, F.; Asada, H.; Koyanagi, T. Effects of annealing and chemical doping on magnetic properties in Co-doped ZnO films. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 104417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.C.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, C.R.; Nahm, H.-H.; Park, C.H.; Jeong, I.K.; Park, S.; Hong, T.E.; et al. Reversible ferromagnetic spin ordering governed by hydrogen in Co-doped ZnO semiconductor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 172514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, B.-S.; Seo, S.-W.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.P.; Jeong, I.I.-K.; Cho, C.R.; Jung, C.U.; Koinuma, H.; et al. A study of the correlation between hydrogen content and magnetism in ZnCoO. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07C304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, W.-K.; Cho, Y.C.; Oh, M.W.; Cho, C.R.; Jeong, S.-Y. Effects of Al doping on the magnetic properties of ZnCoO and ZnCoO:H. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 052412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Mana, B.Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.S.; Gao, X.G.; Wang, C.C.; Hu, B. Effect of substrate temperature on the morphology, structural and optical properties of Zn1−xCoxO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3856–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Cha, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, J.M.; Cho, Y.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.-K.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Cho, C.R.; et al. Ferromagnetism in ZnCoO due to hydrogen-mediated Co-H-Co complexes: How to avoid the formation of Co metal clusters? J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012, 116, 2196–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, I.S.; Chou, H.; Samoshkina, Y.E.; Petrov, D.A.; Lin, H.C.; Chan, W.L.; Sun, S.-J.; Zharkov, S.M.; Bondarenko, G.V.; Platunov, M.S.; et al. Giant hydrogen effect on the structure and physical properties of ZnO and Co-doped ZnO films fabricated by the RF magnetron sputtering in Ar+H2 atmosphere. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2019, 489, 165461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoshkina, Y.E.; Edelman, I.S.; Chou, H.; Lin, H.-C.; Dwivedi, G.D.; Petrov, D.A.; Zharkov, S.M.; Zeer, G.M.; Molokeev, M.S. Structure and physical properties of hydrogenated (Co+Al)-doped ZnO films: Comparative study with Co-doped ZnO films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 264, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edel’man, I.S.; Petrov, D.A.; Ivantsov, R.D.; Zharkov, S.M.; Khaibullin, R.I.; Valeev, V.F.; Nuzhdin, V.I.; Stepanov, A.L. Microstructure and magnetooptics of silicon oxide with implanted nickel nanoparticles. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2011, 113, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orléans, C.; Cerruti, C.; Estournès, C.; Grob, J.J.; Guille, J.L.; Haas, F.; Muller, D.; Richard-Plouet, M.; Stoquert, J.P. Irradiations of implanted cobalt nanoparticles in silica layers. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2003, 209, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Mlack, J.T.; Venkatesan, M.; Stamenov, P. Magnetization process in dilute magnetic oxides. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2501–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, K.L.; Ruta, S.; Anderson, N.R.; Baldomir, D.; Chantrell, R.W.; Serantes, D. Beyond the blocking model to fit nanoparticle ZFC/FC magnetization curves. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoshkina, Y.; Edelman, I.; Chou, H.; Petrov, D.; Zharkov, S.; Neznakhin, D.; Stepanova, E.; Stepanov, A. Magnetic circular dichroism of Co nanoparticles localized in matrices of various types. Materialia 2023, 28, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, C.P.; Livingston, J.D. Superparamagnetism. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, N.A.; Nesmeyanov, M.S. Multi-domain structures in spheroidal Co nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Blythe, H.J.; Dizayee, W.; Heald, S.M.; Gerriu, F.M.; Fox, A.M.; Gehring, G.A. Advantageous use of metallic cobalt in the target for pulsed laser deposition of cobalt-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 072403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.S.; Cho, D.Y.; Choi, Y.N.; Lee, T.W.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, D.; Cho, C.R.; Moriyoshi, C.; et al. Formation of ferromagnetic Co-H-Co complex and spin-polarized conduction band in Co-doped ZnO. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuma, Y.; Asada, H.; Yamamoto, J.; Odawara, F.; Koyanagi, T. Large magnetic circular dichroism of Co clusters in Co-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 142510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varalda, J.; Ribeiro, G.A.P.; Eddrief, M.; Marangolo, M.; George, J.M.; Etgens, V.H.; Mosca, D.H.; de Oliveira, A.J.A. Magnetism and tunneling magnetoresistance of Fe nanoparticles embedded in ZnSe epilayers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torres, J.; Vallés, E.; Gómez, E. Giant magnetoresistance in electrodeposited Co-Ag granular films. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1865–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wu, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, Y. Giant magnetoresistance in transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 252110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Mei, L. Giant magnetoresistance in Fe-In2O3 granular films. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2003, 261, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Q.; Jiang, J.S.; Chien, C.L. Giant magnetoresistance in nonmultilayer magnetic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3749–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Shirolkar, M.M.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Song, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, H. Influences of defects evolvement on the properties of sputtering deposited ZnO:Al films upon hydrogen annealing. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 065020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, M.H.N.; Zheng, R.K.; Li, S.; Ringer, S.R. First-principles investigation of electrical and magnetic properties of ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductors codoped with H. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.Z.; Lu, Y.H.; Tian, Y.F.; Yi, J.B.; Lim, C.C.; Li, Y.F.; Li, G.P.; Wang, D.D.; Yao, B.; Ding, J.; et al. Defect-induced magnetism in undoped wide band gap oxides: Zinc vacancies in ZnO as an example. AIP Adv. 2011, 1, 022152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-C.; Shi, E.-W.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Zhang, H.-W.; Chen, B.-Y.; Song, L.-X.; Wei, S.-Q.; He, B.; Xie, Z. Effect of donor doping on the magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO films. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 307, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Miao, W.; Zou, W.Q.; Xu, M.X.; Zhang, F.M. Enhanced ferromagnetism in single crystalline Co-doped ZnO thin films by Al co-doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 494, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalbout, A.F.; Chen, H.; Whittenburg, S.L. Monte Carlo simulation on the indirect exchange interactions of Co-doped ZnO film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Gas Mixture | Film Thickness (XRFA), nm | Co, % (Δ = ±0.05) | Al, % (Δ = ±0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZO:20 CAZO:20 | Ar + 20% H2 | 71.7 36.9 | 18.9 18.2 | - 7.3 |
| CZO:30 CAZO:30 | Ar + 30% H2 | 53.5 18.8 | 21.7 25.0 | - 10.0 |
| CZO:40 CAZO:40 | Ar + 40% H2 | 37.0 18.0 | 25.6 25.6 | - 10.2 |
| CZO:50 CAZO:50 * | Ar + 50% H2 | 31.6 14.1 | 27.8 * | - * |
| Sample | Gas Mixture | MS at 300 K (emu/cm3) | Mr at 300 K (emu/cm3) | Tb (K) | <D> (nm) | MR at 300 K (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZO:20 | Ar + 20% H2 | 67 | 0.5 | 40 | 3.9 | 0.17 |
| CAZO:20 | 137 | 0 | 90 | 5.2 | 0.06 | |
| CZO:30 | Ar + 30% H2 | 107 | 1.3 | 99 | 5.3 | - |
| CAZO:30 | 251 | 4 | 99 | 5.3 | - | |
| CZO:40 | Ar + 40% H2 | 168 | 2 | 142 | 6 | - |
| CAZO:40 | 325 | 7 | 205 | 6.8 | - | |
| CZO:50 | Ar + 50% H2 | 195 | 10.5 | 184 | 6.6 | 0.3 |
| CAZO:50 | 377 | 25 | 217 | 6.9 | 4 |
| Sample | E1 (cm−1) | E2 (cm−1) | E3 (cm−1) | E4 (cm−1) | E5 (cm−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x0 | dx | x0 | dx | x0 | dx | x0 | dx | x0 | dx | |
| Co-NPs in SiO2 | 11,566 | 4794 | 20,306 | 5063 | 30,094 | 2077 | - | - | - | - |
| CZO:20 | 11,648 | 4794 | 21,251 | 4940 | 31,004 | 2357 | 28,814 | 2856 | - | - |
| CAZO:20 | 11,805 | 4949 | 20,871 | 5221 | 30,701 | 2377 | 26,723 | 4510 | - | - |
| CZO:50 | 10,608 | 4800 | 20,000 | 4957 | 29,313 | 3194 | 24,665 | 4754 | 19,712 | 5630 |
| CAZO:50 | 11,120 | 4814 | 20,006 | 5061 | 29,903 | 2930 | 25,793 | 3748 | 19,838 | 5717 |
| Sample | IE1 | IE2 | IE3 | IE4 | IE5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-NPs in SiO2 | 9300.39 | 6626.99 | 536.72 | - | - |
| CZO:20 | 4.78 × 106 | 4.82 × 106 | 0.54 × 106 | 0.47 × 106 | - |
| CAZO:20 | 12.12 × 106 | 5.75 × 106 | 0.88 × 106 | 3.68 × 106 | - |
| CZO:50 | 28.84 × 106 | 16.37 × 106 | 4.50 × 106 | 10.21 × 106 | 17.26 × 106 |
| CAZO:50 | 81.38 × 106 | 41.29 × 106 | 11.18 × 106 | 26.98 × 106 | 47.75 × 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samoshkina, Y.E.; Rautskii, M.V.; Neznakhin, D.S.; Stepanova, E.A.; Edelman, I.S.; Chou, H. Particles–Matrix Bond in ZnCoO:H and ZnCoAlO:H Films: Issues of Magnetism and Spin Injection. Materials 2023, 16, 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103659
Samoshkina YE, Rautskii MV, Neznakhin DS, Stepanova EA, Edelman IS, Chou H. Particles–Matrix Bond in ZnCoO:H and ZnCoAlO:H Films: Issues of Magnetism and Spin Injection. Materials. 2023; 16(10):3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103659
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamoshkina, Yu. E., M. V. Rautskii, D. S. Neznakhin, E. A. Stepanova, I. S. Edelman, and Hsiung Chou. 2023. "Particles–Matrix Bond in ZnCoO:H and ZnCoAlO:H Films: Issues of Magnetism and Spin Injection" Materials 16, no. 10: 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103659
APA StyleSamoshkina, Y. E., Rautskii, M. V., Neznakhin, D. S., Stepanova, E. A., Edelman, I. S., & Chou, H. (2023). Particles–Matrix Bond in ZnCoO:H and ZnCoAlO:H Films: Issues of Magnetism and Spin Injection. Materials, 16(10), 3659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103659