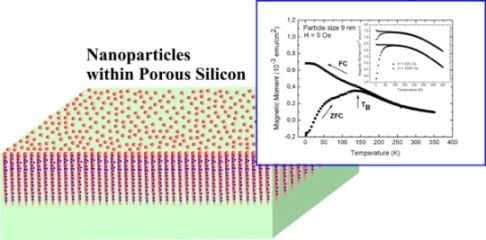
Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in a Silicon Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nanocomposite System
2.1. Fabrication of the Porous Silicon Matrix

2.2. Fabrication of the Iron Oxide Nanoparticles

2.3. Incorporation of Magnetic Nanoparticles into the Pores of Porous Silicon
| Current density [mA/cm2] | Pulse duration [s] | |
|---|---|---|
| Wires (up to a few µm) | 25 | 5 |
| Ellipsoids (up to 500 nm) | 25 | 10 |
| Sphere-like particles (~50 nm) | 25 | 40 |
| Small particles (2–6 nm) | 25 to 50 | 20 |

3. Results and Discussion



3.1. Magnetic Characterization of Porous Silicon with Infiltrated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles






3.2. Magnetic Characterization of Porous Silicon with Deposited Ni Nanoparticles



4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Wei, X.; Skomski, R.; Balamurugan, B.; Sellmyer, D. Magnetism of core-shell Ti:TiO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09B516. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Tsung, Ch.-K.; Yamada, Y.; Yang, P.; Somorjai, G.A. Thermally stable Pt/mesoporous silica core-shell nanocatalysts for high temperature reactions. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, N.; Nigra, M.M.; Nuhfer, T.; Bartel, M.A.; Gellman, A.J. Tailoring the shape of FexPt100−x nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 065602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskos, N.; Typek, J.; Bodziony, T.; Roslaniec, Z.; Narkiewicz, U.; Kawiatkowska, M.; Maryniak, M. Temperature dependence of FMR field of magnetic nanoparticles/polymer composite. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2006, 12, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, U. Preparation of metal oxide or metal nanoparticles in silica via metal coordination to organofunctional trialkoxysilanes. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukatskaya, M.R.; Vyacheslavov, A.S.; Lukashin, A.V.; Tretyakov, Yu.D.; Zhigalina, O.M.; Eliseev, A.A. Cobalt-containing nanocomposites based on zeolites of MFI framework type. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 3866–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials, a decade of alloy development. Mater. Sci. Forum 1999, 312-314, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomsky, R.; Coey, J.M.D. Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 48, 15812–15816. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Murray, C.B. Synthesis of monodisperse cobalt nanocrystals and their assembly into magnetic superlattices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4325:1–4325:6. [Google Scholar]
- Nogues, J.; Sort, J.; Langlais, V.; Doppiu, S.; Dieny, B.; Munoz, J.S.; Surinach, S.; Baro, M.D. Exchange bias in ferromagnetic nanoparticles embedded in an antiferromagnetic matrix. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2005, 2, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, Ph.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, A.G.; Costo, R.; Rebolledo, A.F.; Veintemillas-Erdaguer, S.; Tartaj, P.; Gonzalez-Carreno, T.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J. Progress in the preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejias, R.; Perez-Yagüe, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Cabrera, L.I.; Spada, R.; Acedo, P.; Serna, C.J.; Lazaro, F.J.; Villanueva, A.; Morales, M.P.; Barber, D.F. Dimercaptosuccinic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for magnetically guided in vivo delivery of interferon gamma for cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2938–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomoucka, J.; Drbohlavova, J.; Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Hubalek, J. Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivery. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canham, L.T. Bioactive silicon structure fabrication through nanoetching techniques. Adv. Mater. 1995, 7, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.Ch.; Pacholski, C.; Sailor, M.J. Delivery of nanogram payload using magnetic porous silicon microcarriers. Royal Soc. Chem. 2006, 6, 782–787. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-H.; Derfus, A.M.; Segal, E.; Vecchio, K.S.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Local heating of descrete droplets using magnetic porous silicon-based photonic crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7938–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Föll, H.; Christophersen, M.; Carstensen, J.; Hasse, G. Formation and application of porous silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2002, R39, 93–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P.; Pölt, P.; Krenn, H. Transition metals specifically electrodeposited into porous silicon. Phys. Status Solidi C 2009, 6, 1592–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Pölt, P.; Reichmann, A.; Krenn, H. Self-assembled mesoporous silicon in the crossover between irregular and regular arrangement applicable for Ni filling. Physica E 2007, 38, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Venkatesan, M.; Roca, A.G.; Cabrera, L.; Morales, M.P.; Poelt, P.M.; Albu, M. Magnetic study of Fe3O4-nanoparticles incorporated within mesoporous Silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, K145–K151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubin, S.P.; Koksharov, Yu.A.; Khomutov, G.B.; Yurkov, G.Yu. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, structure and properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2005, 74, 489–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Chourou, M.L.; Sakka, T.; Ogata, Y.H. Filling of mesoporous silicon with copper by electrodeposition from an aqueous solution. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budevski, E.; Staikov, G.; Lorenz, W.J. Electrochemical Phase Formation and Growth. In An Introduction to the Initial Stages of Metal Deposition; VCH: Vancouver, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P.; Pölt, P. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of metal filled double-sided porous silicon samples. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Albu, M.; Poelt, P. Double-sided mesoporous silicon with embedded quasi-regular arranged ferromagnetic nanostructures fabricated by electrodeposition. ECS Trans. 2010, 25, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Poelt, P.; Simic, S.; Krenn, H. Formation of self-assembled metal/silicon nanostructures. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2008, 205, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Homma, T.; Mori, K.; Osaka, T.; Shoji, S. Electrochemical formation process of Si macropore and metal filling for high aspect ratio metal microstructure using single electrolyte system. Electrochemistry 2005, 73, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Fukami, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kawamura, Y.L.; Sakka, T.; Ogata, Y.H. Electrodeposition of noble metals into ordered macropores in p-type silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, D443–D448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkarov, V.M.; Len’shin, A.S.; Agapov, B.L.; Turishchev, S.Yu.; Domashevskaya, E.P. Preparation of porous silicon nanocomposites with iron and cobalt and investigation of their electron structure by X-ray spectroscopy techniques. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2010, 35, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.G.; Anwar, N.; Aylett, B.J.; Earwaker, L.G.; Nasir, M.I.; Farr, J.P.G.; Stiebahl, K.; Keen, J.M. Chemical vapour deposition of metals and metal silicides on the internal surfaces of porous silicon. J. Organomet. Chem. 1992, 437, C7–C12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylett, B.J.; Harding, I.S.; Earwaker, L.G.; Forcey, K.; Giaddui, T. Metallization of porous silicon by chemical vapour infiltration and deposition. Thin Solid Films 1996, 276, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utriainen, M.; Lehto, S.; Niinistö, L.; Dücso, Cs.; Khanh, N.Q.; Horvath, Z.E.; Barsony, I.; Pecz, B. Porous silicon host matrix for deposition by atomic layer epitaxy. Thin Solid Films 1997, 297, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P.; Poelt, P.; Albu, M.; Ali, K.; Reissner, M. Nanotubes consisting of Ni-particles covering the walls of porous silicon. ECS Trans. 2011, 33, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Poelt, P.; Albu, M.; Chernev, B. The interior interfaces of a semiconductor metal nanocomposite and their influence on its physical properties. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2009, 6, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.G.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, N.M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-lrge-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; Poelt, P.; Albu, M. Investigation of a mesoporous silicon based ferromagnetic nanocomposite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Venkatesan, M.; Cabrera, L.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; Poelt, P.; Albu, M. Structural and magnetic characterization of a porous silicon/Fe3O4 composite. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; Ko, S.P.; Liu, H.-L.; Kim, S.; Ju, J.-S.; Kim, Y.K. Sub 5 nm magnetite nanoparticles: Synthesis, microstructure, and magnetic properties. Meter. Lett. 2007, 61, 3124–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, G.F.; Morales, M.P. Field dependence of blocking temperature in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Metastable Nanocrystalline Mater. 2004, 20-21, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denardin, J.D.; Brandl, A.L.; Knobel, M.; Panissod, P.; Pakhomov, A.B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.X. Thermoremanence and zero-field-cooled/field-cooled magnetization study of Cox(SiO2)1−x granular films. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 064422:1–064422:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; Pölt, P. Porous silicon /Fe3O4-nanoparticle composite and its magnetic behavior. ECS Trans. 2008, 16, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Mazo-Zuluaga, J.; Restrepo, J.; Mejia-Lopez, J. Surface anisotropy of a Fe3O4 nanoparticle: A simulation approach. Physica B 2007, 398, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechrakos, D.; Trohidou, K.N. Competition between dipolar and exchange interparticle interactions in magnetic nanoparticle films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 262, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechrakos, D.; Trohidou, K.N. Interplay of dipolar interactions and grain-size distribution in the giant magnetoresistance of granular metals. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allia, P.; Coisson, M.; Knobel, M.; Tiberto, P.; Vinai, F. Magnetic hysteresis based on dipolar interactions in granular magnetic systems. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 12207–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.F.; Diehl, M.R.; Beverly, K.C.; Richman, E.K.; Tolbert, S.H. controlling magnetic coupling between cobalt nanoparticles through nanoscale confinement in hexagonal mesoporous silica. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canham, L.T. Biomedical applications of porous silicon. In Properties of Porous Silicon; Canham, L.T., Ed.; IEE Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, M.; Hernandez-Velez, M.; Pirota, K.; Asenjo, A.; Navas, D.; Velazquez, J.; Vargas, P.; Ramos, C. Arrays of Ni nanowires in alumina membranes: magnetic properties and spatial ordering. Eur. Phys. J. B 2004, 40, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Fähler, S.; Schlörb, H.; Leistner, K.; Schultz, L. Competition between shape anisotropy and magnetoelastic anisotropy in Ni nanowires electrodeposited within alumina templates. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 064421:1–064421:5. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, M.; Pirota, K.; Hernandez-Velez, M.; Prida, V.M.; Navas, D.; Sanz, R.; Batallan, F.; Velazquez, J. Magnetic properties of densely packed arrays of Ni nanowires as a function of their diameter and lattice parameter. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 6642–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Tu, K.-N.; Xie, Y. Theoretical studies of displacement deposition of nickel into porous silicon with ultrahigh aspect ratio. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 3901–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Pölt, P.; Krenn, H. Porous silicon/metal nanocomposite with tailored magnetic properties. Phys. Status Solidi A Appl. Res. 2009, 206, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.H.; Kobayashi, K.; Motoyama, M. Electrochemical metal deposition on silicon. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2006, 10, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, M.; Knez, M.; Gösele, U.; Nielsch, K. Ferromagnetic nanotubes by atomic layer deposition in anodic alumina membranes. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 09J111:1–09J111:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, H.; Lv, L.; Lu, M.; Gu, B.; Du, Y. Metal nanotubes prepared by a sol-gel method followed by a hydrogen reduction procedure. Nanotechnolgy 2006, 17, 5106–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, K.; Granitzer, P.; Pölt, P.; Krenn, H. Transition metals specifically electrodeposited into porous silicon. Phys. Status Solidi C 2009, 6, 1592–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffer, J.; Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX, USA. Magnetically guided drug delivery in porous silicon. Private communication, October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.Ch.; Pacholski, C.; Sailor, M.J. Delivery of nanogram payload using magnetic porous silicon microcarriers. Royal Soc. Chem. 2006, 6, 782–787. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K. Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in a Silicon Matrix. Materials 2011, 4, 908-928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050908
Granitzer P, Rumpf K. Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in a Silicon Matrix. Materials. 2011; 4(5):908-928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050908
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranitzer, Petra, and Klemens Rumpf. 2011. "Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in a Silicon Matrix" Materials 4, no. 5: 908-928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050908
APA StyleGranitzer, P., & Rumpf, K. (2011). Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in a Silicon Matrix. Materials, 4(5), 908-928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050908