Spark Plasma Co-Sintering of Mechanically Milled Tool Steel and High Speed Steel Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
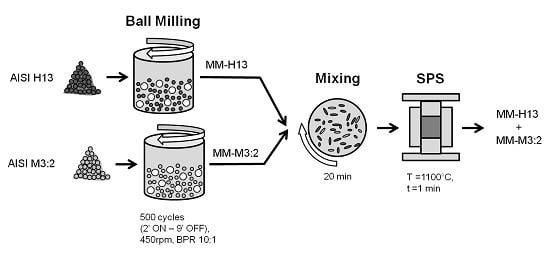
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Mechanical Milling
3.2. Spark Plasma Sintering
3.2.1. Densification
3.2.2. Microstructure
3.2.3. Hardness
3.2.4. Fracture Toughness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berns, H.; Franco, S.D. Effect of coarse hard particles on high-temperature sliding abrasion of new metal matrix composites. Wear 1997, 203–204, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagounis, E.; Lindroos, V.K. Processing and properties of particulate reinforced steel matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 246, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, S.-P.; Turunen, E.; Koskinen, J.; Soderberg, O. Processing hybrid materials for components with improved life-time. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 5160–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zum Gahr, K.-H. Wear by hard particles. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, H.; Von Chuong, N. A new microstructure for PM tooling material. Met. Phys. Adv. Technol. 1996, 6, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Berns, H.; Melander, A.; Weichert, D.; Asnafi, N.; Broeckmann, C.; Groß-Weege, A. A new material for cold forging tools. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1998, 11, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Zadra, M.; Fedrizzi, A. Development of a hybrid tool steel produced by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2009, 24, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Fedrizzi, A.; Zadra, M. Spark plasma sintering of hot work and high speed steel powders for fabrication of a novel tool steel with composite microstructure. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Development of large-size ceramic/metal bulk FGM fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Forum 1999, 308–311, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Aleksamdrova, E.V.; Ilyina, A.M.; Dudina, D.V.; Novoselov, A.N.; Pelve, K.Y.; Grigoryev, E.G. Outside mainstream electronic databases: Review of studies conducted in the USSR and post-Soviet countries on electric current-assisted consolidation of powder materials. Materials 2013, 6, 4375–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Fedrizzi, A.; Zadra, M. Influence of processing parameters and particle size on the properties of hot work and high speed tool steels by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrizzi, A.; Pellizzari, M.; Zadra, M. Influence of particle size ratio on densification behavior of AISI H13/AISI M3:2 powder mixture. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.S.; Volin, T.E. The mechanism of mechanical alloying. Metall. Transact. 1974, 5, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, D.; Courtney, T.H. Modeling of mechanical alloying: Part I. Deformation, coalescence and fragmentation mechanism. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinkaya, C.; Findik, T.; Özbilen, S. An investigation into the effect of experimental parameters on powder grain size of the mechanically milled 17-4 PH stainless steel powders. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoz, H.; Ameyama, K.; Umekawa, S.; Ren, H.; Jaramillo, D.V. The millers’ tale: High-speed steel made harder by attrition. Met. Powder Rep. 2003, 58, 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z. Size and structure evolution of yttria in ODS ferritic alloy powder during mechanical milling and subsequent annealing. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrizzi, A.; Pellizzari, M.; Zadra, M.; Dies, F. Fabrication of Fine Grained Hot Work Tool Steel by Mechanical Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. In Proceedings of the PM2012 Yokohama, Powder Metallurgy World Congress & Exhibition, Yokohama, Japan, 14–18 October 2012.
- ASTM International. Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle; ASTM B962-08; ASTM International: West Coshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials; ASTM E92-82; ASTM International: West Coshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.W.; Jang, J.; Kwon, D. Evaluation of fracture toughness using small notched specimens. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 334, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials; ASTM Standard E399-90; ASTM International: West Coshohocken, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pellizzari, M.; Fedrizzi, A.; Dies, F. Production of a novel hot work tool steel by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. In Proceedings of the 9th International Tooling Conference (TOOL2012), Leoben, Austria, 11–14 September 2012; pp. 207–214.
- Pramanik, A.; Zhang, L.C.; Arsecularatne, J.A. Deformation mechanisms of MMCs under indentation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-L.; Chawla, N. On the correlation between hardness and tensile strength in particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 297, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnberg, L.; Karlsson, A. Influence of powder surface oxidation on some properties of a HIPped martensitic chromium steel. Int. J. Powder Metall. 1988, 24, 107–112. [Google Scholar]













| Material | C | W | Mo | Cr | V | Mn | Si | O | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI H13 | 0.41 | - | 1.60 | 5.10 | 1.10 | 0.35 | 0.90 | 0.0105 | 0.0383 | Bal. |
| AISI M3:2 | 1.28 | 6.40 | 5.00 | 4.20 | 3.10 | - | - | 0.0163 | 0.0559 | Bal. |
| Sample Code | Composition (Weight Fraction) | |
|---|---|---|
| AISI H13 | AISI M3:2 | |
| MM-H13 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| MM-80H13 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| MM-60H13 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| MM-40H13 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| MM-20H13 | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| MM-M3:2 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Material | O (wt %) | N (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| MM-H13 powder | 0.1702 | 0.0978 |
| MM-M3:2 powder | 0.1391 | 0.0950 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellizzari, M.; Fedrizzi, A.; Zadra, M. Spark Plasma Co-Sintering of Mechanically Milled Tool Steel and High Speed Steel Powders. Materials 2016, 9, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060482
Pellizzari M, Fedrizzi A, Zadra M. Spark Plasma Co-Sintering of Mechanically Milled Tool Steel and High Speed Steel Powders. Materials. 2016; 9(6):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060482
Chicago/Turabian StylePellizzari, Massimo, Anna Fedrizzi, and Mario Zadra. 2016. "Spark Plasma Co-Sintering of Mechanically Milled Tool Steel and High Speed Steel Powders" Materials 9, no. 6: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060482
APA StylePellizzari, M., Fedrizzi, A., & Zadra, M. (2016). Spark Plasma Co-Sintering of Mechanically Milled Tool Steel and High Speed Steel Powders. Materials, 9(6), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060482