The Importance of Lassa Fever and Its Disease Management in West Africa
Abstract
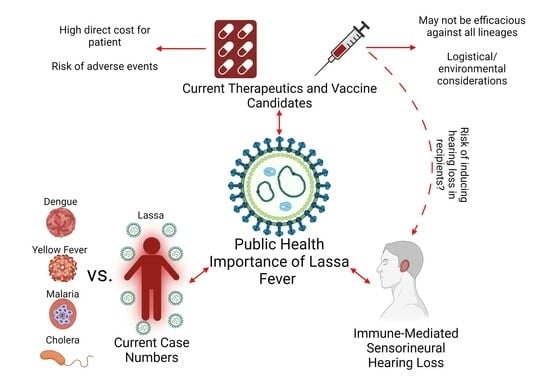
:1. Introduction
2. Current Case Numbers
3. Current Therapeutics
4. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
5. Current Vaccine Candidates
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever: Outbreak Distribution Map; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014.
- Safronetz, D.; Safronetz, D.; Rosenke, K.; Meade-White, K.; Sloan, A.; Maiga, O.; Bane, S.; Martellaro, C.; Scott, D.P.; Sogoba, N.; et al. Temporal analysis of Lassa virus infection and transmission in experimentally infected Mastomys natalensis. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, A.; Oyeyiola, A.; Obadare, A.; Igbokwe, J.; Adesina, A.S.; Onwe, F.; Ukwaja, K.N.; Ajayi, N.A.; Rieger, T.; Gunther, S.; et al. Widespread arenavirus occurrence and seroprevalence in small mammals, Nigeria. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever. 2015. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Olayemi, A.; Cadar, D.; Magassouba, N.; Obadare, A.; Kourouma, F.; Oyeyiola, A.; Fasogbon, S.; Igbokwe, J.; Rieger, T.; Bockholt, S.; et al. New Hosts of The Lassa Virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, A.; Obadare, A.; Oyeyiola, A.; Igbokwe, J.; Fasogbon, A.; Igbahenah, F.; Ortsega, D.; Asogun, D.; Umeh, P.; Vakkai, I.; et al. Arenavirus Diversity and Phylogeography of Mastomys natalensis Rodents, Nigeria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, D.W.; Gibb, R.; Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Ilori, E.A.; Yashe, R.U.; Oladele, S.H.; Amedu, M.O.; Iniobong, A.; Attfield, L.A.; Donnelly, C.A.; et al. Geographical drivers and climate-linked dynamics of Lassa fever in Nigeria. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever: Transmission. 2014. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/transmission/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Ipadeola, O.; Smout, E.; Ilori, E.; Adeyemo, A.; Umeokonkwo, C.; Nwidi, D.; Nwachukwu, W.; Ukponu, W.; Omabe, E.; et al. A cluster of nosocomial Lassa fever cases in a tertiary health facility in Nigeria: Description and lessons learned, 2018. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 83, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylne, A.Q.; Pigott, D.M.; Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.; Duda, K.A.; Messina, J.P.; Weiss, D.J.; Moyes, C.L.; Golding, N.; Hay, S.I. Mapping the zoonotic niche of Lassa fever in Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.A.; Egoh, I.J.; Udensi, N. Epidemiological trends of Lassa fever in Nigeria from 2015–2021: A review. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 20499361211058252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Furuse, Y.; Ilori, E.A.; Ipadeola, O.; Akabike, K.O.; Ahumibe, A.; Ukponu, W.; Bakare, L.; Okwor, T.J.; Joseph, G.; et al. Measures to control protracted large Lassa fever outbreak in Nigeria, 1 January to 28 April 2019. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.E.; Walker, D.H. Pathogenesis of Lassa fever. Viruses 2012, 4, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassa fever. Br. Med. J. 1972, 4, 253–254. [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, A. Lassa Fever: Unveiling the misery of the Nigerian health worker. Ann. Niger. Med. 2017, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever: Signs and Symptoms; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015.
- Walker, D.H.; McCormick, J.B.; Johnson, K.M.; Webb, P.A.; Komba-Kono, G.; Elliott, L.H.; Gardner, J.J. Pathologic and virologic study of fatal Lassa fever in man. Am. J. Pathol. 1982, 107, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Gibb, R.; Moses, L.M.; Redding, D.W.; Jones, K.E. Understanding the cryptic nature of Lassa fever in West Africa. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Lassa Fever. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs179/en/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Prescott, J.B.; Marzi, A.; Safronetz, D.; Robertson, S.J.; Feldmann, H.; Best, S.M. Immunobiology of Ebola and Lassa virus infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, J.K.; Baglole, D.J. Lassa fever: Epidemiology, clinical features, and social consequences. BMJ 2003, 327, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehu, N.Y.; Gomerep, S.S.; Isa, S.E.; Iraoyah, K.O.; Mafuka, J.; Bitrus, N.; Dachom, M.C.; Ogwuche, J.E.; Onukak, A.E.; Onyedibe, K.I.; et al. Lassa Fever 2016 Outbreak in Plateau State, Nigeria-The Changing Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buba, M.I.; Dalhat, M.M.; Nguku, P.M.; Waziri, N.; Mohammad, J.O.; Bomoi, I.M.; Onyiah, A.P.; Onwujei, J.; Balogun, M.S.; Bashorun, A.T.; et al. Mortality Among Confirmed Lassa Fever Cases During the 2015–2016 Outbreak in Nigeria. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, J.G.; Grant, D.S.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Boisen, M.L.; Goba, A.; Hartnett, J.N.; Levy, D.C.; Yenni, R.E.; Moses, L.M.; Fullah, M.; et al. Lassa fever in post-conflict sierra leone. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiosi, J.J.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Shaffer, J.G.; Grant, D.S. Evaluation of Three Clinical Prediction Tools to Predict Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Lassa Fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateer, E.J.; Huang, C.; Shehu, N.Y.; Paessler, S. Lassa fever-induced sensorineural hearing loss: A neglected public health and social burden. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, J.; Reyna, R.A.; Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Urata, S.; Manning, J.T.; Harsell, N.; Cook, R.; Huang, C.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Makishima, T.; et al. CD4 T-cell depletion prevents Lassa fever associated hearing loss in the mouse model. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.B.; King, I.J.; Webb, P.A.; Scribner, C.L.; Craven, R.B.; Johnson, K.M.; Elliott, L.H.; Belmont-Williams, R. Lassa fever: Effective therapy with ribavirin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Prioritizing Diseases for Research and Development in Emergency Contexts. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/prioritizing-diseases-for-research-and-development-in-emergency-contexts (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- CEPI. Priority Diseases. Available online: https://cepi.net/research_dev/priority-diseases/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- McCormick, J.B.; Webb, P.A.; Krebs, J.W.; Johnson, K.M.; Smith, E.S. A prospective study of the epidemiology and ecology of Lassa fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.H.; Ogunyinka, I.A.; Yusuff, K.B.; Ochu, C.L.; Yahaya, M.; Khalid, G.M.; Mutalub, Y.B.; Adeniye, S.B. Knowledge of Lassa fever, its prevention and control practices and their predictors among healthcare workers during an outbreak in Northern Nigeria: A multi-centre cross-sectional assessment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwor, T.J.; Ndu, A.C.; Okeke, T.A.; Aguwa, E.N.; Arinze-Onyia, S.U.; Chinawa, A.; Kassy, W.C.; Ochie, C.N. A review of Lassa fever outbreaks in Nigeria from 1969 to 2017: Epidemiologic profile, determinants and public health response. Niger. J. Med. 2018, 27, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ilori, E.A.; Furuse, Y.; Ipadeola, O.B.; Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Abubakar, A.; Womi-Eteng, O.E.; Ogbaini-Emovon, E.; Okogbenin, S.; Unigwe, U.; Ogah, E.; et al. Epidemiologic and Clinical Features of Lassa Fever Outbreak in Nigeria, January 1–May 6, 2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvignaud, A.; Jaspard, M.; Etafo, I.C.; Gabillard, D.; Serra, B.; Abejegah, C.; le Gal, C.; Abidoye, A.T.; Doutchi, M.; Owhin, S.; et al. Lassa fever outcomes and prognostic factors in Nigeria (LASCOPE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e469–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigeria Centre for Disease Control. Lassa Fever Outbreak in Nigeria. Available online: https://ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/files/sitreps/00235292b8a3f55c01f9ea2eb15c8d3a.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- World Health Organization. Emergency Preparedness, Response: Lassa Fever. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/lassa-fever#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- World Health Organization. On the Frontlines of the Fight against Lassa Fever in Nigeria. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/features/2018/lassa-fever-nigeria/en/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Effiong, F.B.; Makata, V.C.; Elebesunu, E.E.; Bassey, E.E.; Salachi, K.I.; Sagide, M.R.; Abdulameed, H.T.; Uwishema, O. Prospects of malaria vaccination in Nigeria: Anticipated challenges and lessons from previous vaccination campaigns. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajoga, U.A.; Balarabe, H.S.; Olufemi, A.A.; Dalhat, M.M.; Sule, I.B.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Adebowale, A.S.; Adedokun, B.O.; Yahaya, M.; Ajayi, I.O.O.; et al. Trend of malaria cases in Kaduna State using routine surveillance data, 2011–2015. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2019, 32, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbami, A. Epidemiological investigations on arbovirus infections at Igbo-Ora, Nigeria. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1977, 29, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbami, A.H.; Onoja, A.B. Dengue haemorrhagic fever: An emerging disease in Nigeria, West Africa. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otu, A.; Ebenso, B.; Etokidem, A.; Chukwuekezie, O. Dengue fever—An update review and implications for Nigeria, and similar countries. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomhwange, T.; Jean Baptiste, A.E.; Ezebilo, O.; Oteri, J.; Olajide, L.; Emelife, K.; Hassan, S.; Nomhwange, E.R.; Adejoh, K.; Ireye, F.; et al. The resurgence of yellow fever outbreaks in Nigeria: A 2-year review 2017–2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omole, D.O.; Emenike, P.C.; Tenebe, I.T.; Akinde, A.O.; Badejo, A.A. An assessment of water related diseases in a Nigerian community. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugboko, H.U.; Nwinyi, O.C.; Oranusi, S.U.; Oyewale, J.O. Childhood diarrhoeal diseases in developing countries. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adagbada, A.O.; Adesida, S.A.; Nwaokorie, F.O.; Niemogha, M.T.; Coker, A.O. Cholera epidemiology in Nigeria: An overview. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2012, 12, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Guidelines for Lassa Fever Case Management; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. Available online: https://ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/docs/protocols/92_1547068532.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever: Treatment. 2015. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/treatment/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Eberhardt, K.A.; Mischlinger, J.; Jordan, S.; Groger, M.; Gunther, S.; Ramharter, M. Ribavirin for the treatment of Lassa fever: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 87, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.M.; McCormick, J.B.; Webb, P.A.; Smith, E.S.; Elliott, L.H.; King, I.J. Clinical virology of Lassa fever in hospitalized patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, N.A.; Nwigwe, C.G.; Azuogu, B.N.; Onyire, B.N.; Nwonwu, E.U.; Ogbonnaya, L.U.; Onwe, F.I.; Ekaete, T.; Gunther, S.; Ukwaja, K.N. Containing a Lassa fever epidemic in a resource-limited setting: Outbreak description and lessons learned from Abakaliki, Nigeria (January–March 2012). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e1011–e1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogun, D.A.; Adomeh, D.I.; Ehimuan, J.; Odia, I.; Hass, M.; Gabriel, M.; Olschlager, S.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Folarin, O.; Phelan, E.; et al. Molecular diagnostics for lassa fever at Irrua specialist teaching hospital, Nigeria: Lessons learnt from two years of laboratory operation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, A.; van Griensven, J.; van Herp, M.; van den Bergh, R.; Nzomukunda, Y.; Prior, J.; Alders, P.; Jambai, A.; Zachariah, R. Constraints in the diagnosis and treatment of Lassa Fever and the effect on mortality in hospitalized children and women with obstetric conditions in a rural district hospital in Sierra Leone. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.G.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Grant, D.S.; Goba, A.; Momoh, M.; Kanneh, L.; Levy, D.C.; Hartnett, J.N.; Boisen, M.L.; Branco, L.M.; et al. Data set on Lassa fever in post-conflict Sierra Leone. Data Brief 2019, 23, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erameh, C.; Edeawe, O.; Akhideno, P.; Eifediyi, G.; Omansen, T.F.; Wagner, C.; Sarpong, F.; Koch, T.; Wicha, S.; Kurth, F.; et al. Prospective observational study on the pharmacokinetic properties of the Irrua ribavirin regimen used in routine clinical practice in patients with Lassa fever in Nigeria. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.P.; Duvignaud, A.; Jaspard, M.; Malvy, D.; Carroll, M.; Tarning, J.; Olliaro, P.L.; Horby, P.W. Ribavirin for treating Lassa fever: A systematic review of pre-clinical studies and implications for human dosing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, E.L.; Jahrling, P.B. Experimental Lassa fever virus infection successfully treated with ribavirin. Lancet 1979, 1, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Hesse, R.A.; Eddy, G.A.; Johnson, K.M.; Callis, R.T.; Stephen, E.L. Lassa virus infection of rhesus monkeys: Pathogenesis and treatment with ribavirin. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 141, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Peters, C.J.; Stephen, E.L. Enhanced treatment of Lassa fever by immune plasma combined with ribavirin in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 149, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingas, G.; Rosenke, K.; Safronetz, D.; Guedj, J. Lassa viral dynamics in non-human primates treated with favipiravir or ribavirin. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; French, C.E.; Salam, A.P.; Dawson, S.; McAleenan, A.; McGuinness, L.A.; Savovic, J.; Horby, P.W.; Sterne, J.A.C. Lack of Evidence for Ribavirin Treatment of Lassa Fever in Systematic Review of Published and Unpublished Studies. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oestereich, L.; Rieger, T.; Ludtke, A.; Ruibal, P.; Wurr, S.; Pallasch, E.; Bockholt, S.; Krasemann, S.; Munoz-Fontela, C.; Gunther, S. Efficacy of Favipiravir Alone and in Combination with Ribavirin in a Lethal, Immunocompetent Mouse Model of Lassa Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safronetz, D.; Rosenke, K.; Westover, J.B.; Martellaro, C.; Okumura, A.; Furuta, Y.; Geisbert, J.; Saturday, G.; Komeno, T.; Geisbert, T.W.; et al. The broad-spectrum antiviral favipiravir protects guinea pigs from lethal Lassa virus infection post-disease onset. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenke, K.; Feldmann, H.; Westover, J.B.; Hanley, P.W.; Martellaro, C.; Feldmann, F.; Saturday, G.; Lovaglio, J.; Scott, D.P.; Furuta, Y.; et al. Use of Favipiravir to Treat Lassa Virus Infection in Macaques. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1696–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, V.N.; Kann, G.; Ribner, B.S.; Morales, A.; Varkey, J.B.; Mehta, A.K.; Lyon, G.M.; Vanairsdale, S.; Faber, K.; Becker, S.; et al. Favipiravir and Ribavirin Treatment of Epidemiologically Linked Cases of Lassa Fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwafemi, A.; Akhideno, P.; Okogbenin, S. Pharmacokinetics, Tolerability and Safety of Favipiravir Compared to Ribavirin for the Treatment of Lassa Fever: A Randomized Controlled Open Label Phase II Clinical Trial. MediFind. 2022. Available online: https://www.medifind.com/articles/clinical-trial/274001429 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Posakony, J.; Madu, I.G.; Tarcha, E.J.; Lustig, K.H.; Korth, M.J.; Bedard, K.M.; Amberg, S.M. Lassa antiviral LHF-535 protects guinea pigs from lethal challenge. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amberg, S.M.; Snyder, B.; Vliet-Gregg, P.A.; Tarcha, E.J.; Posakony, J.; Bedard, K.M.; Heald, A.E. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of LHF-535, a Potential Treatment for Lassa Fever, in Healthy Adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0095122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogun, D.; Tobin, E.; Momoh, J.; Ochei, O.; Ogbetere, Y.; Shielu, L.; Shielu, L.; Ufuah, F. Medical cost of Lassa fever treatment in Irrua Specialist Teaching Hospital, Nigeria. Int. J. Basic Appl. Innov. Res. 2016, 5, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Sasu, D.D. Monthly Minimum Wage in Nigeria from 2018 to 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1119133/monthly-minimum-wage-in-nigeria/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Osakwe, F. We Pay for Treatment, Lassa Fever Survivors, Relatives Insist. The Guardian. 2018. Available online: https://guardian.ng/news/we-pay-for-treatment-lassa-fever-survivors-relatives-insist/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Etiaba, E.; Onwujekwe, O.; Uzochukwu, B.; Adjagba, A. Investigating payment coping mechanisms used for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria to different socio-economic groups in Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewelukwa, O.; Onoka, C.; Onwujekwe, O. Viewing health expenditures, payment and coping mechanisms with an equity lens in Nigeria. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2013, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.asha.org/public/hearing/sensorineural-hearing-loss/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.K.; Lin, J.R.; Atashband, S.; Irvine, R.A.; Westerberg, B.D. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Heman-Ackah, S.E.; Shaikh, J.A.; Roehm, P.C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Byl, F.M.; Laird, N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1980, 106, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, B.E.; Agrup, C.; Haskard, D.O.; Luxon, L.M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 2010, 375, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, D.M.; McCormick, J.B.; Bennett, D.; Samba, J.A.; Farrar, B.; Machin, S.J.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P. Acute sensorineural deafness in Lassa fever. JAMA 1990, 264, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibekwe, T.S.; Okokhere, P.O.; Asogun, D.; Blackie, F.F.; Nwegbu, M.M.; Wahab, K.W.; Omilabu, S.A.; Akpede, G.O. Early-onset sensorineural hearing loss in Lassa fever. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 268, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmade, A.D.; Segun-Busari, S.; Olajide, T.G.; Ologe, F.E. Profound bilateral sensorineural hearing loss in nigerian children: Any shift in etiology? J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2007, 12, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.J. Measles, mumps, and sensorineural hearing loss. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 830, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, N.; Edward, T.; Sabrina, B.K.; Agnes, N. The prevalence of hearing impairment in the 6 months-5 years HIV/AIDS-positive patients attending paediatric infectious disease clinic at Mulago Hospital. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.E.; Durstenfeld, A.; Roehm, P.C. Viral causes of hearing loss: A review for hearing health professionals. Trends Hear. 2014, 18, 2331216514541361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraff, S.A.; Schleiss, M.R.; Brown, D.K.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Choi, K.Y.; Greinwald, J.H.; Choo, D.I. Macrophage inflammatory proteins in cytomegalovirus-related inner ear injury. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; Reilly, J.S. Sensorineural hearing loss. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1989, 36, 1501–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.E.; Ronca, S.; Tamura, A.; Koma, T.; Seregin, A.V.; Dineley, K.T.; Miller, M.; Cook, R.; Shimizu, N.; Walker, A.G.; et al. Animal Model of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Associated with Lassa Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2920–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Zeng, X.; Cardile, A.P.; Facemire, P.R.; Bell, T.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Shaia, C.I.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Immune-Mediated Systemic Vasculitis as the Proposed Cause of Sudden-Onset Sensorineural Hearing Loss following Lassa Virus Exposure in Cynomolgus Macaques. mBio 2018, 9, e01896-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorba, A.; Corazzi, V.; Bianchini, C.; Aimoni, C.; Pelucchi, S.; Skarzynski, P.H.; Hatzopoulos, S. Autoimmune inner ear disease (AIED): A diagnostic challenge. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 2058738418808680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, P.; Atturo, F.; Di Mario, A.; Portanova, G.; Ralli, M.; De Virgilio, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Hearing loss in autoimmune disorders: Prevalence and therapeutic options. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vambutas, A.; Pathak, S. AAO: Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory (Disease) in Otology: What is New in Immune-Mediated Hearing Loss. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2016, 1, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, B.A.A.; Penido, N.O.; Munhoz, M.S.L.; Bogaz, E.A.; Curi, R.S. Sudden Sensorioneural Hearing Loss and Autoimmune Systemic Diseases. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 21, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Library of Medicine. A Trial to Evaluate the Optimal Dose of MV-LASV (V182-001). ClinicalTrials.gov. (2022). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04055454 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- National Library of Medicine. A Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of rVSVΔG-LASV-GPC Vaccine in Adults in Good General Health. ClinicalTrials.gov. (2022). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04794218 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals. Dose-Ranging Study: Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of INO-4500 in Healthy Volunteers in Ghana. ClinicalTrials.Veeva. (2022). Available online: https://ctv.veeva.com/study/dose-ranging-study-safety-tolerability-and-immunogenicity-of-ino-4500-in-healthy-volunteers-in-gha (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Combredet, C.; Labrousse, V.; Mollet, L.; Lorin, C.; Delebecque, F.; Hurtrel, B.; McClure, H.; Feinberg, M.B.; Brahic, M.; Tangy, F. A molecularly cloned Schwarz strain of measles virus vaccine induces strong immune responses in macaques and transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11546–11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.; Reynard, S.; Carnec, X.; Journeaux, A.; Baillet, N.; Schaeffer, J.; Picard, C.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Allan, R.; Perthame, E.; et al. Vaccines inducing immunity to Lassa virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein protect macaques after a single shot. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.; Reynard, S.; Journeaux, A.; Germain, C.; Hortion, J.; Carnec, X.; Picard, C.; Baillet, N.; Borges-Cardoso, V.; Merabet, O.; et al. A single-shot Lassa vaccine induces long-term immunity and protects cynomolgus monkeys against heterologous strains. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. First FDA-Approved Vaccine for the Prevention of Ebola Virus Disease, Marking a Critical Milestone in Public Health Preparedness and Response; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/first-fda-approved-vaccine-prevention-ebola-virus-disease-marking-critical-milestone-public-health (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Brandly, C.A.; Hanson, R.P. Epizootiology of vesicular stomatitis. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1957, 47, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, J.A.; Fischer, G.F.; Peralta, P.H. Vesicular stomatitis virus in Panama. Human serologic patterns in a cattle raising area. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1967, 86, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freer, G.; Burkhart, C.; Ciernik, I.; Bachmann, M.F.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. Vesicular stomatitis virus Indiana glycoprotein as a T-cell-dependent and -independent antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3650–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haglund, K.; Forman, J.; Krausslich, H.G.; Rose, J.K. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein precursor and envelope proteins from a vesicular stomatitis virus recombinant: High-level production of virus-like particles containing HIV envelope. Virology 2000, 268, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.M.; Vogel, J.E.; Peralta, P.H. Clinical and serological response to laboratory-acquired human infection by Indiana type vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1966, 15, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Stillman, E.A.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses from DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, J.B.; Versteeg, K.M.; Mamaeva, N.; Agans, K.N.; Geisbert, T.W.; Connor, J.H. A Single-Vector, Single-Injection Trivalent Filovirus Vaccine: Proof of Concept Study in Outbred Guinea Pigs. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. 2), S384–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Kretzschmar, E.; Perkins, A.S.; Forman, J.; Price, R.; Buonocore, L.; Kawaoka, Y.; Rose, J.K. Vaccination with a recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus expressing an influenza virus hemagglutinin provides complete protection from influenza virus challenge. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4704–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, S.P.; Ball, L.A.; Barr, J.N.; Wertz, G.T. Efficient recovery of infectious vesicular stomatitis virus entirely from cDNA clones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8388–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, R.M.; Adler, B.; Holland, J.J. Cell-mediated immunity to vesicular stomatitis virus infections in mice. Exp. Cell Biol. 1978, 46, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.K. Rhabdoviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 1221–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, N.F.; Roberts, A.; Buonocore, L.; Rose, J.K. Glycoprotein exchange vectors based on vesicular stomatitis virus allow effective boosting and generation of neutralizing antibodies to a primary isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10903–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, A.; Feldmann, F.; O’Donnell, K.L.; Hanley, P.W.; Messaoudi, I.; Feldmann, H. Preexisting Immunity Does Not Prevent Efficacy of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Filovirus Vaccines in Nonhuman Primates. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, S671–S676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadyga, L.; Stein, D.R.; Qiu, X.; Safronetz, D. Pre-clinical development of a vaccine against Lassa fever. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2018, 44, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbutt, M.; Liebscher, R.; Wahl-Jensen, V.; Jones, S.; Moller, P.; Wagner, R.; Volchkov, V.; Klenk, H.D.; Feldmann, H.; Stroher, U. Properties of replication-competent vesicular stomatitis virus vectors expressing glycoproteins of filoviruses and arenaviruses. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5458–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Jones, S.; Fritz, E.A.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Geisbert, J.B.; Liebscher, R.; Grolla, A.; Stroher, U.; Fernando, L.; Daddario, K.M.; et al. Development of a new vaccine for the prevention of Lassa fever. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, A.; Feldmann, F.; Geisbert, T.W.; Feldmann, H.; Safronetz, D. Vesicular stomatitis virus-based vaccines against Lassa and Ebola viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safronetz, D.; Mire, C.; Rosenke, K.; Feldmann, F.; Haddock, E.; Geisbert, T.; Feldmann, H.A. A recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-based Lassa fever vaccine protects guinea pigs and macaques against challenge with geographically and genetically distinct Lassa viruses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.A.; Broderick, K.E.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Shaia, C.I.; Bell, T.M.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Spik, K.W.; Badger, C.V.; Guttieri, M.C.; Sardesai, N.Y.; et al. Enhanced Efficacy of a Codon-Optimized DNA Vaccine Encoding the Glycoprotein Precursor Gene of Lassa Virus in a Guinea Pig Disease Model When Delivered by Dermal Electroporation. Vaccines 2013, 1, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regules, J.A.; Beigel, J.H.; Paolino, K.M.; Voell, J.; Castellano, A.R.; Hu, Z.; Munoz, P.; Moon, J.E.; Ruck, R.C.; Bennett, J.W.; et al. A Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Ebola Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Shaia, C.I.; Facemire, P.R.; Bell, T.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Shamblin, J.D.; Wollen, S.E.; Broderick, K.E.; Sardesai, N.Y.; et al. A DNA vaccine delivered by dermal electroporation fully protects cynomolgus macaques against Lassa fever. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Wollen, S.E.; Shamblin, J.D.; Zelko, J.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Zeng, X.; Broderick, K.E.; Schmaljohn, C.S. DNA vaccines elicit durable protective immunity against individual or simultaneous infections with Lassa and Ebola viruses in guinea pigs. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Banglore, P.; Cashman, K.A.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Schultheis, K.; Pugh, H.; Nguyen, J.; Humeau, L.M.; Broderick, K.E.; Ramos, S.J. Immunogenicity of a protective intradermal DNA vaccine against lassa virus in cynomolgus macaques. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Patterson, J.; Carrion, R.; Moshkoff, D.; Ticer, A.; Zapata, J.; Brasky, K.; Geiger, R.; Hubbard, G.B.; Bryant, J.; et al. A live attenuated vaccine for Lassa fever made by reassortment of Lassa and Mopeia viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13934–13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.M.; Jokinen, J.D.; Lukashevich, I.S. Attenuated Replication of Lassa Virus Vaccine Candidate ML29 in STAT-1(−/−) Mice. Pathogens 2019, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, R.A.; Maruyama, J.; Mantlo, E.K.; Manning, J.T.; Taniguchi, S.; Makishima, T.; Lukashevich, I.S.; Paessler, S. Depletion of CD4 and CD8 T Cells Reduces Acute Disease and Is Not Associated with Hearing Loss in ML29-Infected STAT1−/− Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, R., Jr.; Patterson, J.L.; Johnson, C.; Gonzales, M.; Moreira, C.R.; Ticer, A.; Brasky, K.; Hubbard, G.B.; Moshkoff, D.; Zapata, J.; et al. A ML29 reassortant virus protects guinea pigs against a distantly related Nigerian strain of Lassa virus and can provide sterilizing immunity. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, R., Jr.; Bredenbeek, P.; Jiang, X.; Tretyakova, I.; Pushko, P.; Lukashevich, I.S. Vaccine Platforms to Control Arenaviral Hemorrhagic Fevers. J. Vaccines Vaccin. 2012, 3, 1000160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Salvato, M.S.; Mansfield, K.; Brasky, K.; Zapata, J.; Cairo, C.; Goicochea, M.; Hoosien, G.E.; Ticer, A.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the ML29 reassortant vaccine for Lassa fever in small non-human primates. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5246–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.C.; Poonia, B.; Bryant, J.; Davis, H.; Ateh, E.; George, L.; Crasta, O.; Zhang, Y.; Slezak, T.; Jaing, C.; et al. An attenuated Lassa vaccine in SIV-infected rhesus macaques does not persist or cause arenavirus disease but does elicit Lassa virus-specific immunity. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.G.; Shapiro, B.J.; Matranga, C.B.; Sealfon, R.; Lin, A.E.; Moses, L.M.; Folarin, O.A.; Goba, A.; Odia, I.; Ehiane, P.E.; et al. Clinical Sequencing Uncovers Origins and Evolution of Lassa Virus. Cell 2015, 162, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehichioya, D.U.; Dellicour, S.; Pahlmann, M.; Rieger, T.; Oestereich, L.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Cadar, D.; Ighodalo, Y.; Olokor, T.; Omomoh, E.; et al. Phylogeography of Lassa Virus in Nigeria. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00929-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, J.T.; Forrester, N.; Paessler, S. Lassa virus isolates from Mali and the Ivory Coast represent an emerging fifth lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, S.R.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Albarino, C.G.; Kainulainen, M.H.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Guerrero, L.W.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Klena, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Spengler, J.R.; et al. The S Genome Segment Is Sufficient to Maintain Pathogenicity in Intra-Clade Lassa Virus Reassortants in a Guinea Pig Model. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Public Health Impact of Diseases Endemic to Nigeria | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Cases per Year | Deaths per Year | Reference |
| Lassa Fever | 500 (suspected) | 25 | [31] |
| 75 (confirmed) | |||
| Malaria | 100,000,000 | 300,000 | [38] |
| Yellow Fever | 4000 (suspected) | 112 | [43] |
| 140 (confirmed) | |||
| Cholera | 3000 | 781 | [46] |
| Dengue | Published case numbers have not been reported but high seropositivity (10–67%) has been observed in Nigerian populations | [40,41,42] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyna, R.A.; Littlefield, K.E.; Shehu, N.; Makishima, T.; Maruyama, J.; Paessler, S. The Importance of Lassa Fever and Its Disease Management in West Africa. Viruses 2024, 16, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020266
Reyna RA, Littlefield KE, Shehu N, Makishima T, Maruyama J, Paessler S. The Importance of Lassa Fever and Its Disease Management in West Africa. Viruses. 2024; 16(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyna, Rachel A., Kirsten E. Littlefield, Nathan Shehu, Tomoko Makishima, Junki Maruyama, and Slobodan Paessler. 2024. "The Importance of Lassa Fever and Its Disease Management in West Africa" Viruses 16, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020266
APA StyleReyna, R. A., Littlefield, K. E., Shehu, N., Makishima, T., Maruyama, J., & Paessler, S. (2024). The Importance of Lassa Fever and Its Disease Management in West Africa. Viruses, 16(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020266