The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions
Abstract
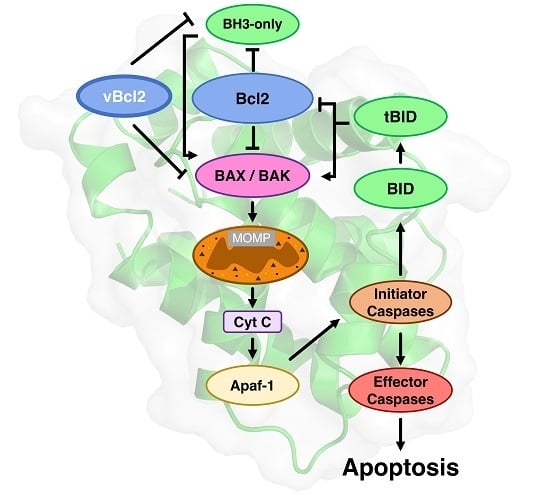
:1. Introduction
2. An Expanding Family of Viral Bcl-2 Orthologues has been Discovered
3. Membrane Interactions
4. Viral Bcl-2-mediated Subversion of Programmed Cell Death
5. Herpesviridae-Encoded Bcl-2 Homologs
6. Poxviridae-Encoded Bcl-2 Homologs
7. Asfarviridae and iridoviridae-Encoded Bcl-2 Homologs
8. Other Functional Roles of Viral Bcl-2 Homologs
9. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Abrams, J.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Fulda, S.; et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardwick, J.M.; Soane, L. Multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvansakul, M.; Hinds, M.G. The Bcl-2 family: Structures, interactions and targets for drug discovery. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvansakul, M.; Hinds, M.G. The structural biology of BH3-only proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 544, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kvansakul, M.; Hinds, M.G. Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family and its mimicry by viral proteins. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbridge, A.R.; Grabow, S.; Strasser, A.; Vaux, D.L. Thirty years of BCL-2: Translating cell death discoveries into novel cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Prior, P.; Salvesen, G.S. The protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity, activation and inhibition. Biochem. J. 2004, 384, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, G.; Niso-Santano, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanave, C.; Santamaria, M.; Saccone, C. Comparative genomics: The evolutionary history of the Bcl-2 family. Gene 2004, 333, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmasek, C.M.; Godzik, A. Evolution of the animal apoptosis network. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouacheria, A.; Rech de Laval, V.; Combet, C.; Hardwick, J.M. Evolution of Bcl-2 homology motifs: Homology versus homoplasy. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouacheria, A.; Brunet, F.; Gouy, M. Phylogenomics of life-or-death switches in multicellular animals: Bcl-2, BH3-Only, and BNip families of apoptotic regulators. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2395–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautureau, G.J.; Day, C.L.; Hinds, M.G. Intrinsically disordered proteins in Bcl-2 regulated apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1808–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamas-Din, A.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, F.; Voss, A.; Kerr, J.B.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Tai, L.; Echeverry, N.; Bouillet, P.; Strasser, A.; Kaufmann, T. BCL-2 family member BOK is widely expressed but its loss has only minimal impact in mice. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.J.; Li, H.; Salvesen, G.S.; Yuan, J.; Wagner, G. Solution structure of BID, an intracellular amplifier of apoptotic signaling. Cell 1999, 96, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.M.; Fushman, D.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; Cowburn, D. Solution structure of the proapoptotic molecule BID: A structural basis for apoptotic agonists and antagonists. Cell 1999, 96, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, L.P.; Shamas-Din, A.; Andrews, D.W. Bid: A Bax-like BH3 protein. Oncogene 2008, 27, S93–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tjandra, N. Structural insights of tBid, the caspase-8-activated Bid, and its BH3 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35840–35851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Bobkov, A.A.; Plesniak, L.A.; Marassi, F.M. Mapping the interaction of pro-apoptotic tBID with pro-survival BCL-XL. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 8704–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, M.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Muller, W.E. Sponge Bcl-2 homologous protein (BHP2-GC) confers distinct stress resistance to human HEK-293 cells. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, M.; Miller, W.E.G. Cell death in Porifera: Molecular players in the game of apoptotic cell death in living fossils. Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.N.; Schmidt, N.; Schade, M.; Pauly, B.; Alexandrova, O.; Bottger, A. Hydra and the evolution of apoptosis. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, M.; Belikov, S.I.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Schroder, H.C.; Hamer, B.; Perovic-Ottstadt, S.; Borejko, A.; Luthringer, B.; Muller, I.M.; Muller, W.E. Axial (apical-basal) expression of pro-apoptotic and pro-survival genes in the lake baikal demosponge Lubomirskia baicalensis. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasi, M.; Pauly, B.; Schmidt, N.; Cikala, M.; Stiening, B.; Kasbauer, T.; Zenner, G.; Popp, T.; Wagner, A.; Knapp, R.T.; et al. The molecular cell death machinery in the simple cnidarian Hydra includes an expanded caspase family and pro- and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Taubenberger, A.; Vos, M.J.; Bottger, A.; Lasi, M.; Lai, F.P.; Fischer, M.; Rottner, K. Monomeric red fluorescent protein variants used for imaging studies in different species. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottger, A.; Alexandrova, O. Programmed cell death in Hydra. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, T.D.; Knack, B.; Ukani, L.; Seneca, F.; Weiss, Y.; Leggat, W. In situ hybridisation detects pro-apoptotic gene expression of a Bcl-2 family member in white syndrome-affected coral. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2015, 117, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caria, S.; Hinds, M.G.; Kvansakul, M. Structural insight into an evolutionarily ancient programmed cell death regulator - the crystal structure of marine sponge BHP2 bound to LB-Bak-2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Dai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Marrack, P.; Kappler, J.W. The structure of a Bcl-xL/Bim fragment complex: Implications for Bim function. Immunity 2003, 19, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvansakul, M.; Wei, A.H.; Fletcher, J.I.; Willis, S.N.; Chen, L.; Roberts, A.W.; Huang, D.C.; Colman, P.M. Structural basis for apoptosis inhibition by Epstein-Barr virus BHRF1. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvansakul, M.; van Delft, M.F.; Lee, E.F.; Gulbis, J.M.; Fairlie, W.D.; Huang, D.C.; Colman, P.M. A structural viral mimic of prosurvival Bcl-2: A pivotal role for sequestering proapoptotic Bax and Bak. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjara, S.; Caria, S.; Dixon, L.K.; Hinds, M.G.; Kvansakul, M. Structural Insight into African Swine Fever Virus A179L-Mediated Inhibition of Apoptosis. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.; Woo, J.S.; Liang, C.; Lee, K.H.; Hong, H.S.; E, X.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, J.U.; Oh, B.H. Structural and biochemical bases for the inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis by viral BCL-2 of murine gamma-herpesvirus 68. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caria, S.; Marshall, B.; Burton, R.L.; Campbell, S.; Pantaki-Eimany, D.; Hawkins, C.J.; Barry, M.; Kvansakul, M. The N Terminus of the Vaccinia Virus Protein F1L Is an Intrinsically Unstructured Region That Is Not Involved in Apoptosis Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14600–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.C.; Bahar, M.W.; Cooray, S.; Chen, R.A.; Whalen, D.M.; Abrescia, N.G.; Alderton, D.; Owens, R.J.; Stuart, D.I.; Smith, G.L.; et al. Vaccinia virus proteins A52 and B14 Share a Bcl-2-like fold but have evolved to inhibit NF-κB rather than apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihan, P.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Hetz, C. BCL-2 family: Integrating stress responses at the ER to control cell demise. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, S.; Pulendran, B.; Lambrecht, B.N. Emerging functions of the unfolded protein response in immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsten, T.; Ross, A.J.; King, A.; Zong, W.X.; Rathmell, J.C.; Shiels, H.A.; Ulrich, E.; Waymire, K.G.; Mahar, P.; Frauwirth, K.; et al. The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bak and Bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hersh, B.M.; Conradt, B.; Zhou, Z.; Riemer, D.; Gruenbaum, Y.; Horvitz, H.R. Translocation of C. elegans CED-4 to nuclear membranes during programmed cell death. Science 2000, 287, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; El Maadidi, S.; Faletti, L.; Haun, F.; Labib, S.; Schejtman, A.; Maurer, U.; Borner, C. How do viruses control mitochondria-mediated apoptosis? Virus Res. 2015, 209, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Garvey, T.L.; Cohen, J.I. The murine gammaherpesvirus-68 M11 protein inhibits Fas- and TNF-induced apoptosis. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2737–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, S.K.; Tseng, C.C.; Rao, L.; White, E. Functional complementation of the adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein with Bcl-2 in the inhibition of apoptosis in infected cells. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6553–6566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.; Huen, D.; Rowe, M.; Dawson, C.; Johnson, G.; Rickinson, A. Epstein-Barr virus-coded BHRF1 protein, a viral homologue of Bcl-2, protects human B cells from programmed cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8479–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.H.; Nicholas, J.; Bellows, D.S.; Hayward, G.S.; Guo, H.G.; Reitz, M.S.; Hardwick, J.M. A Bcl-2 homolog encoded by Kaposi sarcoma-associated virus, human herpesvirus 8, inhibits apoptosis but does not heterodimerize with Bax or Bak. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Petros, A.M.; Virgin, H.W.; Fesik, S.W.; Olejniczak, E.T. Solution structure of a Bcl-2 homolog from Kaposi sarcoma virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3428–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouacheria, A.; Banyai, M.; Rigal, D.; Schmidt, C.J.; Gillet, G. Characterization of vNR-13, the first alphaherpesvirus gene of the bcl-2 family. Virology 2003, 316, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Rivas, C.; Esteban, M.; Escribano, J.M.; Alonso, C. African swine fever virus gene A179L, a viral homologue of bcl-2, protects cells from programmed cell death. Virology 1996, 225, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, S.Y.; Chen, C.; Weng, S.P.; Chan, S.M.; He, J.G. Complete genome sequence analysis of an iridovirus isolated from the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Virology 2005, 339, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.T.; Ting, J.W.; Wu, M.H.; Wu, M.F.; Guo, I.C.; Chang, C.Y. Complete genome sequence of the grouper iridovirus and comparison of genomic organization with those of other iridoviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, K.A.; Opgenorth, A.; Upton, C.; McFadden, G. Myxoma virus M11L ORF encodes a protein for which cell surface localization is critical in manifestation of viral virulence. Virology 1992, 191, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilenko, S.T.; Stewart, T.L.; Meyers, A.F.; Barry, M. Vaccinia virus encodes a previously uncharacterized mitochondrial-associated inhibitor of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14345–14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.F.; Ludwig, H.; Holzapfel, J.; Kvansakul, M.; Chen, L.; Huang, D.C.; Sutter, G.; Knese, M.; Hacker, G. Modified vaccinia virus Ankara protein F1L is a novel BH3-domain-binding protein and acts together with the early viral protein E3L to block virus-associated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvansakul, M.; Yang, H.; Fairlie, W.D.; Czabotar, P.E.; Fischer, S.F.; Perugini, M.A.; Huang, D.C.; Colman, P.M. Vaccinia virus anti-apoptotic F1L is a novel Bcl-2-like domain-swapped dimer that binds a highly selective subset of BH3-containing death ligands. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.; Puthalakath, H.; Caria, S.; Chugh, S.; Doerflinger, M.; Colman, P.M.; Kvansakul, M. Variola virus F1L is a Bcl-2-like protein that unlike its vaccinia virus counterpart inhibits apoptosis independent of Bim. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.; Taylor, J.; Quilty, D.; Barry, M. Ectromelia virus encodes an anti-apoptotic protein that regulates cell death. Virology 2015, 475, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Campbell, S.; Mehta, N.; Thibault, J.; Colman, P.M.; Barry, M.; Huang, D.C.; Kvansakul, M. Sheeppox virus SPPV14 encodes a Bcl-2-like cell death inhibitor that counters a distinct set of mammalian proapoptotic proteins. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11501–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadyga, L.; Lam, S.C.; Okamoto, T.; Kvansakul, M.; Huang, D.C.; Barry, M. Deerpox virus encodes an inhibitor of apoptosis that regulates Bak and Bax. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R.; Caria, S.; Marshall, B.; Barry, M.; Kvansakul, M. Structural basis of Deerpox virus-mediated inhibition of apoptosis. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadyga, L.; Gerig, J.; Stewart, T.; Barry, M. Fowlpox virus encodes a Bcl-2 homologue that protects cells from apoptotic death through interaction with the proapoptotic protein Bak. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11032–11045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anasir, M.I.; Caria, S.; Skinner, M.A.; Kvansakul, M. Structural basis of apoptosis inhibition by the fowlpox virus protein FPV039. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9010–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The genome of canarypox virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, D.; Ledgerwood, E.C.; Hibma, M.H.; Fleming, S.B.; Whelan, E.M.; Mercer, A.A. A novel Bcl-2-like inhibitor of apoptosis is encoded by the parapoxvirus ORF virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7178–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren, R.T.; Iyer, S.; Kluck, R.M. Pore formation by dimeric Bak and Bax: An unusual pore? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, M.; Hammerschmidt, W. Epstein-Barr virus provides a new paradigm: A requirement for the immediate inhibition of apoptosis. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, F.; Cakir, Z.; Reichenbach, F.; Emschermann, F.; Lauterwasser, J.; Kaiser, A.; Ichim, G.; Tait, S.W.; Frank, S.; Langer, H.F.; et al. Differential retrotranslocation of mitochondrial Bax and Bak. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, W.X.; Li, C.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Lindsten, T.; Yu, Q.C.; Yuan, J.; Thompson, C.B. Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Otsuki, Y.; Kataoka, S.; Ito, Y.; Tsujimoto, Y. Multiple subcellular localization of Bcl-2: Detection in nuclear outer membrane, endoplasmic reticulum membrane, and mitochondrial membranes. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 2468–2471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolter, K.G.; Hsu, Y.T.; Smith, C.L.; Nechushtan, A.; Xi, X.G.; Youle, R.J. Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.T.; Wolter, K.G.; Youle, R.J. Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlich, F.; Banerjee, S.; Suzuki, M.; Cleland, M.M.; Arnoult, D.; Wang, C.; Neutzner, A.; Tjandra, N.; Youle, R.J. Bcl-x(L) retrotranslocates Bax from the mitochondria into the cytosol. Cell 2011, 145, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, F.; Cakir, Z.; Reichenbach, F.; Youle, R.J.; Edlich, F. The C-terminal helix of Bcl-x(L) mediates Bax retrotranslocation from the mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenberg, B.; Wang, P.; Keeble, J.A.; Rodriguez-Enriquez, R.; Walker, S.; Owens, T.W.; Foster, F.; Tanianis-Hughes, J.; Brennan, K.; Streuli, C.H.; et al. Bax exists in a dynamic equilibrium between the cytosol and mitochondria to control apoptotic priming. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Youle, R.J.; Tjandra, N. Structure of Bax: Coregulation of dimer formation and intracellular localization. Cell 2000, 103, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltvai, Z.N.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Annan, J.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Crawford, S.A.; Hausmann, G.; Beaumont, J.G.; Parma, L.P.; Chen, L.; Lackmann, M.; Lithgow, T.; Hinds, M.G.; et al. Proapoptotic BH3-only proteins trigger membrane integration of prosurvival Bcl-w and neutralize its activity. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, M.G.; Lackmann, M.; Skea, G.L.; Harrison, P.J.; Huang, D.C.; Day, C.L. The structure of Bcl-w reveals a role for the C-terminal residues in modulating biological activity. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opgenorth, A.; Graham, K.; Nation, N.; Strayer, D.; McFadden, G. Deletion analysis of two tandemly arranged virulence genes in myxoma virus, M11L and myxoma growth factor. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4720–4731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nechushtan, A.; Smith, C.L.; Hsu, Y.T.; Youle, R.J. Conformation of the Bax C-terminus regulates subcellular location and cell death. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2330–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondrial regulation of cell death. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockings, C.; Anwari, K.; Ninnis, R.L.; Brouwer, J.; O’Hely, M.; Evangelista, M.; Hinds, M.G.; Czabotar, P.E.; Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D.; et al. Bid chimeras indicate that most BH3-only proteins can directly activate Bak and Bax, and show no preference for Bak versus Bax. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.; Blose, S.H.; Stillman, B.W. Nuclear envelope localization of an adenovirus tumor antigen maintains the integrity of cellular DNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1984, 4, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Modha, D.; White, E. The E1B 19K protein associates with lamins in vivo and its proper localization is required for inhibition of apoptosis. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, B.A.; Ferreira Lacerda, A.; Drummond, D.J.; Wangen, C.; Eaton, H.E.; Brunetti, C.R. Frog virus 3 open reading frame 97R localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and induces nuclear invaginations. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9199–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaez, B.; Cabezas, M.; Munoz-Moreno, R.; Galindo, I.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Alonso, C. A179L, a new viral Bcl2 homolog targeting Beclin 1 autophagy related protein. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, K.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Bax and Bak Pores: Are We Closing the Circle? Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.A.; Mishra, P.; Baber, J.L.; Strub, M.P.; Tjandra, N. Conformational Heterogeneity in the Activation Mechanism of Bax. Structure 2017, 25, 1310–1316.e1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleicken, S.; Hantusch, A.; Das, K.K.; Frickey, T.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Quantitative interactome of a membrane Bcl-2 network identifies a hierarchy of complexes for apoptosis regulation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, L.; Wurm, C.A.; Bruser, C.; Neumann, D.; Jans, D.C.; Jakobs, S. Bax assembles into large ring-like structures remodeling the mitochondrial outer membrane in apoptosis. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador-Gallego, R.; Mund, M.; Cosentino, K.; Schneider, J.; Unsay, J.; Schraermeyer, U.; Engelhardt, J.; Ries, J.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Bax assembly into rings and arcs in apoptotic mitochondria is linked to membrane pores. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu-Fernandez, V.; Sancho, M.; Genoves, A.; Lucendo, E.; Todt, F.; Lauterwasser, J.; Funk, K.; Jahreis, G.; Perez-Paya, E.; Mingarro, I.; et al. Bax transmembrane domain interacts with prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins in biological membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Fujimoto, L.M.; Hirshman, N.; Bobkov, A.A.; Antignani, A.; Youle, R.J.; Marassi, F.M. Conformation of BCL-XL upon Membrane Integration. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchmore, S.W.; Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Nettesheim, D.; Chang, B.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Wong, S.L.; et al. X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 1996, 381, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Nisan, D.; Fujimoto, L.M.; Antignani, A.; Barnes, A.; Tjandra, N.; Youle, R.J.; Marassi, F.M. Characterization of the membrane-inserted C-terminus of cytoprotective BCL-XL. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 122, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.; Bell, F.; Westphal, D.; Anwari, K.; Gulbis, J.; Smith, B.J.; Dewson, G.; Kluck, R.M. Bak apoptotic pores involve a flexible C-terminal region and juxtaposition of the C-terminal transmembrane domains. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewson, G.; Kratina, T.; Czabotar, P.; Day, C.L.; Adams, J.M.; Kluck, R.M. Bak activation for apoptosis involves oligomerization of dimers via their α6 helices. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavathiotis, E.; Suzuki, M.; Davis, M.L.; Pitter, K.; Bird, G.H.; Katz, S.G.; Tu, H.C.; Kim, H.; Cheng, E.H.; Tjandra, N.; et al. BAX activation is initiated at a novel interaction site. Nature 2008, 455, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Westphal, D.; Dewson, G.; Ma, S.; Hockings, C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F.; Yao, S.; Robin, A.Y.; Smith, B.J.; et al. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell 2013, 152, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, A.Y.; Krishna Kumar, K.; Westphal, D.; Wardak, A.Z.; Thompson, G.V.; Dewson, G.; Colman, P.M.; Czabotar, P.E. Crystal structure of Bax bound to the BH3 peptide of Bim identifies important contacts for interaction. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J.W.; Manion, M.K.; Maguire, B.; Hockenbery, D.M. BCL-XL dimerization by three-dimensional domain swapping. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Grille, J.; Busch, L.K.; Martinez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. Avian reovirus-triggered apoptosis enhances both virus spread and the processing of the viral nonstructural muNS protein. Virology 2014, 462–463, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Sabbatini, P.; Perez, D.; Rao, L.; Modha, D.; White, E. The E1B 19K protein blocks apoptosis by interacting with and inhibiting the p53-inducible and death-promoting Bax protein. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrow, S.N.; White, J.H.; Martinou, I.; Raven, T.; Pun, K.T.; Grinham, C.J.; Martinou, J.C.; Brown, R. Cloning of a Bcl-2 homologue by interaction with adenovirus E1B 19K. Nature 1995, 374, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Wallen, H.D.; Nunez, G.; White, E. E1B 19,000-molecular-weight protein interacts with and inhibits CED-4-dependent, FLICE-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6052–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Petros, A.M.; Virgin, H.W.; Fesik, S.W.; Olejniczak, E.T. Solution structure of the BHRF1 protein from Epstein-Barr virus, a homolog of human Bcl-2. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, A.M.; Letai, A. BH3 domains define selective inhibitory interactions with BHRF-1 and KSHV BCL-2. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbien, A.L.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. The Epstein-Barr virus Bcl-2 homolog, BHRF1, blocks apoptosis by binding to a limited amount of Bim. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5663–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.L.; Long, H.M.; Stylianou, J.; Thomas, W.A.; Leese, A.; Bell, A.I.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Mautner, J.; Rickinson, A.B.; Rowe, M. An Epstein-Barr virus anti-apoptotic protein constitutively expressed in transformed cells and implicated in burkitt lymphomagenesis: The Wp/BHRF1 link. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.L.; Yim, C.; Gustafson, E.; Graf, T.; Sage, D.R.; Hanify, K.; Williams, L.; Fingeroth, J.; Finberg, R.W. Epstein-Barr virus encodes a novel homolog of the bcl-2 oncogene that inhibits apoptosis and associates with Bax and Bak. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5181–5185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bellows, D.S.; Howell, M.; Pearson, C.; Hazlewood, S.A.; Hardwick, J.M. Epstein-Barr virus BALF1 is a BCL-2-like antagonist of the herpesvirus antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procko, E.; Berguig, G.Y.; Shen, B.W.; Song, Y.; Frayo, S.; Convertine, A.J.; Margineantu, D.; Booth, G.; Correia, B.E.; Cheng, Y.; et al. A computationally designed inhibitor of an Epstein-Barr viral Bcl-2 protein induces apoptosis in infected cells. Cell 2014, 157, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caria, S.; Chugh, S.; Nhu, D.; Lessene, G.; Kvansakul, M. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of Epstein-Barr virus BHRF1 in complex with a benzoylurea peptidomimetic. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2012, 68, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarid, R.; Sato, T.; Bohenzky, R.A.; Russo, J.J.; Chang, Y. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes a functional Bcl-2 homologue. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Lampe, M.; Gunther, T.; Brune, W. The Viral Bcl-2 Homologs of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and Rhesus Rhadinovirus Share an Essential Role for Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, V.E.; Cheng, E.H.; Veliuona, M.; Zou, S.; Clem, R.J.; Mayer, M.L.; Hardwick, J.M. Herpesvirus saimiri encodes a functional homolog of the human Bcl-2 oncogene. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4118–4122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Virgin, H.W., 4th; Latreille, P.; Wamsley, P.; Hallsworth, K.; Weck, K.E.; Dal Canto, A.J.; Speck, S.H. Complete sequence and genomic analysis of murine γherpesvirus 68. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5894–5904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.J.; Ebrahimi, B.C.; Dutia, B.M.; Nash, A.A.; Stewart, J.P. Murine γherpesvirus M11 gene product inhibits apoptosis and is expressed during virus persistence. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Colbert, C.L.; Becker, N.; Wei, Y.; Levine, B. Molecular basis of the regulation of Beclin 1-dependent autophagy by the γ-herpesvirus 68 Bcl-2 homolog M11. Autophagy 2008, 4, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmacher, V.S.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; Dionne, C.A.; Kedersha, N.L.; Vater, C.A.; Han, J.W.; Lutz, R.J.; Watanabe, S.; Cahir McFarland, E.D.; et al. A cytomegalovirus-encoded mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis structurally unrelated to Bcl-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12536–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowski, M.; Norris, K.L.; Cleland, M.M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Youle, R.J. Role of Bax and Bak in mitochondrial morphogenesis. Nature 2006, 443, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J. Cytomegalovirus proteins vMIA and m38.5 link mitochondrial morphogenesis to Bcl-2 family proteins. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6232–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Edlich, F.; Bermejo, G.A.; Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J.; Tjandra, N. Structural mechanism of Bax inhibition by cytomegalovirus protein vMIA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20901–20906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cam, M.; Handke, W.; Picard-Maureau, M.; Brune, W. Cytomegaloviruses inhibit Bak- and Bax-mediated apoptosis with two separate viral proteins. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzur, M.; Fleming, P.; Huang, D.C.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Andoniou, C.E. Virally mediated inhibition of Bax in leukocytes promotes dissemination of murine cytomegalovirus. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoult, D.; Skaletskaya, A.; Estaquier, J.; Dufour, C.; Goldmacher, V.S. The murine cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor m38.5 binds Bax and blocks Bax-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, P.; Kvansakul, M.; Voigt, V.; Kile, B.T.; Kluck, R.M.; Huang, D.C.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Andoniou, C.E. MCMV-mediated inhibition of the pro-apoptotic Bak protein is required for optimal in vivo replication. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handke, W.; Luig, C.; Popovic, B.; Krmpotic, A.; Jonjic, S.; Brune, W. Viral inhibition of BAK promotes murine cytomegalovirus dissemination to salivary glands. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3592–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.M.; Gillet, G.; Burnside, J.; Thomas, S.J.; Neiman, P. Role of Nr13 in regulation of programmed cell death in the bursa of Fabricius. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.; Godzik, A.; Reed, J.C. Bcl-B, a novel Bcl-2 family member that differentially binds and regulates Bax and Bak. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12481–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouacheria, A.; Arnaud, E.; Venet, S.; Lalle, P.; Gouy, M.; Rigal, D.; Gillet, G. Nrh, a human homologue of Nr-13 associates with Bcl-Xs and is an inhibitor of apoptosis. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5846–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautureau, G.J.; Yabal, M.; Yang, H.; Huang, D.C.; Kvansakul, M.; Hinds, M.G. The restricted binding repertoire of Bcl-B leaves Bim as the universal BH3-only prosurvival Bcl-2 protein antagonist. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautureau, G.J.; Day, C.L.; Hinds, M.G. The structure of Boo/Diva reveals a divergent Bcl-2 protein. Proteins 2010, 78, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.; Woo, J.S.; Liang, C.; Lee, K.H.; Jung, J.U.; Oh, B.H. An insight into the mechanistic role of Beclin 1 and its inhibition by prosurvival Bcl-2 family proteins. Autophagy 2008, 4, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, M.; Zhai, D.; Jin, C.; Aleshin, A.E.; Stec, B.; Reed, J.C.; Liddington, R.C. Vaccinia virus N1L protein resembles a B cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family protein. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Willis, S.N.; Wei, A.; Smith, B.J.; Fletcher, J.I.; Hinds, M.G.; Colman, P.M.; Day, C.L.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, D.C. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, C.; Czabotar, P.E.; Hinds, M.G.; Day, C.L. Structural plasticity underpins promiscuous binding of the prosurvival protein A1. Structure 2008, 16, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.N.; Chen, L.; Dewson, G.; Wei, A.; Naik, E.; Fletcher, J.I.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, D.C. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Meusburger, S.; Hawkins, C.J.; Riglar, D.T.; Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D.; Huang, D.C.; Adams, J.M. Apoptosis is triggered when prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins cannot restrain Bax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18081–18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Thibault, J.; Mehta, N.; Colman, P.M.; Barry, M.; Kvansakul, M. Structural insight into BH3 domain binding of vaccinia virus antiapoptotic F1L. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8667–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.M.; Quilty, D.; Banadyga, L.; Barry, M. The vaccinia virus protein F1L interacts with Bim and inhibits activation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39728–39739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, A.; Cross, J.R.; Downward, J.; Way, M. Interaction of F1L with the BH3 domain of Bak is responsible for inhibiting vaccinia-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilenko, S.T.; Banadyga, L.; Bond, D.; Barry, M. The vaccinia virus F1L protein interacts with the proapoptotic protein Bak and inhibits Bak activation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14031–14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Hazes, B.; Kvansakul, M.; Colman, P.; Barry, M. Vaccinia virus F1L interacts with Bak using highly divergent Bcl-2 homology domains and replaces the function of Mcl-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.L.; Wasilenko, S.T.; Barry, M. Vaccinia virus F1L protein is a tail-anchored protein that functions at the mitochondria to inhibit apoptosis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, H.; Barry, M.; Lee, S.F.; Sun, X.; Graham, K.; Stone, J.; Bleackley, R.C.; McFadden, G. M11L: A novel mitochondria-localized protein of myxoma virus that blocks apoptosis of infected leukocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Barrett, J.W.; Nazarian, S.H.; Everett, H.; Gao, X.; Bleackley, C.; Colwill, K.; Moran, M.F.; McFadden, G. Myxoma virus M11L prevents apoptosis through constitutive interaction with Bak. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7097–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E.; Corbett, K.D.; Berger, J.M.; McFadden, G.; Handel, T.M. Structure of M11L: A myxoma virus structural homolog of the apoptosis inhibitor, Bcl-2. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, D.; Ledgerwood, E.C.; Tyndall, J.D.; Hibma, M.H.; Ueda, N.; Fleming, S.B.; Mercer, A.A. The orf virus inhibitor of apoptosis functions in a Bcl-2-like manner, binding and neutralizing a set of BH3-only proteins and active Bax. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadyga, L.; Veugelers, K.; Campbell, S.; Barry, M. The fowlpox virus BCL-2 homologue, FPV039, interacts with activated Bax and a discrete subset of BH3-only proteins to inhibit apoptosis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7085–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilan, J.G.; Lu, Z.; Afonso, C.L.; Kutish, G.F.; Sussman, M.D.; Rock, D.L. An African swine fever virus gene with similarity to the proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and the Epstein-Barr virus gene BHRF1. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4391–4394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galindo, I.; Hernaez, B.; Diaz-Gil, G.; Escribano, J.M.; Alonso, C. A179L, a viral Bcl-2 homologue, targets the core Bcl-2 apoptotic machinery and its upstream BH3 activators with selective binding restrictions for Bid and Noxa. Virology 2008, 375, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.W.; Huang, Y.J.; John, J.A.; Chang, Y.N.; Yuan, C.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Yeh, C.H.; Shen, S.T.; Lin, F.P.; Tsui, W.H.; et al. Iridovirus Bcl-2 protein inhibits apoptosis in the early stage of viral infection. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piya, S.; White, E.J.; Klein, S.R.; Jiang, H.; McDonnell, T.J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Fueyo, J. The E1B19K oncoprotein complexes with Beclin 1 to regulate autophagy in adenovirus-infected cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlic, M.; Faustin, B.; Postigo, A.; Yu, E.C.; Proell, M.; Gombosuren, N.; Krajewska, M.; Flynn, R.; Croft, M.; Way, M.; et al. Vaccinia virus F1L protein promotes virulence by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7808–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.; Zhai, D.; Jin, C.; Gerlic, M.; Reed, J.C.; Liddington, R. Structural determinants of caspase-9 inhibition by the vaccinia virus protein, F1L. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 30748–30758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, D.; Yu, E.; Jin, C.; Welsh, K.; Shiau, C.W.; Chen, L.; Salvesen, G.S.; Liddington, R.; Reed, J.C. Vaccinia virus protein F1L is a caspase-9 inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5569–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooray, S.; Bahar, M.W.; Abrescia, N.G.; McVey, C.E.; Bartlett, N.W.; Chen, R.A.; Stuart, D.I.; Grimes, J.M.; Smith, G.L. Functional and structural studies of the vaccinia virus virulence factor N1 reveal a Bcl-2-like anti-apoptotic protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Motes, C.M.; Cooray, S.; Ren, H.; Almeida, G.M.F.; McGourty, K.; Bahar, M.W.; Stuart, D.I.; Grimes, J.M.; Graham, S.C.; Smith, G.L. Inhibition of Apoptosis and NF-κB Activation by Vaccinia Protein N1 Occur via Distinct Binding Surfaces and Make Different Contributions to Virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002430. [Google Scholar]
- Fedosyuk, S.; Grishkovskaya, I.; de Almeida Ribeiro, E., Jr.; Skern, T. Characterization and structure of the vaccinia virus NF-κB antagonist A46. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3749–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Heo, L.; Seok, C.; Choe, J. Structure of vaccinia virus A46, an inhibitor of TLR4 signaling pathway, shows the conformation of VIPER motif. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidel, S.; Maluquer de Motes, C.; Mansur, D.S.; Strnadova, P.; Smith, G.L.; Graham, S.C. Vaccinia virus protein A49 is an unexpected member of the B-cell Lymphoma (Bcl)-2 protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5991–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalverda, A.P.; Thompson, G.S.; Vogel, A.; Schroder, M.; Bowie, A.G.; Khan, A.R.; Homans, S.W. Poxvirus K7 protein adopts a Bcl-2 fold: Biochemical mapping of its interactions with human DEAD box RNA helicase DDX3. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedosyuk, S.; Bezerra, G.A.; Radakovics, K.; Smith, T.K.; Sammito, M.; Bobik, N.; Round, A.; Ten Eyck, L.F.; Djinovic-Carugo, K.; Uson, I.; et al. Vaccinia Virus Immunomodulator A46: A Lipid and Protein-Binding Scaffold for Sequestering Host TIR-Domain Proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Schroder, M.; Khan, A.R. Structural basis for targeting of human RNA helicase DDX3 by poxvirus protein K7. Structure 2009, 17, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, M.; Baran, M.; Bowie, A.G. Viral targeting of DEAD box protein 3 reveals its role in TBK1/IKKepsilon-mediated IRF activation. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, D.; Giam, M.; Hughes, P.D.; Siggs, O.M.; Heger, K.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Adams, J.M.; Strasser, A.; Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D.; et al. The role of BH3-only protein Bim extends beyond inhibiting Bcl-2-like prosurvival proteins. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncet, D.; Larochette, N.; Pauleau, A.L.; Boya, P.; Jalil, A.A.; Cartron, P.F.; Vallette, F.; Schnebelen, C.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; et al. An anti-apoptotic viral protein that recruits Bax to mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22605–22614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, J.R.; Postigo, A.; Blight, K.; Downward, J. Viral pro-survival proteins block separate stages in Bax activation but changes in mitochondrial ultrastructure still occur. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, P.F.; Fearnhead, H.O. Viral hijacking of host caspases: An emerging category of pathogen-host interactions. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins-McMillen, D.; Kim, J.H.; Nogalski, M.T.; Stevenson, E.V.; Chan, G.C.; Caskey, J.R.; Cieply, S.J.; Yurochko, A.D. Human Cytomegalovirus Promotes Survival of Infected Monocytes via a Distinct Temporal Regulation of Cellular Bcl-2 Family Proteins. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2356–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Virus-Encoded Pro-Survival Bcl-2 | Reference |
|---|---|
| γ-herpesviruses 68 M11 | [45] |
| Adenovirus E1B19K | [46] |
| Epstein-Barr virus BHRF1 | [34,47] |
| Epstein-Barr virus BALF1 | [34,47] |
| Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus Ks-Bcl-2 | [48,49] |
| Turkey herpesvirus vnr-13 | [50] |
| African swine fever virus A179L | [36,51] |
| Grouper iridovirus GIV66 | [52,53] |
| Myxoma virus M11L | [35,54] |
| Vaccinia virus F1L | [55,56,57] |
| Variola virus F1L | [58] |
| Ectromelia virus EMV025 | [59] |
| Sheeppox virus SPPV14 | [60] |
| Deerpox virus DPV022 | [61,62] |
| Fowlpox virus FPV029 | [63,64] |
| Canarypox CNP058 | [65] |
| Lumpy skin disease virus LD17 | [60] |
| Orfvirus ORFV125 | [66] |
| Poxviral Bcl-2 | ||||||
| Pro-death | SPPV14 | M11L | MVA_F1L | VAR_F1L | DPV022 | FPV039 |
| Bad | >2000 | >1000 | NB | NB | NB | 653 |
| Bid | 341 | 100 | NB | 3200 | NB | 2 |
| Bik | >2000 | >1000 | NB | NB | NB | 30 |
| Bim | 26 | 5 | 250 | NB | 340 | 10 |
| Bmf | 67 | 100 | NB | NB | NB | 16 |
| Hrk | 63 | >1000 | NB | NB | NB | 24 |
| Noxa | >2000 | >1000 | NB | NB | NB | 28 |
| Puma | 65 | >1000 | NB | NB | NB | 24 |
| Bak | 46 | 50 | 4300 | 2640 | 6930 | 76 |
| Bax | 32 | 75 | 1850 | 960 | 4040 | 76 |
| Beclin-1 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | NB | n/a |
| Asfarviral Bcl-2 | Herpesviral Bcl-2 | |||||
| A179L | BHRF1 | Ks-Bcl-2 | M11 | N1L | ||
| Bad | 258 | >2000 | >1000 | NB | >1000 | |
| Bid | 26 | 109 | 112 | 232 | 152 | |
| Bik | 190 | >2000 | >1000 | NB | n/a | |
| Bim | 6 | 18 | 29 | 131 | 72 | |
| Bmf | 254 | >2000 | >1000 | 300 | n/a | |
| Hrk | 1487 | >1000 | >1000 | 719 | n/a | |
| Noxa | 1575 | >2000 | >1000 | 132 | n/a | |
| Puma | 31 | 70 | 69 | 370 | n/a | |
| Bak | 29 | 150 | <50 | 76.3 | 71 | |
| Bax | 26 | 1,400 | 980 | 690 | n/a | |
| Beclin-1 | n/a | n/a | 40.2 | n/a | ||
| Human Bcl-2 | Sponge Bcl-2 | |||||
| Bcl-2 | Bcl-w | Bcl-xL | Mcl-1 | A1 | BHP2 | |
| Bad | 16 | 30 | 5.3 | >100,000 | 15,000 | NB |
| Bid | 6800 | 40 | 82 | 2100 | 1 | NB |
| Bik | 850 | 12 | 43 | 1700 | 58 | NB |
| Bim | 2.6 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 2.4 | 1 | NB |
| Bmf | 3 | 9.8 | 9.7 | 1100 | 180 | NB |
| Hrk | 320 | 49 | 3.7 | 370 | 46 | 3760 |
| Noxa | >100,000 | >100,000 | >100,000 | 24 | 20 | NB |
| Puma | 3.3 | 5.1 | 6.3 | 5 | 1 | NB |
| Bak | >1000 | 500 | 50 | 10 | 3 | 66 |
| Bax | 100 | 58 | 130 | 12 | n/a | NB |
| Beclin-1 | n/a | n/a | 2300 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kvansakul, M.; Caria, S.; Hinds, M.G. The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions. Viruses 2017, 9, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100290
Kvansakul M, Caria S, Hinds MG. The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions. Viruses. 2017; 9(10):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100290
Chicago/Turabian StyleKvansakul, Marc, Sofia Caria, and Mark G. Hinds. 2017. "The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions" Viruses 9, no. 10: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100290
APA StyleKvansakul, M., Caria, S., & Hinds, M. G. (2017). The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions. Viruses, 9(10), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100290