Skull Bone Regeneration Using Chitosan–Siloxane Porous Hybrids—Long-Term Implantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Porous Hybrids
2.2. In Vivo Animal Experiments
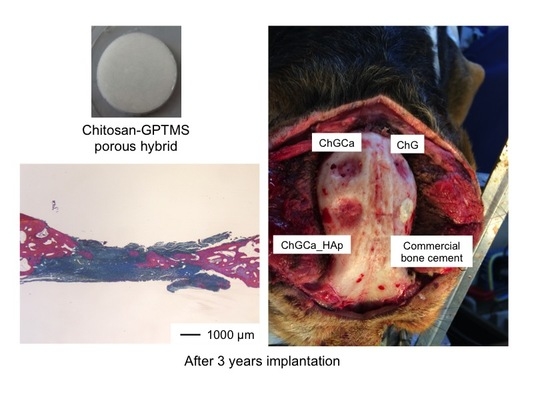
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanan, A.; Haines, S.J. Repairing holes in the head: A history of cranioplasty. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Czirjak, S.; Szeifert, G.T. Surgical experience with frontolateral keyhole craniotomy through a superciliary skin incision. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindert, E.V.; Perneczky, A.; Fries, G.; Pierangeli, E. The supraorbital keyhole approach to supratentorial aneurysms; concept and technique. Surg. Neurol. 1998, 49, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl-Dieter, L. Reliability of cranial flap fixation techniques: Comparative experimental evaluation of suturing, titanium miniplates, and a new rivet-like titanium clamp (CranioFix). Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 902–905. [Google Scholar]
- Ohata, K.; Haque, M.; Tsuruno, T.; Morino, M.; Soares, S.B., Jr.; Hakuda, A. Craniotomy repair with titanium miniplates. J. Clin. Neurosci. 1998, 5, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, P.D.; Morawetz, R.B.; Zeiger, E.; Pincock, J.L. Reconstruction of cranial defects with porous hydroxyapatite blocks. Neurosurgery 1989, 25, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T. Reconstruction of surgical skull defects with hydroxyapatite ceramic buttons and granules. Acta Neurochir. 1988, 90, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Hara, H.; Okudera, H.; Takemae, T.; Sugita, K. Usefulness of ceramic implants in neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 1987, 21, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easwer, H.V.; Rajeev, A.; Varma, H.K.; Vijayan, S.; Bhattacharya, R.N. Cosmetic and radiological outcome following the use of synthetic hydroxyapatite porous-dense bilayer burr-hole buttons. Acta Neurochir. 2007, 149, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujovny, M.; Aviles, A.; Agner, C. An innovative approach for cranioplasty using hydroxyapatite cement. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 48, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, P.D.; Friedman, C.D.; Jones, K.; Chow, L.C.; Sisson, G.A. Experimental hydroxyapatite cement cranioplasty. Plat. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 90, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheggen, R.; Merten, H.A. Correction of skull defects using hydroxyapatite cement (HAC)—Evidence derived from animal experiments and clinical experience. Acta Neurochir. 2001, 143, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanela, M.E.; Coventry, M.D.; MacCarty, C.S.; Miller, W.E. The fate of patients with methyl methacrylate cranioplasty. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1972, 54, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, L. Tissue reaction to methyl methacrylate monomer: A comparative study in the rabbit’s ear on the toxicity of methyl metacrylate of varying composition. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1976, 47, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Burm, J.S.; Yang, W.Y.; Kang, S.Y. Vascularized bipedicled pericranial flaps for reconstruction of chronic scalp ulcer occurring after cranioplasty. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2013, 40, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanus, G.Z.; Tanriverdi, T.; Ulu, M.O.; Kafadar, A.M.; Tanriover, N.; Ozien, F. Use of Cortoss as an alternative material in calvarial defects: The first clinical results in cranioplasty. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2008, 19, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Hirano, N.; Ishihara, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Matsuura, K. Calcium phosphate cement leakage after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures: Risk factor analysis for cement leakage. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 2, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Herford, A.S.; Famà, F.; Bramanti, E.; Fiorillo, L.; Lauritano, F.; Sambataro, S.; Troiano, G.; Laino, L. Facial bone reconstruction using both marine or non-marine bone substitutes: Evaluation of current outcomes in a systematic literature review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R. Reprint of: Review of bioactive glass: From Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, S58–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A.; Lopes, M.A.; Santos, J.D.; Fernandes, M.H. Cytocompatibility of MG63 cells on chitosan-organosiloxane hybrid membranes. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A.; Lopes, M.A.; Santos, J.D.; Costa, M.A.; Fernandes, M.H. Physical, chemical and in vitro biological profile of chitosan hybrid membrane as a function of organosiloxane concentration. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Okayama, T.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A. Synthesis and cytocompatibility of porous chitosan-silicate hybrids for tissue engineering scaffold application. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirosaki, Y. Preparation of organic-inorganic hybrids with silicate network for the medical applications. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 120, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Furuse, M.; Asano, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Kuroiwa, T. Use of chitosan-siloxane porous hybrid scaffold as novel burr hole covers. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2016, 5, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan, J.A. Histological and Histochemical Methods. Theory and Practice; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Bloxham, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, H.; Mori, T.; Fujinaga, T. Topical formulations and wound healing applications of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Yamada, H.; Tanaka, I.; Kaba, N.; Matsuura, M.; Okumura, M.; Kadosawa, T.; Fujinaga, T. Accelerating effects of chitosan for healing at early phase of experimental open wound in dogs. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Nakamura, F.; Murakami, M.; Okumura, M.; Kadosawa, T.; Fujinaga, T. Evaluation effects of chitosan for the extra-cellular matrix production by fibroblasts and the growth factors production by macrophages. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynos, I.D.; Edgar, A.J.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.K. Ionic products on bioactive glass dissolution increase proliferation of human osteoblasts and induce insulin-like growth factor II mRNA expression and protein synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Tsuru, K.; Moribayashi, H.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Gibson, I.R.; Osaka, A. Preparation of osteocompatible Si(IV)-enriched chitosan-silicate hybrids. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirosaki, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A.; Asano, T. Preparation of porous chitosan-siloxane hybrids coated with hydroxyapatite particles. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, A.J.; Sen, S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 2006, 126, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shirosaki, Y.; Furuse, M.; Asano, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kuroiwa, T. Skull Bone Regeneration Using Chitosan–Siloxane Porous Hybrids—Long-Term Implantation. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020070
Shirosaki Y, Furuse M, Asano T, Kinoshita Y, Kuroiwa T. Skull Bone Regeneration Using Chitosan–Siloxane Porous Hybrids—Long-Term Implantation. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleShirosaki, Yuki, Motomasa Furuse, Takuji Asano, Yoshihiko Kinoshita, and Toshihiko Kuroiwa. 2018. "Skull Bone Regeneration Using Chitosan–Siloxane Porous Hybrids—Long-Term Implantation" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020070
APA StyleShirosaki, Y., Furuse, M., Asano, T., Kinoshita, Y., & Kuroiwa, T. (2018). Skull Bone Regeneration Using Chitosan–Siloxane Porous Hybrids—Long-Term Implantation. Pharmaceutics, 10(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020070