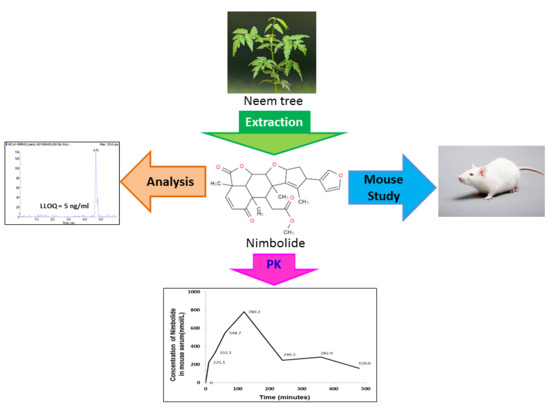
A Sensitive Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Nimbolide in Mouse Serum: Application to a Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Stock Solutions, Calibration Standards, and Quality Control Samples
2.3. Calibrator and Quality Control Sample Preparation
2.4. LC-MS/MS System and Configurations
2.5. Construction of Standard Curve
2.6. Validation Strategy
2.7. Matrix Effect Assessment
2.8. Recovery Assessment
2.9. Stability Assessment
2.9.1. Freeze and Thaw Stability
2.9.2. Bench-Top Stability
2.10. Drug Measurement in Mouse Serum Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Selection of Internal Standards
3.2. Extraction Protocol Optimization
3.3. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Optimization
3.4. Selectivity, Carry-Over and Linearity
3.5. Accuracy and Precision
3.6. Matrix Effect
3.7. Recovery
3.8. Stability
3.9. Application of LC-MS/MS Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roses, A.D. Pharmacogenetics and drug development: The path to safer and more effective drugs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, I. The State of Innovation in Drug Development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieling, J. LC-MS-MS Experiences with Internal Standards. Chromatographia 2002, 55, S107–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Matrix effect in quantitative LC/MS/MS analyses of biological fluids: A method for determination of finasteride in human plasma at picogram per milliliter concentrations. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochanakij, S.; Thebtaranonth, Y.; Yenjai, C.; Yuthavong, Y. Nimbolide, a constituent of Azadirachta indica, inhibits Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1985, 16, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- RRojanapo, W.; Suwanno, S.; Somjaree, R.; Glinsukon, T.; Thebtaranont, Y. Mutagenic and Antibacterial Activity Testing of Nimbolide and Nimbic Acid. J. Sci. Soc. Thail. 1985, 111, 177–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Wesley, S.D.; Pradeep Singh, N.D.; Malathi, R.; Rajan, S.S. Insect antifeedant activity of tetranortriterpenoids from the Rutales. A perusal of structural relations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4484–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand Solomon, K.; Malathi, R.; Rajan, S.S.; Anitha, G.; Josepha Lourdu Raj, J.; Narasimhan, S.; Suresh, G.; Gopalakrishnan, G. The isomeric compounds nimbolide and isonimbolide. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2005, 61, o70–o72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, P.; Anandan, R.; Nagini, S. Evaluation of Azadirachta indica Leaf Fractions for in Vitro Antioxidant Potential and Protective Effects against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage to pBR322 DNA and Red Blood Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6990–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Ray, D.; Anjum, F.; Hassan, M.I. Search of potential inhibitor against New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 from a series of antibacterial natural compounds. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.M.; Venkata, K.C.N.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Potential of neem (Azadirachta indica L.) for prevention and treatment of oncologic diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, K.K.; Mishra, S.K. Development of a Sensitive HPTLC Method for Quantification of Nimbolide in Azadirachta indica and Its Dosage Form. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, N.A.; Dey, A.; Singh, G.; Easwari, T. Development and validation of HPLC method for quantitative estimation of nimbolide in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- FDA Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001.
- Cohen, E.; Quistad, G.B.; Casida, J.E. Cytotoxicity of nimbolide, epoxyazadiradione and other limonoids from neem insecticide. Life Sci. 1996, 58, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.H.; Mohan, K.C.; Rao, A.J.; Nagini, S. Nimbolide a limonoid from Azadirachta indica inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human choriocarcinoma (BeWo) cells. Investig. New Drugs 2009, 27, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Prasad, S.; Reuter, S.; Kannappan, R.; Yadav, V.R.; Ravindran, J.; Hema, P.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Nair, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Modification of cysteine 179 of IkappaBalpha kinase by nimbolide leads to down-regulation of NF-kappaB-regulated cell survival and proliferative proteins and sensitization of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35406–35417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.K.; Kobori, M.; Takenaka, M.; Nakahara, K.; Shinmoto, H.; Isobe, S.; Tsushida, T. Antiproliferative effect on human cancer cell lines after treatment with nimbolide extracted from an edible part of the neem tree (Azadirachta indica). Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, K.; Priyadarsini, R.V.; Anitha, P.; Ramalingam, K.; Sakthivel, R.; Purushothaman, G.; Singh, A.K.; Karunagaran, D.; Nagini, S. Nimbolide, a neem limonoid abrogates canonical NF-kappaB and Wnt signaling to induce caspase-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma (HepG2) cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 681, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, P.; Mercy, A.B.; Arunkamar, R.; Sharmila, G.; Bhat, F.A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Singh, P.R.; Arunakaran, J. Nimbolide inhibits invasion and migration, and down-regulates uPAR chemokine gene expression, in two breast cancer cell lines. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarsini, R.V.; Manikandan, P.; Kumar, G.H.; Nagini, S. The neem limonoids azadirachtin and nimbolide inhibit hamster cheek pouch carcinogenesis by modulating xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes, DNA damage, antioxidants, invasion and angiogenesis. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.H.; Priyadarsini, R.V.; Vinothini, G.; Letchoumy, P.V.; Nagini, S. The neem limonoids azadirachtin and nimbolide inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in an animal model of oral oncogenesis. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talalay, P. Chemoprotection against cancer by induction of Phase 2 enzymes. BioFactors 2000, 12, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Phan, D.D.; Zhang, J.; Ong, P.S.; Thuya, W.L.; Soo, R.A.; Wong, A.L.; Yong, W.P.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, P.C.; et al. Anticancer properties of nimbolide and pharmacokinetic considerations to accelerate its development. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Warrier, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Arfuso, F. Potential Role of Natural Compounds as Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Cancer. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G. Bioactive natural products in cancer prevention and therapy: Progress and promise. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Chai, E.Z.; Kanchi, M.M.; Kar, S.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ramar, P.S.; Looi, C.Y.; et al. Cancer prevention and therapy through the modulation of transcription factors by bioactive natural compounds. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.S.; Yang, S.F.; Sethi, G.; Hu, D.N. Natural bioactives in cancer treatment and prevention. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 182835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Sethi, G.; Kuo, P.L. Novel medicines and strategies in cancer treatment and prevention. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 474078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by dietary agents: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guide to Achieving Reliable Quantitative LC-MS Measurements, 1st ed.; Sargent, M. (Ed.) RSC Analytical Methods Committee: Teddington, UK, 2013; pp. 47–48. ISBN 978-0-948926-27-3. [Google Scholar]
- NCBI PubChem Compound Database. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Wang, L.-Z.; Goh, S.-H.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Thuya, W.-L.; Lau, J.-Y.A.; Wan, S.-C.; Lee, S.-C.; Ho, P.C.; Goh, B.-C. Validation of a Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Exemestane and Its Metabolites, 17β-Hydroxyexemestane and 17β-Hydroxyexemestane-17-O-β-d-Glucuronide: Application to Human Pharmacokinetics Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baira, S.M.; Khurana, A.; Somagoni, J.; Srinivas, R.; Godugu, C.; Talluri, M.K. First report on the pharmacokinetic profile of nimbolide, a novel anticancer agent in oral and intravenous administrated rats by LC/MS method. J. Chromatogr. B. Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1092, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, P.; Gunadharini, D.N.; Senthilkumar, K.; Banudevi, S.; Arunkumar, R.; Benson, C.S.; Sharmila, G.; Arunakaran, J. Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by nimbolide through extrinsic and intrinsic pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 215, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, C.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Siveen, K.S.; Arfuso, F.; Samym, R.P.; Deivasigamanim, A.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; et al. Nimbolide-Induced Oxidative Stress Abrogates STAT3 Signaling Cascade and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate Model. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Nimbolide | Exemestane | Paclitaxel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 466.5 | 296.4 | 853.9 |
| LogP | 2.2 | 3.1 | 2.5 |
| H bond acceptors | 7 | 2 | 15 |
| H bond donors | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Chemical structure |  |  |  |
| Interval | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Quantified Concentration (Mean ± S.D., ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (CV, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day | 15.0 | 14.7 ± 1.8 | 98.2 | 12.3 |
| 300.0 | 327.8 ± 15.0 | 109.3 | 4.6 | |
| 900.0 | 872.3 ± 109.9 | 96.9 | 12.6 | |
| Inter-day | 15.0 | 14.2 ± 2.0 | 94.3 | 13.9 |
| 300.0 | 330.5 ± 16.7 | 110.2 | 5.0 | |
| 900.0 | 934.8 ± 124.5 | 103.9 | 13.3 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Matrix Effect on Nimbolide (%) | Matrix Effect on IS (%) | Relative Matrix Effect on Nimbolide | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.0 | 33.7 | 85.1 | 0.396 | 39.0 |
| 300.0 | 32.2 | 0.378 | 39.5 | |
| 900.0 | 34.3 | 0.403 | 39.3 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Stability (Mean ± S.D., %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bench-Top | Freeze-Thaw | ||||
| 2 h | 4 h | 1 Cycle | 3 Cycles | 6 Cycles | |
| 15.0 | 108.4 ± 3.4 | 93.6 ± 4.2 | 100.5 ± 4.9 | 86.4 ± 3.7 | 113.0 ± 7.5 |
| 300.0 | 88.8 ± 2.2 | 100.1 ± 10.5 | 101.7 ± 9.4 | 93.2 ± 12.0 | 105.1 ± 1.6 |
| 900.0 | 112.2 ± 6.2 | 101.9 ± 14.5 | 95.0 ± 5.0 | 97.3 ± 1.4 | 107.7 ± 9.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Phan, D.-D.K.; Syn, N.; Xiang, X.; Song, H.; Thuya, W.L.; Yang, S.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Kumar, A.P.; Yong, W.P.; et al. A Sensitive Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Nimbolide in Mouse Serum: Application to a Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030123
Wang L, Phan D-DK, Syn N, Xiang X, Song H, Thuya WL, Yang S, Wong AL-A, Kumar AP, Yong WP, et al. A Sensitive Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Nimbolide in Mouse Serum: Application to a Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030123
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingzhi, Do-Dang Khoa Phan, Nicholas Syn, Xiaoqiang Xiang, Hongyan Song, Win Lwin Thuya, Shili Yang, Andrea Li-Ann Wong, Alan Prem Kumar, Wei Peng Yong, and et al. 2018. "A Sensitive Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Nimbolide in Mouse Serum: Application to a Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030123
APA StyleWang, L., Phan, D. -D. K., Syn, N., Xiang, X., Song, H., Thuya, W. L., Yang, S., Wong, A. L. -A., Kumar, A. P., Yong, W. P., Sethi, G., Ho, P. C. -L., & Goh, B. C. (2018). A Sensitive Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Nimbolide in Mouse Serum: Application to a Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030123