Dynamic Light Scattering of Biopharmaceutics—Can Analytical Performance Be Enhanced by Laser Power?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Aspects: Scattering by Small Optically Soft Particles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparations
3.2. Light Scattering Instruments
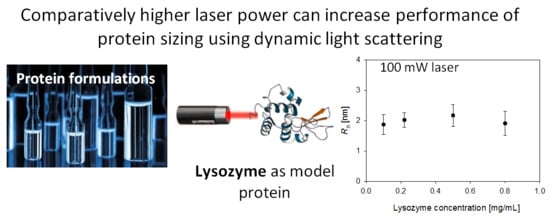
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Sensitivity of a Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Instrument
4.2. Sensitivity in Protein Solution Measurement: Theoretical Approach
4.3. Sensitivity in Protein Solution Measurement: Experimental Approach
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffold, F.; Cerbino, R. New trends in light scattering. Is any measurement method optimal for all aggregate sizes and types? Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 12, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frokjaer, S.; Otzen, D.E. Protein drug stability: A formulation challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Val, I.J.; Kontoravdi, C.; Nagy, J.M. Towards the implementation of quality by design to the production of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies with desired glycosylation patterns. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 1505–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.H.; Motskin, M.; Philpott, A.J.; Routh, A.F.; Shanahan, C.M.; Duer, M.J.; Skepper, J.N. The effect of particle agglomeration on the formation of a surface-connected compartment induced by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles inhuman monocyte-derived macrophages. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.; Swiatek, G. Protein Purification. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2009, 5, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical approval trends in 2009. BioPharm Int. 2010, 23, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.S.; Bishop, S.M.; Shah, A.U.; Sathish, H.A. Formulation development of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies using high-throughput fluorescence and static light scattering techniques: Role of conformational and colloidal stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurganov, B.I. Kinetics of protein aggregation. Quantitative estimation of the chaperoneelike activity in testtsystems based on suppression of protein aggregation. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.; Barnett, G.V.; Pathak, J.A.; Roberts, C.J.; Sarangapani, P.S. Protein aggregation, particle formation, characterization & rheology. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Protein aggregation and its inhibition in biopharmaceutics. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 289, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorber, B.; Fischer, F.; Bailly, M.; Roy, H.; Kern, D. Protein analysis by dynamic light scattering: Methods and techniques for students. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2012, 40, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panchal, J.; Kotarek, J.; Marszal, E.; Topp, E.M. Analyzing subvisible particles in protein drug products: A comparison of dynamic light scattering (DLS) and resonant mass measurement (RMM). AAPS J. 2014, 16, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro-Pérez, C.; Ojeda-Mendoza, G.J.; Rojas-Ochoa, L.F. Three dimensional cross-correlation dynamic light scattering by non-ergodic turbid media. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 244902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, I.D.; Scheffold, F. Modulated 3D cross-correlation light scattering: Improving turbid sample characterization. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 123107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.; Cherubin, P.; Cilenti, L.; Teter, K.; Huo, Q. A simple and fast method to study the hydrodynamic size difference of protein disulfide isomerase in oxidized and reduced form using gold nanoparticles and dynamic light scattering. Analyst 2016, 141, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karow, A.R.; Götzl, J.; Garidel, P. Resolving power of dynamic light scattering for protein and polystyrene nanoparticles. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Soliwoda, K.; Kadziola, K.; Tkacz-Szczesna, B.; Celichowski, G.; Cichomski, M.; Szmaja, W.; Grobelny, J. Detection limits of DLS and UV-Vis spectroscopy in characterization of polydisperse nanoparticles colloids. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 313081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, E.R.; Pomeroy, W.R.M.; Vaughan, J.M. Measurement of Rayleigh ratio for several pure liquids using a laser and monitored photon counting. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 62, 3188–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Correlations between the Rayleigh ratio and the wavelength for toluene and benzene. Chem. Phys. 2010, 367, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaud, T.; Cardinaux, F.; Bergenholtz, J.; Stradner, A.; Schurtenberger, P. Phase separation and dynamical arrest for particles interacting with mixed potentials—The case of globular proteins revisited. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Engelsman, J.; Garidel, P.; Smulders, R.; Koll, H.; Smith, B.; Bassarab, S.; Seidl, A.; Hainzl, O.; Jiskoot, W. Strategies for the assessment of protein aggregates in pharmaceutical biotech product development. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunitani, M.; Wolfe, S.; Rana, S.; Apicella, C.; Levi, V.; Dollinger, G. Classical light scattering quantitation of protein aggregates: Off-line spectroscopy versus HPLC detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 16, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.E.; Robinson, J.; Matthews, G.; Muschol, M. Amyloid protofibrils of lysozyme nucleate and grow via oligomer fusion. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Concentration (mg/mL) | Intercept | Scaled Count Rate (kHz/mW) | Rh (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 6.2 ± 0.02 | 1.94 ± 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 5.2 ± 0.08 | 2.20 ± 0.3 |
| 2 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 3.2 ± 0.05 | 2.04 ± 0.2 |
| 1 | N.A * | N.A * | N.A * |
| 0.8 | N.A * | N.A * | N.A * |
| 0.5 | N.A * | N.A * | N.A * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aleandri, S.; Vaccaro, A.; Armenta, R.; Völker, A.C.; Kuentz, M. Dynamic Light Scattering of Biopharmaceutics—Can Analytical Performance Be Enhanced by Laser Power? Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030094
Aleandri S, Vaccaro A, Armenta R, Völker AC, Kuentz M. Dynamic Light Scattering of Biopharmaceutics—Can Analytical Performance Be Enhanced by Laser Power? Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030094
Chicago/Turabian StyleAleandri, Simone, Andrea Vaccaro, Ricardo Armenta, Andreas Charles Völker, and Martin Kuentz. 2018. "Dynamic Light Scattering of Biopharmaceutics—Can Analytical Performance Be Enhanced by Laser Power?" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030094
APA StyleAleandri, S., Vaccaro, A., Armenta, R., Völker, A. C., & Kuentz, M. (2018). Dynamic Light Scattering of Biopharmaceutics—Can Analytical Performance Be Enhanced by Laser Power? Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030094