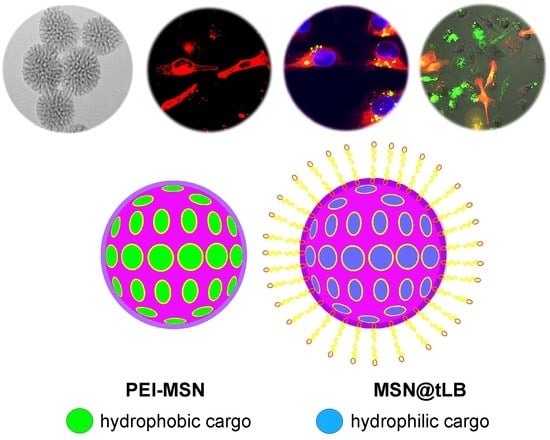
Factors Affecting Intracellular Delivery and Release of Hydrophilic Versus Hydrophobic Cargo from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on 2D and 3D Cell Cultures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Functionalization of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN)
2.2. Loading of DiD
2.3. Loading of Calcein
2.4. Lipid Bilayer Coating
2.5. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.6. Hydrophobic Drug Release
2.7. Hydrophilic Drug Release Live Cell Imaging
2.8. Confluency Measurements
2.9. Organotypic 3D Cell Culture
2.10. Addition of MSNs to Cell Culture
2.11. Live Cell Imaging of Organotypic 3D Cultures
3. Results
3.1. Intracellular Uptake and Localization of Non-Loaded PEI-MSNs
3.2. Factors Affecting Intracellular Release on Cellular Level
3.3. Factors Affecting Intracellular Release on Organoid Level
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Surface Charge on Intracellular Trafficking and Release
4.2. Effect of Surface Hydrophobicity on Intracellular Release
4.3. Effect of Surface Coating (PEI vs LB) on the Labeling Efficiency of Loaded Dye in 3D Organoids
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stark, W.J.; Stoessel, P.R.; Wohlleben, W.; Hafner, A. Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5793–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. Nanoscale Iron Particles for Environmental Remediation: An Overview. J. Nanopart. Res. 2003, 5, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Tambe, P.; Paknikar, K.M.; Gajbhiye, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cutting-edge theranostics: Advancement from merely a carrier to tailor-made smart delivery platform. J. Control Release 2018, 287, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Drug delivery/imaging multifunctionality of mesoporous silica-based composite nanostructures. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, E.; Canham, L.; Santos, H.A. Mesoporous Biomaterials: A Lexicon and Structured Bibliography of Reviews. Mesoporous Biomater. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Exogenous/Endogenous-Triggered Mesoporous Silica Cancer Nanomedicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 1800268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Pan, J.; Liu, S.; Lu, G.Q. (Max) Advances in Multicompartment Mesoporous Silica Micro/Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications. Ann. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2018, 9, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bate-Eya, L.T.; Bergman, L.; Peuhu, E.; Duchanoy, A.; Fortelius, L.E.; Landor, S.; Toivola, D.M.; Linden, M.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for targeted inhibition of notch signaling in cancer. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knežević, N.; Durand, J.O. Targeted treatment of cancer with nanotherapeutics based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chempluschem 2015, 80, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Multifunctional MSNs provide solutions for multidrug resistance issues SC. Drug Discov. Today 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticle Delivery of Cancer Drugs. Ann. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, T.-G.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Endocytosis and intracellular transport of nanoparticles: Present knowledge and need for future studies. Nano Today 2011, 6, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Sun, J.; Zhai, Y.; He, Z. The endocytosis and intracellular fate of nanomedicines: Implication for rational design. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vercauteren, D.; Deschout, H.; Remaut, K.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; Jones, A.T.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Dynamic Colocalization Microscopy To Characterize Intracellular Trafficking of Nanomedicines. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7874–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.M.; Park, Y.I.L.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.M.; Yoo, B.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, K.T.; Hyeon, T.; et al. Endocytosis, intracellular transport, and exocytosis of lanthanide-doped upconverting nanoparticles in single living cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9080–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, G.J.; McMahon, H.T. Mechanisms of Endocytosis. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 857–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Karaman, D.; Sen Prabhakar, N.; Tadayon, S.; Duchanoy, A.; Toivola, D.M.; Rajput, S.; Näreoja, T.; Rosenholm, J.M. Design considerations for mesoporous silica nanoparticulate systems in facilitating biomedical applications. Open Mater. Sci. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Haartman, E.; Lindberg, D.; Prabhakar, N.; Rosenholm, J.M. On the intracellular release mechanism of hydrophobic cargo and its relation to the biodegradation behavior of mesoporous silica nanocarriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominska, M.; Dykxhoorn, D.M. Breaking down the barriers: SiRNA delivery and endosome escape. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Meinander, A.; Peuhu, E.; Niemi, R.; Eriksson, J.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Targeting of porous hybrid silica nanoparticles to cancer cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Desai, D.; Rosenholm, J.M. Tethered lipid bilayer gates: Toward extended retention of hydrophilic cargo in porous nanocarriers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjonen, A.; Alanko, J.; Veltel, S.; Ivaska, J. Distinct recycling of active and inactive β1 integrins. Traffic 2012, 13, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Gaspar, V.M.; Carvalho, M.P.; Correia, I.J. 3D tumor spheroids: An overview on the tools and techniques used for their analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant, S.; Johnston, P.A. The production of 3D tumor spheroids for cancer drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2017, 23, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.-W.; Gao, J.-Q. Application of 3D cultured multicellular spheroid tumor models in tumor-targeted drug delivery system research. J. Control Release 2018, 270, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härmä, V.; Virtanen, J.; Mäkelä, R.; Happonen, A.; Mpindi, J.-P.; Knuuttila, M.; Kohonen, P.; Lötjönen, J.; Kallioniemi, O.; Nees, M. A Comprehensive Panel of Three-Dimensional Models for Studies of Prostate Cancer Growth, Invasion and Drug Responses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, B.; Ghajar, C.M.; Bissell, M.J. The need for complex 3D culture models to unravel novel pathways and identify accurate biomarkers in breast cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69–70, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Penninkangas, A.; Linden, M. Amino-functionalization of large-pore mesoscopically ordered silica by a one-step hyperbranching polymerization of a surface-grown polyethyleneimine. Chem. Commun. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Linden, M. Wet-chemical analysis of surface concentration of accessible groups on different amino-functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 silicas. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härmä, V.; Schukov, H.-P.; Happonen, A.; Ahonen, I.; Virtanen, J.; Siitari, H.; Åkerfelt, M.; Lötjönen, J.; Nees, M. Quantification of Dynamic Morphological Drug Responses in 3D Organotypic Cell Cultures by Automated Image Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Zhang, J.; Sandholm, J.; Lehtimäki, J.; Grönroos, T.; Tuomela, J.; Rosenholm, J.M. Lipid Bilayer-Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for Tumor-Targeted Delivery of Zoledronic Acid in Vivo. Mol. Pharm. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Dammer, E.B.; Ren, R.-J.; Wang, G. The endosomal-lysosomal system: From acidification and cargo sorting to neurodegeneration. Trans. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Peuhu, E.; Eriksson, J.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Targeted intracellular delivery of hydrophobic agents using mesoporous hybrid silica nanoparticles as carrier systems. Nano Lett. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiao, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X. Wetting transition in nanochannels for biomimetic free-blocking on-demand drug transport. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6269–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Gulin-Sarfraz, T.; Mamaeva, V.; Niemi, R.; Özliseli, E.; Desai, D.; Antfolk, D.; Von Haartman, E.; Lindberg, D.; Prabhakar, N.; et al. Prolonged Dye Release from Mesoporous Silica-Based Imaging Probes Facilitates Long-Term Optical Tracking of Cell Populations in Vivo. Small 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, R.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Von Haartman, E.; Hemming, J.; Genze, F.; Bergman, L.; Simmet, T.; Linden, M.; Sahlgren, C. Active targeting of mesoporous silica drug carriers enhances?-secretase inhibitor efficacy in an in vivo model for breast cancer. Nanomedicine 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiolini, L.; Valetti, S.; Cohen, B.; Feiler, A.; Douhal, A. Fluorescence imaging of antibiotic clofazimine encapsulated within mesoporous silica particle carriers: Relevance to drug delivery and the effect on its release kinetics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 11899–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, N.; Näreoja, T.; Von Haartman, E.; Karaman, D.S.; Jiang, H.; Koho, S.; Dolenko, T.A.; Hänninen, P.E.; Vlasov, D.I.; Ralchenko, V.G.; et al. Core-shell designs of photoluminescent nanodiamonds with porous silica coatings for bioimaging and drug delivery II: Application. Nanoscale 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Stace-Naughton, A.; Jiang, X.; Brinker, C.J. Porous Nanoparticle Supported Lipid Bilayers (Protocells) as Delivery Vehicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1354–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeung, T.; Gilbert, G.E.; Shi, J.; Silvius, J.; Kapus, A.; Grinstein, S. Membrane phosphatidylserine regulates surface charge and protein localization. Science 2008, 319, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Versatile Intracellular Drug Delivery Platform; Åbo Akademi University: Turku, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Karaman, D.S.; Paul, P.; Björk, E.M.; Odén, M.; Eriksson, J.E.; Rosenholm, J.M. Targeted delivery of a novel anticancer compound anisomelic acid using chitosan-coated porous silica nanorods for enhancing the apoptotic effect. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desai, D.; Åkerfelt, M.; Prabhakar, N.; Toriseva, M.; Näreoja, T.; Zhang, J.; Nees, M.; Rosenholm, J.M. Factors Affecting Intracellular Delivery and Release of Hydrophilic Versus Hydrophobic Cargo from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on 2D and 3D Cell Cultures. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040237
Desai D, Åkerfelt M, Prabhakar N, Toriseva M, Näreoja T, Zhang J, Nees M, Rosenholm JM. Factors Affecting Intracellular Delivery and Release of Hydrophilic Versus Hydrophobic Cargo from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on 2D and 3D Cell Cultures. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(4):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040237
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesai, Diti, Malin Åkerfelt, Neeraj Prabhakar, Mervi Toriseva, Tuomas Näreoja, Jixi Zhang, Matthias Nees, and Jessica M. Rosenholm. 2018. "Factors Affecting Intracellular Delivery and Release of Hydrophilic Versus Hydrophobic Cargo from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on 2D and 3D Cell Cultures" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 4: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040237
APA StyleDesai, D., Åkerfelt, M., Prabhakar, N., Toriseva, M., Näreoja, T., Zhang, J., Nees, M., & Rosenholm, J. M. (2018). Factors Affecting Intracellular Delivery and Release of Hydrophilic Versus Hydrophobic Cargo from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on 2D and 3D Cell Cultures. Pharmaceutics, 10(4), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040237