Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator
Abstract
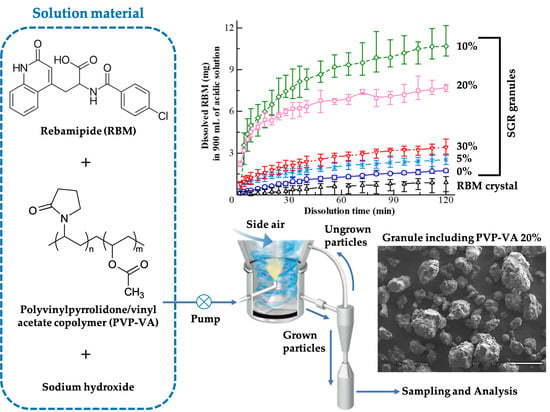
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Granule Preparation Using a Continuous-Spray Granulator
2.3. Physical Property Measurements
2.4. Stability Testing at Different Humidities by X-Ray Diffractometry
2.5. Thermal Analysis
2.6. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
2.7. Tablet Preparation and Dissolution Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Physical Properties
3.2. Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersion
3.3. Molecular State
3.4. Dissolution Ability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ku, M.S.; Dulin, W. A biopharmaceutical classification-based Right-First-Time formulation approach to reduce human pharmacokinetic variability and project cycle time from First-In-Human to clinical Proof-Of-Concept. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K. Modification of physicochemical characteristics of active pharmaceutical ingredients and application of supersaturatable dosage forms for improving bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrut, M.; Jung, J.; Leboeuf, F. Enhancement of dissolution rate of poorly-soluble active ingredients by supercritical fluid processes: Part I: Micronization of neat particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 288, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, D.E.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Taylor, L.S. Understanding the Behavior of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Systems during Dissolution. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liversidge, G.G.; Cundy, K.C. Particle size reduction for improvement of oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs: I. Absolute oral bioavailability of nanocrystalline danazol in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 125, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitipamula, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bansal, A.K.; Biradha, K.; Cheney, M.L.; Choudhury, A.R.; Desiraju, G.R.; Dikundwar, A.G.; Dubey, R.; Duggirala, N.; et al. Polymorphs, Salts, and Cocrystals: What’s in a Name? Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitha, J.; Milecki, J.; Fales, H.; Pannell, L.; Uekama, K. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: Preparation and characterization; effects on solubility of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 29, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical Applications of Solid Dispersion Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, A.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Co-Amorphous Solid Dispersions for Solubility and Absorption Improvement of Drugs: Composition, Preparation, Characterization and Formulations for Oral Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, M.H.; Suryanarayanan, R. Effect of Organic Acids on Molecular Mobility, Physical Stability, and Dissolution of Ternary Ketoconazole Spray-Dried Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: Preparation, characterization and stabilization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, M.H.; DeVault, M.; Kuwata, K.T.; Suryanarayanan, R. Drug-Excipient Interactions: Effect on Molecular Mobility and Physical Stability of Ketoconazole–Organic Acid Coamorphous Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.S.; Matzger, A.J. Probing the Interplay between Amorphous Solid Dispersion Stability and Polymer Functionality. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.M.; Dudhedia, M.S.; Zimny, E. Hot Melt Extrusion: Development of an Amorphous Solid Dispersion for an Insoluble Drug from Mini-scale to Clinical Scale. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, S.K.; Garg, V.; Gulati, M.; Vaidya, Y. Optimization of spray drying process for formulation of solid dispersion containing polypeptide-k powder through quality by design approach. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ormes, J.D.; Higgins, J.D.; Taylor, L.S. Impact of Surfactants on the Crystallization of Aqueous Suspensions of Celecoxib Amorphous Solid Dispersion Spray Dried Particles. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, V.; Lou, X.; Osterling, D.J.; Stolarik, D.F.; Jenkins, G.; Gao, W.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Relationship between amorphous solid dispersion in vivo absorption and in vitro dissolution: Phase behavior during dissolution, speciation, and membrane mass transport. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Xu, W.; Taylor, L.S.; Marsac, P.J.; Byrn, S.R. Crystalline solid dispersion-a strategy to slowdown salt disproportionation in solid state formulations during storage and wet granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on Absorption of Eutectic Mixture. I. A Comparison of the Behavior of Eutectic Mixture of Sulfathiazole and that of Ordinary Sulfathiazole in Man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-Melt Extrusion: From Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayersohn, M.; Gibaldi, M. New Method of Solid-State Dispersion for Increasing Dissolution Rates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1966, 55, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Nagira, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, Y. Solid dispersion particles of amorphous indomethacin with fine porous silica particles by using spray-drying method. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Taylor, L.S. Influence of Different Polymers on the Crystallization Tendency of Molecularly Dispersed Amorphous Felodipine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 2692–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Handa, T.; Alonzo, D.E.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of polymer type on the dissolution profile of amorphous solid dispersions containing felodipine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, T.; Nogata, A.; Demachi, M.; Umeki, N.; Itai, S.; Yunoki, N.; Nemoto, M. Particle Design for Taste-Masking Using a Spray-Congealing Technique. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraeve, A.; Monteyne, T.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; Beer, T. De Process analytical tools for monitoring, understanding, and control of pharmaceutical fluidized bed granulation: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elversson, J.; Millqvist-Fureby, A.; Alderborn, G.; Elofsson, U. Droplet and Particle Size Relationship and Shell Thickness of Inhalable Lactose Particles During Spray Drying. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Uchida, S.; Kanada, K.; Namiki, N. Effect of granule properties on rough mouth feel and palatability of orally disintegrating tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Rebamipide: A gastrointestinal protective drug with pleiotropic activities. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 4, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Takahashi, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Ashizawa, K.; Otsuka, M. Performance of an acoustically mixed pharmaceutical dry powder delivered from a novel inhaler. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausner, H.H. Friction conditions in a mass of metal powder. Int. J. Powder Metall. 1967, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, R.L. Evaluating flow properties of solids. Chem. Eng. 1965, 72, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Couchman, P.R.; Karasz, F.E. A Classical Thermodynamic Discussion of the Effect of Composition on Glass-Transition Temperatures. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. The Relationship Between the Glass Transition Temperature and the Water Content of Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Nie, H.; Byrn, S.; Lubach, J.W. Investigation of Drug–Excipient Interactions in Lapatinib Amorphous Solid Dispersions Using Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petereit, H.-U.; Weisbrod, W. Formulation and process considerations affecting the stability of solid dosage forms formulated with methacrylate copolymers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 47, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, N.; de Villiers, M.M.; Yu, L. Inhibiting Surface Crystallization of Amorphous Indomethacin by Nanocoating. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5148–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckton, G.; Yonemochi, E.; Hammond, J.; Moffat, A. The use of near infra-red spectroscopy to detect changes in the form of amorphous and crystalline lactose. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 168, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, A.P.; Mehta, S.C.; Higuchi, W.I. Dissolution rates of high energy sulfathiazole-povidone coprecipitates II: Characterization of form of drug controlling its dissolution rate via solubility studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 65, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Kakumanu, V.K.; Bansal, A.K. Stability and Solubility of Celecoxib-PVP Amorphous Dispersions: A Molecular Perspective. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, M.M.; Motawaa, A.M.; Samaha, M.W. In sight into tadalafil – block copolymer binary solid dispersion: Mechanistic investigation of dissolution enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Batch No. | RBM 1 (g) | PVP-VA 2 (g) | NaOH 3 (g) | H2O 4 (g) | Total (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 179.65 | 0 | 20.35 | 1800 | 2000 |
| 2 | 170.67 | 10 | 19.33 | 1800 | 2000 |
| 3 | 161.68 | 20 | 18.32 | 1800 | 2000 |
| 4 | 143.72 | 40 | 16.28 | 1800 | 2000 |
| 5 | 125.75 | 60 | 14.25 | 1800 | 2000 |
| PVP-VA 1 (%) | ρB2 (g/cm3) | ρT3 (g/cm3) | AR 4 (°) | HR 5 | CI 6 (%) | D50 7 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 43.9 ± 4.99 | 1.88 ± 0.02 | 46.9 ± 0.65 | 4.18 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 40.3 ± 4.59 | 1.67 ± 0.14 | 40.0 ± 5.23 | 11.2 ± 0.12 |
| 10 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 39.5 ± 3.98 | 1.29 ± 0.03 | 22.7 ± 1.76 | 44.2 ± 0.17 |
| 20 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 36.3 ± 4.54 | 1.39 ± 0.05 | 27.8 ± 2.79 | 32.5 ± 0.21 |
| 30 | 0.61 ± 0.00 | 0.76 ± 0.00 | 27.9 ± 4.16 | 1.26 ± 0.00 | 20.4 ± 0.14 | 72.7 ± 2.99 |
| PVP-VA (%) | Tg expt1 (°C) | Tg calc2 (°C) | ΔTg 3 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 215.4 | n/a | n/a |
| 5 | 206.9 | 202.0 | 4.9 |
| 10 | 203.9 | 194.3 | 9.6 |
| 20 | 191.7 | 175.0 | 16.7 |
| 30 | 178.7 | 157.5 | 21.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, R.; Hattori, Y.; Horie, Y.; Kamada, H.; Nagato, T.; Otsuka, M. Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040159
Tanaka R, Hattori Y, Horie Y, Kamada H, Nagato T, Otsuka M. Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040159
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Ryoma, Yusuke Hattori, Yukun Horie, Hitoshi Kamada, Takuya Nagato, and Makoto Otsuka. 2019. "Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040159
APA StyleTanaka, R., Hattori, Y., Horie, Y., Kamada, H., Nagato, T., & Otsuka, M. (2019). Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator. Pharmaceutics, 11(4), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040159