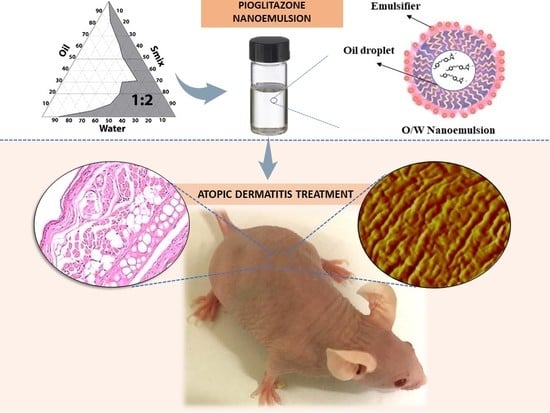
Topical Pioglitazone Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Characterization and Efficacy in Hairless Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams and Preparation of PGZ-NE
2.3. Characterization of PGZ-NE
2.4. In vitro Release Study
2.5. Ex vivo Permeation Study
2.6. Efficacy Studies: Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis
2.6.1. Animals and Study Protocol
2.6.2. Biomechanical Skin Properties Evaluation
2.6.3. Skin Evaluation by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.6.4. Histological Analysis
2.6.5. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Determination
2.6.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagram and Formulation
3.2. Characterization of PGZ-NE
3.3. In Vitro Release Study
3.4. Ex Vivo Permeation Study
3.5. Efficacy Studies: Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis
3.5.1. Biomechanical Skin Properties Evaluation
3.5.2. Skin Evaluation by AFM
3.5.3. Histological Analysis
3.5.4. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Determination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misery, L.; Huet, F.; Gouin, O.; Stander, S.; Deleuran, M. Current pharmaceutical developments in atopic dermatitis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 46, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, C.B. Atopic dermatitis. Medicine 2017, 45, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.M. Early immunologic changes during the onset of atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverberg, J.I. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serra-Baldrich, E.; De Frutos, J.O.; Jauregui, I.; Armario-Hita, J.C.; Silvestre, J.F.; Herraez, L.; Martin-Santiago, A.; Valero, A.; Sastre, J. Changing perspectives in atopic dermatitis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2018, 46, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schakel, K.; Dobel, T.; Bosselmann, I. Future treatment options for atopic dermatitis—small molecules and beyond. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 73, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Alexis, A.F.; Beck, L.A.; Block, J.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Fonacier, L.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Paller, A.S.; Pariser, D.; Silverberg, J.I.; et al. Expert perspectives on management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A multidisciplinary consensus addressing current and emerging therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Verma, A.; Pathak, K. Exploring preclinical and clinical effectiveness of nanoformulations in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: Safety aspects and patent reviews. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2017, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, C.; Moulari, B.; Beduneau, A.; Fantini, O.; Pin, D.; Pellequer, Y.; Lamprecht, A. Size dependent skin penetration of nanoparticles in murine and porcine dermatitis models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 100, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luesakul, U.; Puthong, S.; Sansanaphongpricha, K.; Muangsin, N. Quaternized chitosan-coated nanoemulsions: A novel platform for improving the stability, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and transdermal properties of plai extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matougui, N.; Boge, L.; Groo, A.C.; Umerska, A.; Ringstad, L.; Bysell, H.; Saulnier, P. Lipid-based nanoformulations for peptide delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Katiyar, S.S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S. Nanoemulsion loaded gel for topical co-delivery of clobitasol propionate and calcipotriol in psoriasis. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, D.; Chen, H.; Du, D.; Mao, C.; Wan, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Hydrogel-thickened nanoemulsion system for topical delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 353, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, K.A.; Ullah, K.; Shah, A.; Jones, D.S.; Singh, T.R.R. Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Villena, M.J.; Fernandez-Campos, F.; Calpena-Campmany, A.C.; Bozal-De Febrer, N.; Ruiz-Martinez, M.A.; Clares-Naveros, B. Novel microparticulate systems for the vaginal delivery of nystatin: Development and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, K.; Mitoma, C.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, M. Protective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists in skin barrier and inflammation. Immunobiology 2018, 223, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; Sahebkar, A.; Maffioli, P. The role of various peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands in clinical practice. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, V.; Galdo, J.A.; Mathews, S.T. Hypoglycemic agents and potential anti-inflammatory activity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 9, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, L.; Burgdorf, S.; Dani, I.; Saijo, K.; Flossdorf, J.; Hucke, S.; Alferink, J.; Nowak, N.; Beyer, M.; Mayer, G.; et al. The nuclear receptor ppar gamma selectively inhibits Th17 differentiation in a t cell-intrinsic fashion and suppresses cns autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.C.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Calpena, A.C.; Rodriguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Fabrega, M.J.; Garduno-Ramirez, M.L.; Clares, B. Nanoemulsion strategy of pioglitazone for the treatment of skin inflammatory diseases. Nanomedicine 2019, 19, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana-Seoane, M.; Peleteiro, A.; Laguna, R.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Bioadhesive emulsions for control release of progesterone resistant to vaginal fluids clearance. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Abreu, M.; Espinoza, L.C.; Rodriguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Fabrega, M.J.; Espina, M.; Garcia, M.L.; Calpena, A.C. Human skin permeation studies with ppargamma agonist to improve its permeability and efficacy in inflammatory processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, K.; Rhodes, C. Effect compaction pressure on the dissolution efficiency of some direct compression systems. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1972, 47, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bhushan, B. Nanomechanical and nanotribological characterization of two synthetic skins with and without skin cream treatment using atomic force microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.W., Jr.; Gad, S.C.; Julien, M. A review of the nonclinical safety of transcutol (R), a highly purified form of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (degee) used as a pharmaceutical excipient. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khateb, K.; Ozhmukhametova, E.K.; Mussin, M.N.; Seilkhanov, S.K.; Rakhypbekov, T.K.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. In situ gelling systems based on pluronic F127/pluronic F68 formulations for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welin-Berger, K.; Neelissen, J.; Bergenstahl, B. In vitro permeation profile of a local anaesthetic compound from topical formulations with different rheological behaviour—verified by in vivo efficacy data. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Chatterjee, B. Potential and future scope of nanoemulgel formulation for topical delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.W.; Musakhanian, J. Skin penetration and permeation properties of transcutol (R)-neat or diluted mixtures. Aaps Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 3512–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal applications of poloxamer 407-based hydrogels: An overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espinoza, L.C.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Clares, B.; Rodriguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Halbaut, L.; Canas, M.A.; Calpena, A.C. Formulation strategies to improve nose-to-brain delivery of donepezil. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moner, V.; Fernandez, E.; Calpena, A.C.; Garcia-Herrera, A.; Cocera, M.; Lopez, O. A lamellar body mimetic system for the treatment of oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis in hairless mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeom, M.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, B.; Han, J.J.; Chung, G.H.; Choi, H.D.; Lee, H.; Hahm, D.H. Oral administration of glucosylceramide ameliorates inflammatory dry-skin condition in chronic oxazolone-induced irritant contact dermatitis in the mouse ear. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 67, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milam, E.C.; Jacob, S.E.; Cohen, D.E. Contact dermatitis in the patient with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, C.S.; Bae, I.H.; Choi, J.K.; Park, Y.H.; Park, M. A novel, topical, nonsteroidal, trpv1 antagonist, pac-14028 cream improves skin barrier function and exerts anti-inflammatory action through modulating epidermal differentiation markers and suppressing th2 cytokines in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 91, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, N.; Sato, W.J.; Kelly, A.; Ganguli-Indra, G.; Indra, A.K. Epidermal lipids: Key mediators of atopic dermatitis pathogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, M.; Dunn-Galvin, A.; Hourihane, J.O.; Murray, D.; Campbell, L.E.; Mclean, W.H.; Irvine, A.D. Skin barrier dysfunction measured by transepidermal water loss at 2 days and 2 months predates and predicts atopic dermatitis At 1 year. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, J.M.; Folster-Holst, R.; Baranowsky, A.; Schunck, M.; Winoto-Morbach, S.; Neumann, C.; Schutze, S.; Proksch, E. Impaired sphingomyelinase activity and epidermal differentiation in atopic dermatitis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proksch, E.; Folster-Holst, R.; Jensen, J.M. Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation in eczema. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 43, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vry, C.G.; Valdez, M.; Lazarov, M.; Muhr, E.; Buelow, R.; Fong, T.; Iyer, S. Topical application of a novel immunomodulatory peptide, Rdp58, reduces skin inflammation in the phorbol ester-induced dermatitis model. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizuno, K.; Morizane, S.; Takiguchi, T.; Iwatsuki, K. Dexamethasone but not tacrolimus suppresses tnf-alpha-induced thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in lesional keratinocytes of atopic dermatitis model. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danso, M.O.; Van Drongelen, V.; Mulder, A.; Van Esch, J.; Scott, H.; Van Smeden, J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Tnf-alpha and Th2 cytokines induce atopic dermatitis-like features on epidermal differentiation proteins and stratum corneum lipids in human skin equivalents. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.G.; Mickle-Kawar, B.M.; Gallucci, R.M. Il-6 deficiency exacerbates skin inflammation in a murine model of irritant dermatitis. J. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 10, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarini, A.A.; French, L.E.; Hofbauer, G.F. Interrupting Il-6-receptor signaling improves atopic dermatitis but associates with bacterial superinfection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, D.S.; Pereira, T.A.; Maciel, N.R.; Bortoloto, J.; Viera, G.S.; Oliveira, G.C.; Rocha-Filho, P.A. Formation and stability of oil-In-water nanoemulsions containing rice bran oil: In vitro and in vivo assessments. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, V.; Gopal, A.; Kumar, D.; Gopalkrishnan, A.; Pathak, N.N.; Kurade, N.P.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Topical pluronic F-127 gel application enhances cutaneous wound healing in rats. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, L.; Calpena, A.C.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Espinoza, L.C.; Rincon, M.; Bozal, N.; Domenech, O.; Rodriguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Clares, B. Thermoreversible gel-loaded amphotericin B for the treatment of dermal and vaginal candidiasis. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| β-actin | FW: GTGGGGCGCCCCAGGCACCA RV: CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
| IL-17 | FW: TTTTCAGCAAGGAATGTGGA RV: TTCATTGTGGAGGGCAGAC |
| IL-6 | FW: TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC RV: TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTCC |
| TNF-α | FW: AACTAGTGGTGCCAGCCGAT RV: CTTCACAGAGCAATGACTCC |
| Components | (%) |
|---|---|
| Pioglitazone (1 mg/mL) | |
| Capryol 90 (propylene glycol monocaprylate), | 8 |
| Labrasol (caprylocaproyl polyoxyl-8 glycerides) | 19 |
| Transcutol-P (diethylene glycol monoethyl ether) | 38 |
| Water | 17 |
| Pluronic F127 (Poloxamer 407) | 18 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza, L.C.; Vera-García, R.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Domènech, Ò.; Badia, J.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Clares, B.; Calpena, A.C. Topical Pioglitazone Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Characterization and Efficacy in Hairless Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030255
Espinoza LC, Vera-García R, Silva-Abreu M, Domènech Ò, Badia J, Rodríguez-Lagunas MJ, Clares B, Calpena AC. Topical Pioglitazone Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Characterization and Efficacy in Hairless Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(3):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030255
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza, Lupe Carolina, Rodrigo Vera-García, Marcelle Silva-Abreu, Òscar Domènech, Josefa Badia, María J. Rodríguez-Lagunas, Beatriz Clares, and Ana Cristina Calpena. 2020. "Topical Pioglitazone Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Characterization and Efficacy in Hairless Mouse Model" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 3: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030255
APA StyleEspinoza, L. C., Vera-García, R., Silva-Abreu, M., Domènech, Ò., Badia, J., Rodríguez-Lagunas, M. J., Clares, B., & Calpena, A. C. (2020). Topical Pioglitazone Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Characterization and Efficacy in Hairless Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics, 12(3), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030255