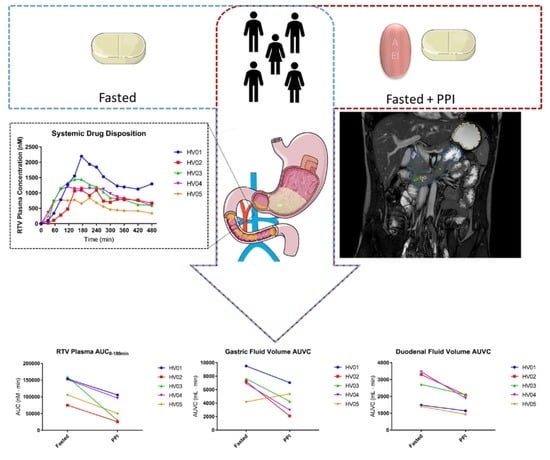
Exploring the Effect of Esomeprazole on Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volumes and Absorption of Ritonavir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.2. Study Medication
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Clinical Trial Design
- Control condition: Oral intake of one Norvir tablet (100 mg ritonavir) with 240 mL of tap water after a fasting period of 12 h.
- PPI condition: Oral intake of one Norvir tablet (100 mg ritonavir) with 240 mL of tap water after a fasting period of 12 h preceded by a once-daily dose of the PPI esomeprazole (40 mg, i.e., one Nexium tablet) for three days (including the morning of the trial).
2.2.2. Clinical Trial Protocol
2.2.3. Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volume via MRI
2.2.4. Ritonavir Systemic Drug Exposure by LC-MS/MS
Sample Preparation
LC—MS/MS Analysis
2.2.5. Data Presentation
3. Results
3.1. Systemic Disposition of Ritonavir
3.2. Gastric Fluid Volume
3.3. Duodenal Fluid Volume
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Strand, D.S.; Kim, D.; Peura, D.A. 25 years of proton pump inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, D.J.B. Time to halt the overprescribing of proton pump inhibitors Inappropriate use of proton pump inhibitors can cause a range of side effects and even harm to patients. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Jensen, R.T. Association of long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy with bone fractures and effects on absorption of calcium, vitamin B12, iron, and magnesium. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segregur, D.; Flanagan, T.; Mann, J.; Moir, A.; Karlsson, E.M.; Hoch, M.; Carlile, D.; Sayah-Jeanne, S.; Dressman, J. Impact of Acid-Reducing Agents on Gastrointestinal Physiology and Design of Biorelevant Dissolution Tests to Reflect These Changes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3461–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, A.; Back, D.; Fletcher, C.; Robinson, L.; Unsworth, J.; Tolowinska, I.; Schutz, M.; Pozniak, A.L.; Gazzard, B.; Boffito, M. Effect of omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of saquinavir-500 mg formulation with ritonavir in healthy male and female volunteers. Aids 2006, 20, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denissen, J.F.; Grabowski, B.A.; Johnson, M.K.; Buko, A.M.; Kempf, D.J.; Thomas, S.B.; Surber, B.W. Metabolism and disposition of the HIV-1 protease inhibitor ritonavir (ABT-538) in rats, dogs, and humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 489–501. [Google Scholar]
- Wedemeyer, R.S.; Blume, H. Pharmacokinetic drug interaction profiles of proton pump inhibitors: An update. Drug Saf. 2014, 37, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, T.; Hassan-Alin, M.; Hasselgren, G.; Röhss, K. Drug interaction studies with esomeprazole, the (S)-isomer of omeprazole. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, A.M.; Quinney, S.K.; Fadda, H.M.; Foster, D.R. Effect of Gastric Fluid Volume on the in Vitro Dissolution and in Vivo Absorption of BCS Class II Drugs: A Case Study with Nifedipine. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton, S.C. Role of physiological intestinal water in oral absorption. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gursoy, O.; Memiş, D.; Sut, N. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on gastric juice volume, gastric pH and gastric intramucosal pH in critically ill patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2008, 28, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepisi, R.; Fusco, S.; Sganga, F.; Falcone, B.; Vetrano, D.L.; Abbatecola, A.; Corica, F.; Maggio, M.; Ruggiero, C.; Fabbietti, P.; et al. Inappropriate use of proton pump inhibitors in elderly patients discharged from acute care hospitals. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2016, 20, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Abeele, J.; Kostantini, C.; Barker, R.; Kourentas, A.; Mann, J.C.; Vertzoni, M.; Beato, S.; Reppas, C.; Tack, J.; Augustijns, P. The effect of reduced gastric acid secretion on the gastrointestinal disposition of a ritonavir amorphous solid dispersion in fasted healthy volunteers: An in vivo–in vitro investigation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 105377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, D.; Krill, S.L.; Schmitt, E.A.; Fort, J.J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, W.; Porter, W.R. Physicochemical considerations in the preparation of amorphous ritonavir–poly (ethylene glycol) 8000 solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiolka, T.; Van Den Abeele, J.; Augustijns, P.; Arora, S.; Dressman, J. Biorelevant Two-Stage in Vitro Testing for rDCS Classification and in PBPK Modeling–Case Example Ritonavir. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.; Koziolek, M.; Kühn, J.-P.; Weitschies, W. Interindividual and intraindividual variability of fasted state gastric fluid volume and gastric emptying of water. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, C.; Fröhlich, C.P.; Giessmann, T.; Siegmund, W.; Mönnikes, H.; Hosten, N.; Weitschies, W. Intestinal fluid volumes and transit of dosage forms as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudie, D.M.; Murray, K.; Hoad, C.L.; Pritchard, S.E.; Garnett, M.C.; Amidon, G.L.; Gowland, P.A.; Spiller, R.C.; Amidon, G.E.; Marciani, L. Quantification of gastrointestinal liquid volumes and distribution following a 240 mL dose of water in the fasted state. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunfeld, N.G.; Touw, D.J.; Mathot, R.A.; Mulder, P.G.H.; Van Schaik, R.H.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kooiman, J.C.; Geus, W.P. A comparison of the acid-inhibitory effects of esomeprazole and pantoprazole in relation to pharmacokinetics and CYP2C19 polymorphism. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.; Röhss, K.; Bredberg, E.; Hassan-Alin, M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of esomeprazole, the S-isomer of omeprazole. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Koziolek, M.; Saleh, M.; Schneider, F.; Garbacz, G.; Kühn, J.P.; Weitschies, W. Gastric Emptying and Small Bowel Water Content after Administration of Grapefruit Juice Compared to Water and Isocaloric Solutions of Glucose and Fructose: A Four-Way Crossover MRI Pilot Study in Healthy Subjects. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béïque, L.; Giguère, P.; La Porte, C.; Angel, J. Interactions between protease inhibitors and acid-reducing agents: A systematic review. HIV Med. 2007, 8, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcos, P.N.; Moreira, S.A.; Navarro, M.T.; Bech, N.; Quatkemeyer, A.; Smith, P.F.; Brennan, B.J. Effect of meal and antisecretory agents on the pharmacokinetics of danoprevir/ritonavir in healthy volunteers. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.L.; Klein, C.E.; Woodward, W.C.; King, K.R.; Naylor, C.; Awni, W.; Brun, S. Lack of effect of gastric acid-reducing agents on the pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ritonavir in HIV-infected patients. AIDS Patient Care STDS 2007, 21, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.; Bhargava, V.; Aalam, S.; Scadeng, M.; Mittal, R.K. Effect of proton pump inhibition on the gastric volume: Assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagelada, J.R.; Longstreth, G.F.; Deering, T.B.; Summerskill, W.H.; Go, V.L. Gastric secretion and emptying after ordinary meals in duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology 1977, 73, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rominger, J.M.; Chey, W.Y.; Chang, T.M. Plasma secretin concentrations and gastric pH in healthy subjects and patients with digestive diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1981, 26, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Barbuskaite, D.; Tozzi, M.; Giannuzzo, A.; Sørensen, C.E.; Novak, I. Proton pump inhibitors inhibit pancreatic secretion: Role of gastric and non-gastric H+/ K+-ATPases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.; Knipp, G.; Zografi, G. Assessing the performance of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1355–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.; Granneman, G.R.; Bertz, R.J. Ritonavir: Clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 35, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, N.; Stillhart, C.; Lindenberg, M.; Wagner, B.; Kowalski, K.; Guerini, E.; Djebli, N.; Meneses-Lorente, G. Physiologically Based Absorption Modelling to Explore the Impact of Food and Gastric pH Changes on the Pharmacokinetics of Entrectinib. AAPS J. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambayashi, A.; Dressman, J.B. Predicting the Changes in Oral Absorption of Weak Base Drugs under Elevated Gastric pH Using an in Vitro–in Silico–in Vivo Approach: Case Examples—Dipyridamole, Prasugrel, and Nelfinavir. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dodd, S.; Kollipara, S.; Sanchez-Felix, M.; Kim, H.; Meng, Q.; Beato, S.; Heimbach, T. Prediction of ARA/PPI Drug-Drug Interactions at the Drug Discovery and Development Interface. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bermejo, M.; Hens, B.; Dickens, J.; Mudie, D.; Paixão, P.; Tsume, Y.; Shedden, K.; Amidon, G.L. A mechanistic physiologically-based biopharmaceutics modeling (PBBM) approach to assess the in vivo performance of an orally administered drug product: From IVIVC to IVIVP. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hens, B.; Bolger, M.B. Application of a Dynamic Fluid and pH Model to Simulate Intraluminal and Systemic Concentrations of a Weak Base in GastroPlusTM. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Sequence 1 | Sequence 2 | Sequence 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | T2-weighted turbo spin-echo | T2/T1 TrueFISP | T2-weighted turbo spin-echo |
| Plane | Coronal | Coronal | Axial |
| Repetition time (ms) | 591.75 | 4.83 | 579.66 |
| Echo time (ms) | 120 | 2.41 | 120 |
| Acquisition matrix | 344 · 300 | 328 · 329 | 288 · 250 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Interslice gap (mm) | 0.6 | 0 | 0.6 |
| Number of averages | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Acquisition time (s) | 23.67 | 18.45 | 22.57 |
| Time (min) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Methanol (%) | 0.1% FA in Water (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.500 | 65 | 35 |
| 2.60 | 0.500 | 65 | 35 |
| 3.00 | 0.500 | 95 | 5 |
| 4.00 | 0.500 | 95 | 5 |
| 4.50 | 0.500 | 65 | 35 |
| 6.00 | 0.500 | 65 | 35 |
| Compound | Transition (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ritonavir | 721.20 > 139.96 | 66 | Quantification |
| 721.20 > 296.11 | 18 | Identification | |
| Lopinavir | 629.35 > 155.15 | 49 | Quantification |
| Control | PPI | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (nM) | 1129 (833.0–2194) | 826.6 (329.6–1302) |
| tmax (min) | 192.5 (175–240) | 225 (175–270) |
| AUC0-480min (nmol·min/L) | 3.8 · 105 (2.6 · 105–5.9 · 105) | 2.5 · 105 (1.2 · 105–3.2 · 105) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Waal, T.; Rubbens, J.; Grimm, M.; Vandecaveye, V.; Tack, J.; Weitschies, W.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Exploring the Effect of Esomeprazole on Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volumes and Absorption of Ritonavir. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070670
de Waal T, Rubbens J, Grimm M, Vandecaveye V, Tack J, Weitschies W, Brouwers J, Augustijns P. Exploring the Effect of Esomeprazole on Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volumes and Absorption of Ritonavir. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(7):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070670
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Waal, Tom, Jari Rubbens, Michael Grimm, Vincent Vandecaveye, Jan Tack, Werner Weitschies, Joachim Brouwers, and Patrick Augustijns. 2020. "Exploring the Effect of Esomeprazole on Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volumes and Absorption of Ritonavir" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 7: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070670
APA Stylede Waal, T., Rubbens, J., Grimm, M., Vandecaveye, V., Tack, J., Weitschies, W., Brouwers, J., & Augustijns, P. (2020). Exploring the Effect of Esomeprazole on Gastric and Duodenal Fluid Volumes and Absorption of Ritonavir. Pharmaceutics, 12(7), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070670