PLGA Microspheres of hGH of Preserved Native State Prepared Using a Self-Regulated Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Vivo Rat Model
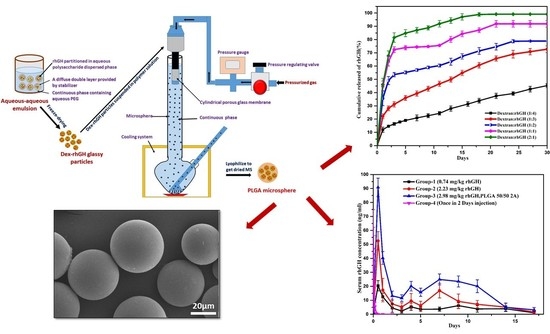
2.3. Formulation of rhGH-Dextran Particles
2.4. Preparation of rhGH-DMP Loaded Microspheres by SPG Membrane Emulsion and Sedimentation Method
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Particle Size Distribution of rhGH Loaded Dextran Micro Particles
2.7. Encapsulation and Loading Efficiency of rhGH in Microspheres
2.8. Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.9. Circular Dichroism (CD)-Spectroscopy
2.10. In Vitro Release Profile
2.11. In Vivo Release Study
2.12. In Vivo Efficacy Study
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Dextran Particles and PLGA Microspheres
3.2. Conformational Stability of rhGH During the Microencapsulation Process
3.3. In Vitro Release Study
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Studies in SD Rats
3.5. Efficacy Assays of rhGH Microspheres
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, O.L.; Jaworowicz, W.; Cleland, J.L.; Bailey, L.; Charnis, M.; Duenas, E.; Wu, C.; Shepard, D.; Magil, S.; Last, T. The stabilization and encapsulation of human growth hormone into biodegradable microspheres. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambi, T.; Li, Y.; Lee, D.S. Injectable hydrogels for sustained release of therapeutic agents. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.R.; Biller, B.M.K.; Cook, D.; Baptista, J.; Silverman, B.L.; Dao, L.; Attie, K.M.; Fielder, P.; Maneatis, T.; Lippe, B. Efficacy of a long-acting growth hormone (GH) preparation in patients with adult GH deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 6431–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, L.; Tian, F.-R.; ZhuGe, D.-L.; ZhuGe, Q.-C.; Shen, B.-X.; Jin, B.-H.; Huang, J.-P.; Wu, M.-Z.; Fan, L.-X.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; et al. Implantable porous gelatin microspheres sustained release of bFGF and improved its neuroprotective effect on rats after spinal cord injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, S.E.; Desai, K.H.; Zhang, L.; Olsen, K.F.; Schwendeman, S.P. Self-healing microencapsulation of biomacromolecules without organic solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10800–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendeman, S.P.; Costantino, H.R.; Gupta, R.K.; Siber, G.R.; Klibanov, A.M.; Langer, R. Stabilization of tetanus and diphtheria toxoids against moisture-induced aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11234–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.K.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Biodegradable polymeric microspheres with “open/closed” pores for sustained release of human growth hormone. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, T.V.; Doijad, R.C.; Yadav, A.V. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Spray Dried Sustained Release Microspheres of Gemcitabine Hydrochloride. Curr. Pharma Res. 2019, 9, 3247–3268. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, N.-Q.; Zhou, J.; Walker, J.; Li, L.; Hong, J.K.Y.; Olsen, K.F.; Tang, J.; Ackermann, R.; Wang, Y.; Qin, B.; et al. Microencapsulation of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres by spray-drying. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Ho, M.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Kang, M.J. Improved Drug Loading and Sustained Release of Entecavir-loaded PLGA Microsphere Prepared by Spray Drying Technique. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2019, 40, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yuan, M.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Ci, T.; Ke, X. Liquid jet breakup: A new method for the preparation of poly lactic-co-glycolic acid microspheres. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 137, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Zhu, J.; Wu, F.; Yuan, W.; Geng, L.L.; Zhu, H. Preparing polymer-based sustained-release systems without exposing proteins to water-oil or water-air interfaces and cross-linking reagents. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T. Process for Producing Polymeric Microspheres 2019. U.S. Patent Application No. 1,047,101,3B2, 12 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, J.L.; Jones, A.J.S. Stable formulations of recombinant human growth hormone and interferon-γ for microencapsulation in biodegradable mircospheres. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Ma, G.; Meng, F.-T.; Su, Z.-G. Preparation of uniform-sized PLA microcapsules by combining Shirasu Porous Glass membrane emulsification technique and multiple emulsion-solvent evaporation method. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, T.A.; Li, C.H. Circular dichroism studies on human pituitary growth hormone and ovine pituitary lactogenic hormone. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendeman, S.P. Recent advances in the stabilization of proteins encapsulated in injectable PLGA delivery systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2002, 19, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaga, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kitagawa, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Mizushima, Y.; Igarashi, R. A novel sustained-release formulation of insulin with dramatic reduction in initial rapid release. J. Control. Release 2002, 79, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendeman, S.P.; Shah, R.B.; Bailey, B.A.; Schwendeman, A.S. Injectable controlled release depots for large molecules. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imamura, K.; Ogawa, T.; Sakiyama, T.; Nakanishi, K. Effects of types of sugar on the stabilization of protein in the dried state. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Schwendeman, S.P. Stabilization and controlled release of bovine serum albumin encapsulated in poly (d,l-lactide) and poly(ethylene glycol) microsphere blends. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, M.C.; Carpenter, J.F.; Randolph, T.W. Effects of phase separating systems on lyophilized hemoglobin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Pack, D.W.; Klibanov, A.M.; Langer, R. Visual evidence of acidic environment within degrading poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) microspheres. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Mallery, S.R.; Schwendeman, S.P. Stabilization of proteins encapsulated in injectable poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, W.M. Drug Delivery: Engineering Principles for Drug Therapy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; ISBN 019802469X. [Google Scholar]
- Leelarasamee, N.; Howard, S.A.; Malanga, C.J.; Luzzi, L.A.; Hogan, T.F.; Kandzari, S.J.; Ma, J.K.H. Kinetics of drug release from polylactic acid—hydrocortisone microcapsules. J. Microencapsul. 1986, 3, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Jin, T. Preparation of protein-loaded sustained-release microspheres via ‘solid-in-oil-in-hydrophilic oil-in-ethanol (S/O/hO/E)’emulsification. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Group-1 | Group-2 | Group-3 | Group-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0.744 mg/kg rhGH) | (2.23 mg/kg rhGH) | (2.98 mg/kg rhGH, PLGA 50/50 2A) | (Once in 2 Days Injection) | |
| Tmax (day) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0139 (0.3 h) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 20.43 ± 4.99 | 52.52 ± 8.44 | 90.82 ± 8.01 | 46.71 ± 26.72 |
| AUC (0–1 d) (ng·day/mL) | 22.21 ± 5.15 | 42.92 | 82.95 ± 6.22 | 4.44 ± 1.89 |
| AUC (0–2 d) (ng·day/mL) | 28.88 ±7.84 | 48.46 ± 2.34 | 81.63 ± 6.24 | 4.44 ± 1.89 |
| AUC (0–14 d) (ng.day/mL) | 80.15 ± 22.61 | 158.48 ± 53.05 | 311.59 ± 48.89 | - |
| Early burst (%) | 27.71 | 27.09 | 26.62 | - |
| DI (dosage form index) (0–2 d) | 4.54 | 7.09 | 6.9 | 85.19 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diana, J.N.; Tao, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, M.; Kumar, C.U.; Wu, F.; Jin, T. PLGA Microspheres of hGH of Preserved Native State Prepared Using a Self-Regulated Process. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070683
Diana JN, Tao Y, Du Q, Wang M, Kumar CU, Wu F, Jin T. PLGA Microspheres of hGH of Preserved Native State Prepared Using a Self-Regulated Process. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(7):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070683
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiana, Jebun Nessa, Ying Tao, Qiran Du, Meng Wang, Chinta Uday Kumar, Fei Wu, and Tuo Jin. 2020. "PLGA Microspheres of hGH of Preserved Native State Prepared Using a Self-Regulated Process" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 7: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070683
APA StyleDiana, J. N., Tao, Y., Du, Q., Wang, M., Kumar, C. U., Wu, F., & Jin, T. (2020). PLGA Microspheres of hGH of Preserved Native State Prepared Using a Self-Regulated Process. Pharmaceutics, 12(7), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070683