The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence
Abstract
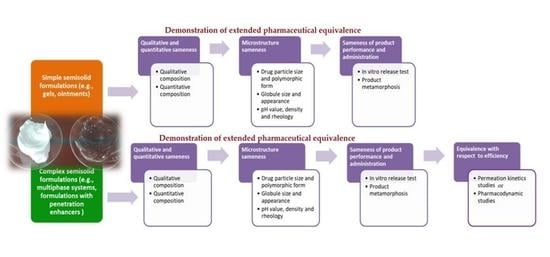
:1. Introduction
2. Demonstration of Extended Pharmaceutical Equivalence of Topical Semisolid Drug Products
2.1. Evaluation of Qualitative (Q1) and Quantitative (Q2) Sameness
2.2. Comparative Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
2.3. Evaluation of Product Performances—In Vitro Release Test
3. Demonstration of Equivalence with Respect to Efficacy of Topical Semisolid Drug Products
3.1. In Vitro Permeation Test
3.2. Stratum Corneum (SC) Sampling
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwa, M.C.; Tegtmeyer, K.; Welty, L.J.; Raney, S.G.; Luke, M.C.; Xu, S.; Kong, B. The relationship between the number of available therapeutic options and government payer (medicare part D) spending on topical drug products. Arch. Derm. Res. 2020, 312, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenn, J.; Brown, M. Cost-Effective Approaches for Successful Generic Dermal Drug Product Authorization. Available online: http://staging.ondrugdelivery.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/ONdrugDel-SKIN-DRUG-DELI-84-Mar-2018-Medpharm.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Wu, K.; Yeoh, T.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Osborne, D.W. Quality Assessment of API in Semisolid Topical Drug Products. In The Role of Microstructure in Topical Drug Product Development, 1st ed.; Langley, N., Michniak-Kohn, B., Osborne, D.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 36, pp. 109–154. [Google Scholar]
- Shanley, A. Topical Formulation: Moving from Art to Science. APIs, Excipients, and Manufacturing 2016, Supplement to Pharmaceutical Technology 40 (9). Available online: https://www.pharmtech.com/view/topical-formulation-moving-art-science (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Raney, S.G.; Franz, T.J.; Lehman, P.A.; Lionberger, R.; Chen, M.L. Pharmacokinetics-based approaches for bioequivalence evaluation of topical dermatological drug products. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 54, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, T.; Pantelić, I.; Lunter, D.; Đorđević, S.; Marković, B.; Ranković, D.; Daniels, R.; Savić, S. Critical quality attributes, in vitro release and correlated in vitro skin permeation-In vivo tape stripping collective data for demonstrating therapeutic (non)equivalence of topical semisolids: A case study of “ready-to-use” vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, Y.S.; Xu, X.; Rahman, Z.; Yang, Y.; Katragadda, U.; Lionberger, R.; Peters, J.R.; Uhl, K.; Khan, M.A. Development of performance matrix for generic product equivalence of acyclovir topical creams. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, V.; Wairkar, S. Current regulatory scenario and alternative surrogates methods to establish bioequivalence of topical generic products. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, A.; Shah, V.P.; Bashaw, E.D.; Benfeldt, E.; Davit, B.; Ganes, D.; Ghosh, T.; Kanfer, I.; Kasting, G.B.; Katz, L.; et al. Current challenges in bioequivalence, quality, and novel assessment technologies for topical products. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.P.; Yacobi, A.; Rădulescu, F.Ş.; Miron, D.S.; Lane, M.E. A science based approach to topical drug classification system (TCS). Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. Bioequivalence of topical generic products. Part 2. Paving the way to a tailored regulatory system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, P.; Musazzi, U.M.; Casiraghi, A.; Rocco, P. Old active ingredients in new medicinal products: Is the regulatory path coherent with patients’ expectations? Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US FDA Product-Specific Guidances for Generic Drug Development. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/psg/index.cfm (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), EMA. Draft Guideline on Quality and Equivalence of Topical Products, CHMP/QWP/708282/2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/draft-guideline-quality-equivalence-topical-products_en.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Miranda, M.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. Quality and equivalence of topical products: A critical appraisal. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 148, 105082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, A.; Veiga, F.; Vitorino, C.; Figueiras, A. A tutorial for developing a topical cream formulation based on the quality by design approach. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Rădulescu, F.Ş.; Miron, D.; Yacobi, A. Commonality between BCS and TCS. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.K.; Raw, A.; Lionberger, R.; Yu, L. Generic development of topical dermatologic products: Formulation development, process development, and testing of topical dermatologic products. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghavan, L.; Brown, M.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Ng, S.; Sammeta, S. In vitro release tests as a critical quality attribute in topical product development. In The Role of Microstructure in Topical Drug Product Development, 1st ed.; Langley, N., Michniak-Kohn, B., Osborne, D.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 36, pp. 47–87. [Google Scholar]
- Baynes, R.; Riviere, J.; Franz, T.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.; Lehman, P.; Peyrou, M.; Toutain, P.L. Challenges obtaining a biowaiver for topical veterinary dosage forms. J. Vet. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 35, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sharma, P.; Panda, A.; Parajuli, S.; Badani Prado, R.M.; Kundu, S.; Repka, M.A.; Ureña-Benavides, E.; Narasimha Murthy, S. Effect of surfactant on quality and performance attributes of topical semisolids. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Gupta, S.S.; Kalluri, H.; Lowenborg, M.; Bhatia, K.; Warner, K. Rheological characterization in the development of topical drug products. In The Role of Microstructure in Topical Drug Product Development, 1st ed.; Langley, N., Michniak-Kohn, B., Osborne, D.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 36, pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Pleguezuelos-Villa, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Hernández, M.J.; Nácher, A.; Peris, D.; Hidalgo, I.; Soler, L.; Sallan, M.; Merino, V. Relationship between rheological properties, in vitro release and in vivo equivalency of topical formulations of diclofenac. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryscio, D.R.; Sathe, P.M.; Lionberger, R.; Yu, L.; Bell, M.A.; Jay, M.; Hilt, J.Z. Spreadability measurements to assess structural equivalence (Q3) of topical formulations-a technical note. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2008, 9, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões, A.; Miranda, M.; Cardoso, C.; Veiga, F.; Vitorino, C. Rheology by design: A regulatory tutorial for analytical method validation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangas-Sanjuán, V.; Pleguezuelos-Villa, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Hernández, M.J.; Nácher, A.; García-Arieta, A.; Peris, D.; Hidalgo, I.; Soler, L.; Sallan, M.; et al. Assessment of the inter-batch variability of Microstructure Parameters in Topical Semisolids and Impact on the Demonstration of Equivalence. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, M.; Cova, T.; Augusto, C.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. Diving into batch-to-batch variability of topical products—A regulatory bottleneck. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Mangas-Sanjuán, V.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Merino, V.; García-Arieta, A. Influence of inter- and intra-batch variability on the sample size required for demonstration of equivalent microstructure of semisolid dosage forms. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, J.; Monleón-Getino, T.; Merino, V.; Peris, D.; Soler, L. Statistical methods for quality equivalence of topical products. 0.5 Mg/g Betamethasone Ointment as a Case-Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Namjoshi, S.; Dabbaghi, M.; Roberts, M.S.; Grice, J.E.; Mohammed, Y. Quality by design: Development of the quality target product profile (QTPP) for semisolid topical products. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simões, A.; Veiga, F.; Vitorino, C. Progressing towards the sustainable development of cream formulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, D.W.; Dahl, K.; Parikh, H. Determination of particle size and microstructure in topical pharmaceuticals. In The Role of Microstructure in Topical Drug Product Development, 1st ed.; Langley, N., Michniak-Kohn, B., Osborne, D.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 36, pp. 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, N.S.; Krishnaiah, Y.S.R.; Xu, X.; Zidan, A.S.; Raney, S.; Cruz, C.N.; Ashraf, M. Identification of critical formulation parameters affecting the in vitro release, permeation, and rheological properties of the acyclovir topical cream. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.S. Critical Quality Attributes (Q3 Characterization) of Topical Semisolid Products. 2016. Available online: http://www.pharmtech.com/pharmtech-webcasts (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Tiffner, K.I.; Kanfer, I.; Augustin, T.; Raml, R.; Raney, S.G.; Sinner, F. A comprehensive approach to qualify and validate the essential parameters of an in vitro release test (IVRT) method for acyclovir cream, 5. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. aQbD as a platform for IVRT method development—A regulatory oriented approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, V. Fast Screening Methods for the Analysis of Topical Drug Products. Processes 2020, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SUPAC-SS. Guidance for Industry Nonsterile Semisolid Dosage Forms. Scale-Up and Postapproval Changes: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls; In Vitro Release Testing and In Vivo Bioequivalence Documentation; Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Rockville, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mekjaruskul, C.; Beringhs, A.O.; Luo, W.C.; Xu, Q.; Halquist, M.; Qin, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X. Impact of membranes on in vitro release assessment: A case study using dexamethasone. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2021, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patere, S.; Newman, B.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Mekjaruskul, C.; Jay, M.; Lu, X. Influence of in vitro release methods on assessment of tobramycin ophthalmic ointments. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.F.; Rouse, J.; Sanderson, D.; Eccleston, G. A comparative study of transmembrane diffusion and permeation of ibuprofen across synthetic membranes using franz diffusion cells. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nallagundla, S.; Patnala, S.; Kanfer, I. Comparison of in vitro release rates of acyclovir from cream formulations using vertical diffusion cells. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2014, 15, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marto, J.; Baltazar, D.; Duarte, A.; Fernandes, A.; Gouveia, L.; Militão, M.; Salgado, A.; Simões, S.; Oliveira, E.; Ribeiro, H.M. Topical gels of etofenamate: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. FDA Draft Guidance on Acyclovir. 2016. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/psg/Acyclovir_topical%20cream_RLD%2021478_RV12-16.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Purazi, P.; Rath, S.; Ramanah, A.; Kanfer, I. Assessment of “Sameness” and/or Differences between Marketed Creams Containing Miconazole Nitrate Using a Discriminatory in vitro Release Testing (IVRT) Method. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudyahoto, N.A.; Rath, S.; Ramanah, A.; Kanfer, I. In Vitro release resting (IVRT) of topical hydrocortisone acetate creams: A novel approach using positive and negative controls. Dissolution Technol. 2020, 27, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Kanfer, I. A validated IVRT method to assess topical creams containing metronidazole using a novel approach. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habjanič, N.; Kerec Kos, M.; Kristan, K. Sensitivity of different in vitro performance tests and their in vivo relevance for calcipotriol/betamethasone ointment. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US FDA Guidance for Industry: Topical Dermatologic Corticosteroids: In Vivo Bioequivalence. 1995. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70931/download (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Shin, S.H.; Rantou, E.; Raney, S.G.; Ghosh, P.; Hassan, H.; Stinchcomb, A. Cutaneous pharmacokinetics of acyclovir cream 5% products: Evaluating bioequivalence with an in vitro permeation test and an adaptation of scaled average bioequivalence. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. Bioequivalence of topical generic products. Part 1: Where are we now? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCCS/1358/10 Basic Criteria for in Vitro Assessment of Dermal Absorption of Cosmetic Ingredient. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/91793089-8206-4975-a6c9-078770655851 (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- OECD. OECD Guidance Notes on Dermal Absorption Draft 22 October 2010; OECD: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 1–53. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/testing/oecd-guidelines-testing-chemicals-related-documents.htm (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Guideline on Quality of Transdermal Patches; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2014; Volume 44, pp. 1–28. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/quality-transdermal-patches (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Neupane, R.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Renukuntla, J.; Babu, R.J.; Tiwari, A.K. Alternatives to biological skin in permeation studies: Current trends and possibilities. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zsikó, S.; Csányi, E.; Kovács, A.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Gácsi, A.; Berkó, S. Novel in vitro investigational methods for modeling skin permeation: Skin PAMPA, Raman mapping. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensado, A.; Chiu, W.S.; Cordery, S.F.; Rantou, E.; Bunge, A.L.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Guy, R.H. Stratum corneum sampling to assess bioequivalence between topical acyclovir products. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guidance for Industry: Topical Dermatological Drug Product NDAs and ANDAs—In Vivo Bioavailability, Bioequivalence, In Vitro Release, and Associated Studies. Draft Guidance; FDA Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Rockville, MD, USA, 1998.
- Navidi, W.; Hutchinson, A.; N’Dri-Stempfer, B.; Bunge, A. Determining bioequivalence of topical dermatological drug products by tape-stripping. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2008, 35, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Dri-Stempfer, B.; Navidi, W.C.; Guy, R.H.; Bunge, A.L. Optimizing metrics for the assessment of bioequivalence between topical drug products. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Ramanah, A.; Bon, C.; Kanfer, I. Application of a dermatopharmacokinetic (DPK) method for bioequivalence assessment of topical metronidazole creams. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 23, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdin, D.; Kanfer, I.; Ducharme, M.P. Novel Approach for the bioequivalence assessment of topical cream formulations: Model-based analysis of tape stripping data correctly concludes BE and BIE. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalozou, E.; Babiskin, A.; Zhao, L. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling to support bioequivalence and approval of generic products: A case for diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%. CPT Pharm. Syst. Pharm. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/index.cfm (accessed on 18 April 2021).

| Drug | Semisolid Dosage Form | Qualitative and Quantitative Sameness Evaluation | Physicochemical Characterization | In Vitro Release Testing | In Vitro Skin Permeation Testing | Additional In Vivo Study | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acyclovir | Ointment | + | + | + | 2019 | ||
| Acyclovir | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2016 | |
| Bexarotene | Gel | + | + | + | + | 2019 | |
| Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride | Ointment | + | + | + | 2018 | ||
| Clindamycin phosphate | Gel | + | + | + | 2020 | ||
| Clindamycin phosphate and Tretinoin | Gel | + | + | + | 2020 | ||
| Crisaborole | Ointment | + | + | + | + | PK | 2019 |
| Crotamiton | Cream | + | 2016 | ||||
| Dapsone | Gel | + | + | + | + | PK | 2019 |
| Docosanol | Cream | + | + | + | 2017 | ||
| Doxepin hydrochloride | Cream | + | + | + | + | PK | 2019 |
| Gentamicin sulfate | Cream Ointment | + | 2017 | ||||
| Hydrocortisone | Cream | + | 2017 | ||||
| Ivermectin | Cream | + | + | + | + | PK | 2019 |
| Lidocaine | Ointment | + | + | 2016 | |||
| Luliconazole | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2018 | |
| Metronidazole | Gel | + | + | + | 2019 | ||
| Metronidazole | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2019 | |
| Nystatin and Triamcinolone acetonide | Cream Ointment | + | 2017 | ||||
| Oxymetazoline hydrochloride | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2019 | |
| Ozenoxacin | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2019 | |
| Penciclovir | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2018 | |
| Pimecrolimus | Cream | + | + | + | + | 2019 | |
| Silver sulfadiazine | Cream | + | + | + | 2017 | ||
| Tacrolimus | Ointment | + | + | + | + | 2018 | |
| Tretinoin | Gel | + | + | + | 2020 | ||
| Tretinoin | Cream | + | + | + | CES | 2020 |
| Parameter | Short Description | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane inertness | Evaluation of drug binding to membrane should be performed by immersing membrane in solution of drug at concentration relevant to average drug concentration in the receptor solution at the end of the test. | The recovery of drug in solution should be within the range 100% ± 5% [44] |
| Drug solubility in the receptor medium | Evaluation of drug solubility in the receptor mediums should be performed to confirm its suitability to maintain sink conditions during the study. | Drug concentration in the receptor medium should not exceed 30% of its maximum solubility in the receptor medium [14] |
| Linearity, precision and reproducibility | The R2 value of the in vitro release rate (IVRR) (slope) should be calculated across the sampling times throughout the IVRT study duration, for three IVRT runs with a set of six [44] or 12 [12] diffusion cells on 3 different days. Precision and reproducibility should be assessed from intra-/inter-run data analysis. Intra−/inter-operator precision and reproducibility should be also assessed. | Linearity: Minimum R2 > 0.9 across the study duration is required [14,44]. Precision and reproducibility: CV for the intra- and inter-run variability should be <10% [14] or <15% [44] |
| Sensitivity, specificity and selectivity | Sensitivity should be assessed by comparing the IVRR from the formulations with high (200%), low (50%) and nominal drug concentration (100% of label claim). The specificity should be assessed by determining whether the changes of IVRR are proportional to the different drug concentration in the formulations. The selectivity should be assessed by determining the capability of IVRT method to statistically differentiate the IVRRs from the altered formulations (caused by changes in drug content, CQAs (e.g., drug particle size or product rheological profile), critical manufacturing variables or quantitative excipient composition). | Sensitivity: mean IVRR (low drug concentration) < mean IVRR (nominal drug concentration) < mean IVRR (high drug concentration); Specificity: minimum R2 value ≥ 0.90 of the correlation of formulation concentration to average IVRR; Selectivity: CI between altered product formulations should fall outside the limits 90–111% [14] or 75.00–133.33% [44] |
| Robustness | Robustness testing should include minor variations in the method parameters (mixing rate, temperature, amount of formulation applied and receptor medium composition) | The mean IVRR of runs under altered conditions should be within ±15% of the mean IVRR in the regular parameter setting [44] |
| Recovery | The recovery should be calculated by dividing the average cumulative amount released at the last point in time with the applied dose in donor chamber. | The dose depletion ≤30% has no influence on the steady-state conditions for drug release [35,36,45,46,47] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilić, T.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S. The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050710
Ilić T, Pantelić I, Savić S. The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050710
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlić, Tanja, Ivana Pantelić, and Snežana Savić. 2021. "The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050710
APA StyleIlić, T., Pantelić, I., & Savić, S. (2021). The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050710