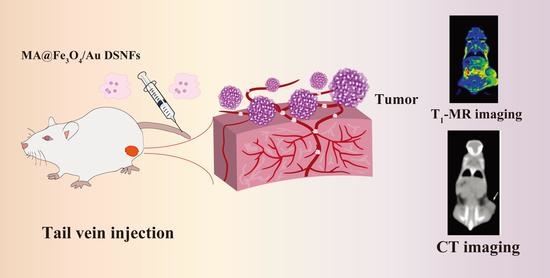
Macrophage-Laden Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Dual-Mode CT/MR Imaging of Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4/Au DSNFs
2.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake Assays
2.3. In Vivo MR and CT Imaging of Breast Tumor Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Fe3O4/Au DSNFs
3.2. In Vitro T1-Weighted MR Images
3.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake Assays
3.4. In Vivo MR and CT Imaging of Breast Tumor Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Bhattarai, P.; Dai, Z.; Chen, X. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2053–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Tao, L.; Yao, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Luquot, L. Microscopic Determination of Remaining Oil Distribution in Sandstones with Different Permeability Scales Using Computed Tomography Scanning. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2019, 141, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, X.; Wei, K.; Liu, Z. RGD-Tagged Microbubbles Generated by Versatile Fabrication Protocols for In Vitro Cell Targeting and In Vivo Mouse Imaging of Tumor Vascularization. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2020, 12, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Zhao, Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Gambhir, S.S.; Emelianov, S. Miniature gold nanorods for photoacoustic molecular imaging in the second near-infrared optical window. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonn, G.A.; Fan, R.E.; Ghanouni, P.; Wang, N.; Brooks, J.D.; Loening, A.; Daniel, B.L.; To’O, K.J.; Thong, A.E.; Leppert, J.T. Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging Interpretation Varies Substantially Across Radiologists. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.A.; Khlebtsov, N.G. Gold Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine: Recent Advances and Prospects. Acta Nat. 2011, 3, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.-R.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.-M.; Zhang, X.-X. Synthesis of orientedly bioconjugated core/shell Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanoparticles for cell separation. Talanta 2011, 85, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, X.; Shen, M. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Functionalization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for MR Imaging Applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joumaa, N.; Toussay, P.; Lansalot, M.; Elaissari, A. Surface modification of iron oxide nanoparticles by a phosphate-based macromonomer and further encapsulation into submicrometer polystyrene particles by miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 46, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, P.; Sun, W.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. Hyaluronic acid-modified Fe3O4@Au core/shell nanostars for multimodal imaging and photothermal therapy of tumors. Biomaterials 2015, 38, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H. Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: A review. Talanta 2018, 184, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-M.; Wang, L.-L. Molybdenum disulfide nanoflower-chitosan-Au nanoparticles composites based electrochemical sensing platform for bisphenol A determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauceda, H.E.; Salazar, F.; Pérez, L.A.; Garzón, I.L. Size and Shape Dependence of the Vibrational Spectrum and Low-Temperature Specific Heat of Au Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 25160–25168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Dendrimer-Stabilized Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Multimode Imaging-Guided Combination Therapy of Tumors. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1801612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, A.J.; Davis, M.E. Increased brain uptake of targeted nanoparticles by adding an acid-cleavable linkage between transferrin and the nanoparticle core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12486–12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.-H.; Sheinin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Oupický, D. Tumor-Penetrating Nanoparticles for Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Combined Photodynamic and Hypoxia-Activated Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Singh, A.K.; Khan, S.A.; Senapati, D.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Gold Nano-Popcorn-Based Targeted Diagnosis, Nanotherapy Treatment, and In Situ Monitoring of Photothermal Therapy Response of Prostate Cancer Cells Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18103–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamarov, K.; Sviridov, A.; Xu, W.; Malo, M.; Andreev, V.; Timoshenko, V.; Lehto, V.-P. Nano Air Seeds Trapped in Mesoporous Janus Nanoparticles Facilitate Cavitation and Enhance Ultrasound Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35234–35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shao, M.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z. Facile Preparation of Multifunctional Upconversion Nanoprobes for Multimodal Imaging and Dual-Targeted Photothermal Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7385–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhao, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Shen, M. 131 I-Labeled Multifunctional Polyphosphazene Nanospheres for SPECT Imaging-Guided Radiotherapy of Tumors. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2019, 8, e1901299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Nie, Y.; Liao, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, C. Overcoming the Reticuloendothelial System Barrier to Drug Delivery with a “Don’t-Eat-Us” Strategy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13015–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.; Kabanov, A. Cell-mediated drug delivery to the brain. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, A. Red Cell-Mediated Therapy: Opportunities and Challenges. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 1997, 23, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, M.; Clavreul, A.; Venier-Julienne, M.-C.; Passirani, C.; Sindji, L.; Schiller, P.; Montero-Menei, C.; Menei, P. Mesenchymal stem cells as cellular vehicles for delivery of nanoparticles to brain tumors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8393–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboody, K.S.; Brown, A.; Rainov, N.G.; Bower, K.A.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Small, J.E.; Herrlinger, U.; Ourednik, V.; Black, P.M.; et al. Neural stem cells display extensive tropism for pathology in adult brain: Evidence from intracranial gliomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12846–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tian, Q.; Xie, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.-P. Macrophages-Mediated Delivery of Small Gold Nanorods for Tumor Hypoxia Photoacoustic Imaging and Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15251–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Gendelman, H.E.; Kabanov, A. Cell-mediated drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Auffinger, B.; Spencer, D.A.; Miska, J.; Chang, A.L.; Kane, J.R.; Young, J.S.; Kanojia, D.; Qiao, J.; Mann, J.F.; et al. Single dose GLP toxicity and biodistribution study of a conditionally replicative adenovirus vector, CRAd-S-pk7, administered by intracerebral injection to Syrian hamsters. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Shi, X.; Cao, X. Stem cell-mediated delivery of nanogels loaded with ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles for enhanced tumor MR imaging. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4904–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wei, R.; Wang, C.; Feng, M. Tunneling Nanotubular Expressways for Ultrafast and Accurate M1 Macrophage Delivery of Anticancer Drugs to Metastatic Ovarian Carcinoma. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1078–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, P.; Thomas, S.; Morgan-Stevenson, V.; Maliken, B.D.; Gochanour, E.; Boukhar, S.; Yeh, M.M.; Kowdley, K.V. Iron alters macrophage polarization status and leads to steatohepatitis and fibrogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, R.; Shi, X.; Cao, X. Macrophage-Laden Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Dual-Mode CT/MR Imaging of Tumors. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13070995
Peng Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Gao Y, Guo R, Shi X, Cao X. Macrophage-Laden Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Dual-Mode CT/MR Imaging of Tumors. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13070995
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yucheng, Xiaomeng Wang, Yue Wang, Yue Gao, Rui Guo, Xiangyang Shi, and Xueyan Cao. 2021. "Macrophage-Laden Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Dual-Mode CT/MR Imaging of Tumors" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13070995
APA StylePeng, Y., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Gao, Y., Guo, R., Shi, X., & Cao, X. (2021). Macrophage-Laden Gold Nanoflowers Embedded with Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Dual-Mode CT/MR Imaging of Tumors. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13070995