Selinexor and the Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export: A New Perspective on the Treatment of Sarcomas and Other Solid and Non-Solid Tumors
Abstract
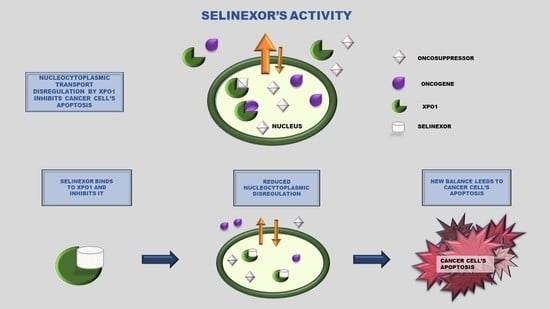
:1. Introduction
2. Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE): Selinexor
3. Pre-Clinical Studies
3.1. Lung Cancer
3.2. Breast Cancer
3.3. Pancreatic Cancer
3.4. Melanoma
3.5. Renal Cell Cancer
3.6. Glioblastoma Multiforme
3.7. Osteosarcoma
4. Clinical Studies
4.1. Gynecologic Cancer
4.2. Multiple Myeloma
4.3. Leukemia and Lymphoma
5. Selinexor in Soft Tissue Sarcomas (STS). A Landscape on the Medical Approach
5.1. Chemotherapy
5.2. Targeted Therapy
6. Selinexor: Preliminary Results as STS Treatment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorokin, A.V.; Kim, E.R.; Ovchinnikov, L.P. Nucleocytoplasmic Transport of Proteins. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 1439–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaurralde, E.; Kutay, U.; von Kobbe, C.; Mattaj, I.W.; Görlich, D. The Asymmetric Distribution of the Constituents of the Ran System Is Essential for Transport into and out of the Nucleus. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6535–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, F.R.; Klebe, C.; Kretschmer, J.; Wittinghofer, A.; Ponstingl, H. RanGAP1 Induces GTPase Activity of Nuclear Ras-Related Ran. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matunis, M.J.; Coutavas, E.; Blobel, G. A Novel Ubiquitin-like Modification Modulates the Partitioning of the Ran-GTPase-Activating Protein RanGAP1 between the Cytosol and the Nuclear Pore Complex. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.J.; Oaks, J.J.; Santhanam, R.; Neviani, P.; Harb, J.G.; Ferenchak, G.; Ellis, J.J.; Landesman, Y.; Eisfeld, A.K.; Gabrail, N.Y.; et al. Preclinical and Clinical Efficacy of XPO1/CRM1 Inhibition by the Karyopherin Inhibitor KPT-330 in Ph+ Leukemias. Blood 2013, 122, 3034–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayi-Smith, A.F.; van der Watt, P.J.; Leaner, V.D. Interfering with Nuclear Transport as a Means of Interrupting Transcription Factor Activity in Cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2019, 29, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.; Cautain, B.; de Pedro, N.; Link, W. Targeting nucleocytoplasmic transport in cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noske, A.; Weichert, W.; Niesporek, S.; Röske, A.; Buckendahl, A.-C.; Koch, I.; Sehouli, J.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C. Expression of the Nuclear Export Protein Chromosomal Region Maintenance/Exportin 1/Xpo1 Is a Prognostic Factor in Human Ovarian Cancer. Cancer 2008, 112, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yue, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, L.-W.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Y. Prognostic Value of CRM1 in Pancreas Cancer. Clin. Investig. Med. 2009, 32, E315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhao, H.; Shen, Z.; Chen, P.; Sun, Y.-J.; Tang, L.-N.; Zheng, S.-E. The Expression of CRM1 Is Associated with Prognosis in Human Osteosarcoma. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L.; Sun, L.; Cheng, C. Expression of CRM1 in Human Gliomas and Its Significance in P27 Expression and Clinical Prognosis. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 153–159; discussion 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Watt, P.J.; Maske, C.P.; Hendricks, D.T.; Parker, M.I.; Denny, L.; Govender, D.; Birrer, M.J.; Leaner, V.D. The Karyopherin Proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin Beta1, Are Overexpressed in Cervical Cancer and Are Critical for Cancer Cell Survival and Proliferation. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stommel, J.M.; Marchenko, N.D.; Jimenez, G.S.; Moll, U.M.; Hope, T.J.; Wahl, G.M. A Leucine-Rich Nuclear Export Signal in the P53 Tetramerization Domain: Regulation of Subcellular Localization and P53 Activity by NES Masking. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Henderson, B.R. Identification of a Functional Nuclear Export Sequence in BRCA1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38589–38596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benzeno, S.; Diehl, J.A. C-Terminal Sequences Direct Cyclin D1-CRM1 Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 56061–56066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henderson, B.R. Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Shuttling of APC Regulates Beta-Catenin Subcellular Localization and Turnover. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosin-Arbesfeld, R.; Townsley, F.; Bienz, M. The APC Tumour Suppressor Has a Nuclear Export Function. Nature 2000, 406, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latré de Laté, P.; Pépin, A.; Assaf-Vandecasteele, H.; Espinasse, C.; Nicolas, V.; Asselin-Labat, M.L.; Bertoglio, J.; Pallardy, M.; Biola-Vidamment, A. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Promotes the Nuclear Exclusion of FOXO3 in a Crm1-Dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5594–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, J.J.; Stoffel, M. Nuclear Export-Independent Inhibition of Foxa2 by Insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24816–24824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirski, S.E.L.; Sparks, K.E.; Friedrich, B.; Köhler, M.; Mo, Y.-Y.; Beck, W.T.; Cole, S.P.C. Topoisomerase II Binds Importin Alpha Isoforms and Exportin/CRM1 but Does Not Shuttle between the Nucleus and Cytoplasm in Proliferating Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalid, O.; Toledo Warshaviak, D.; Shechter, S.; Sherman, W.; Shacham, S. Consensus Induced Fit Docking (CIFD): Methodology, Validation, and Application to the Discovery of Novel Crm1 Inhibitors. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neggers, J.E.; Vercruysse, T.; Jacquemyn, M.; Vanstreels, E.; Baloglu, E.; Shacham, S.; Crochiere, M.; Landesman, Y.; Daelemans, D. Identifying Drug-Target Selectivity of Small-Molecule CRM1/XPO1 Inhibitors by CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abraham, S.A.; Holyoake, T.L. Redirecting Traffic Using the XPO1 Police. Blood 2013, 122, 2926–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapalombella, R.; Sun, Q.; Williams, K.; Tangeman, L.; Jha, S.; Zhong, Y.; Goettl, V.; Mahoney, E.; Berglund, C.; Gupta, S.; et al. Selective Inhibitors of Nuclear Export Show That CRM1/XPO1 Is a Target in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 4621–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gravina, G.L.; Mancini, A.; Sanita, P.; Vitale, F.; Marampon, F.; Ventura, L.; Landesman, Y.; McCauley, D.; Kauffman, M.; Shacham, S.; et al. KPT-330, a Potent and Selective Exportin-1 (XPO-1) Inhibitor, Shows Antitumor Effects Modulating the Expression of Cyclin D1 and Survivin [Corrected] in Prostate Cancer Models. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sexton, R.; Mahdi, Z.; Chaudhury, R.; Beydoun, R.; Aboukameel, A.; Khan, H.Y.; Baloglu, E.; Senapedis, W.; Landesman, Y.; Tesfaye, A.; et al. Targeting Nuclear Exporter Protein XPO1/CRM1 in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Razak, A.R.; Mau-Soerensen, M.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Shields, A.F.; Unger, T.J.; Saint-Martin, J.R.; Carlson, R.; Landesman, Y.; McCauley, D.; et al. First-in-Class, First-in-Human Phase I Study of Selinexor, a Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export, in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4142–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosicki, S.; Simonova, M.; Spicka, I.; Pour, L.; Kriachok, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Pylypenko, H.; Auner, H.W.; Leleu, X.; Doronin, V.; et al. Once-per-Week Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone versus Twice-per-Week Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Multiple Myeloma (BOSTON): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Sun, H.; Hattori, N.; Chien, W.; Sun, Q.; Sudo, M.; E-Ling, G.L.; Ding, L.; Lim, S.L.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; et al. KPT-330 Has Antitumour Activity against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Saltarski, J.M.; White, M.A.; Scaglioni, P.P.; Gerber, D.E. Therapeutic Targeting of Nuclear Export Inhibition in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Holloway, M.P.; Nguyen, K.; McCauley, D.; Landesman, Y.; Kauffman, M.G.; Shacham, S.; Altura, R.A. XPO1 (CRM1) Inhibition Represses STAT3 Activation to Drive a Survivin-Dependent Oncogenic Switch in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azmi, A.S.; Aboukameel, A.; Bao, B.; Sarkar, F.H.; Philip, P.A.; Kauffman, M.; Shacham, S.; Mohammad, R.M. Selective Inhibitors of Nuclear Export Block Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Reduce Tumor Growth in Mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazim, S.; Malafa, M.P.; Coppola, D.; Husain, K.; Zibadi, S.; Kashyap, T.; Crochiere, M.; Landesman, Y.; Rashal, T.; Sullivan, D.M.; et al. Selective Nuclear Export Inhibitor KPT-330 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Gemcitabine in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salas Fragomeni, R.A.; Chung, H.W.; Landesman, Y.; Senapedis, W.; Saint-Martin, J.-R.; Tsao, H.; Flaherty, K.T.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Cusack, J.C. CRM1 and BRAF Inhibition Synergize and Induce Tumor Regression in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wettersten, H.I.; Landesman, Y.; Friedlander, S.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Weiss, R.H. Specific Inhibition of the Nuclear Exporter Exportin-1 Attenuates Kidney Cancer Growth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.L.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; McCauley, D.; Jones, K.; Perry, J.A.; Hsu, J.H.-R.; Ramkissoon, L.A.; Maire, C.L.; Hubbell-Engler, B.; Knoff, D.S.; et al. Preclinical Antitumor Efficacy of Selective Exportin 1 Inhibitors in Glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2015, 17, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuetze, S.M.; Wathen, J.K.; Lucas, D.R.; Choy, E.; Samuels, B.L.; Staddon, A.P.; Ganjoo, K.N.; von Mehren, M.; Chow, W.A.; Loeb, D.M.; et al. SARC009: Phase 2 study of dasatinib in patients with previously treated, high-grade, advanced sarcoma. Cancer 2016, 122, 868–874, Epub 28 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Cesne, A.; Marec-Berard, P.; Blay, J.Y.; Gaspar, N.; Bertucci, F.; Penel, N.; Bompas, E.; Cousin, S.; Toulmonde, M.; Bessede, A.; et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) targeting in patients with advanced osteosarcomas: Results from the PEMBROSARC study. Eur. J. Cancer. 2019, 119, 151–157, Epub 21 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Fallois, M.; Kosyna, F.K.; Mandl, M.; Landesman, Y.; Dunst, J.; Depping, R. Selinexor decreases HIF-1α via inhibition of CRM1 in human osteosarcoma and hepatoma cells associated with an increased radiosensitivity. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 2025–2033, Epub 15 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corno, C.; Stucchi, S.; De Cesare, M.; Carenini, N.; Stamatakos, S.; Ciusani, E.; Minoli, L.; Scanziani, E.; Argueta, C.; Landesman, Y.; et al. FoxO-1 Contributes to the Efficacy of the Combination of the XPO1 Inhibitor Selinexor and Cisplatin in Ovarian Carcinoma Preclinical Models. Biochem. Pharm. 2018, 147, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergote, I.B.; Lund, B.; Peen, U.; Umajuridze, Z.; Mau-Sorensen, M.; Kranich, A.; Van Nieuwenhuysen, E.; Haslund, C.; Nottrup, T.; Han, S.N.; et al. Phase 2 Study of the Exportin 1 Inhibitor Selinexor in Patients with Recurrent Gynecological Malignancies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 156, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Kornblau, S.M.; Ruvolo, V.; Dilip, A.; Duvvuri, S.; Davis, R.E.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Coombes, K.R.; Zhang, N.; et al. Prognostic Impact and Targeting of CRM1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4166–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Savona, M.; Baz, R.; Andreeff, M.; Gabrail, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Savoie, L.; Mau-Sorensen, P.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Yee, K.; et al. A Phase 1 Clinical Trial of Single-Agent Selinexor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, M.; Ishizawa, J.; Ruvolo, V.; Dilip, A.; Quintás-Cardama, A.; McDonnell, T.J.; Neelapu, S.S.; Kwak, L.W.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; et al. Induction of P53-Mediated Transcription and Apoptosis by Exportin-1 (XPO1) Inhibition in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, J.; Savona, M.; Baz, R.; Mau-Sorensen, P.M.; Gabrail, N.; Garzon, R.; Stone, R.; Wang, M.; Savoie, L.; Martin, P.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export with Selinexor in Patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 3175–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, I.; Verweij, J.; Gelderblom, H.; Hartmann, J.T.; Schöffski, P.; Blay, J.-Y.; Kerst, J.M.; Sufliarsky, J.; Whelan, J.; Hohenberger, P.; et al. Doxorubicin Alone versus Intensified Doxorubicin plus Ifosfamide for First-Line Treatment of Advanced or Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma: A Randomised Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beaino, M.; Araujo, D.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Lin, P.P. Synovial Sarcoma: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment Identification of New Biologic Targets to Improve Multimodal Therapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, M.L.; Maki, R.; Venkatraman, E.; Geller, G.; Lovegren, M.; Aghajanian, C.; Sabbatini, P.; Tong, W.; Barakat, R.; Spriggs, D.R. Gemcitabine and Docetaxel in Patients with Unresectable Leiomyosarcoma: Results of a Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, P. The Story of Imatinib in GIST—A Journey through the Development of a Targeted Therapy. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2018, 41, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Garrett, C.R.; Blackstein, M.E.; Shah, M.H.; Verweij, J.; McArthur, G.; Judson, I.R.; Heinrich, M.C.; Morgan, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Sunitinib in Patients with Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour after Failure of Imatinib: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.-K.; Blay, J.-Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Regorafenib for Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours after Failure of Imatinib and Sunitinib (GRID): An International, Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurwitz, H.; Dowlati, A.; Savage, S.; Fernando, N.; Lasalvia, S.; Whitehead, B.; Suttle, B.; Collins, D.; Ho, P.; Pandite, L. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of oral administration of GW786034 in pts with solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Blay, J.-Y.; Chawla, S.P.; Kim, D.-W.; Bui-Nguyen, B.; Casali, P.G.; Schöffski, P.; Aglietta, M.; Staddon, A.P.; Beppu, Y.; et al. Pazopanib for Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma (PALETTE): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, W.D.; Wagner, A.J.; Schöffski, P.; Martin-Broto, J.; Krarup-Hansen, A.; Ganjoo, K.N.; Yen, C.-C.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; Spira, A.; Kawai, A.; et al. Effect of Doxorubicin Plus Olaratumab vs. Doxorubicin Plus Placebo on Survival in Patients With Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcomas: The ANNOUNCE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, R.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Czaplinski, J.T.; Anatone, A.J.; Sicinska, E.T.; Fletcher, J.A.; Demetri, G.D.; Wagner, A.J. Preclinical Activity of Selinexor, an Inhibitor of XPO1, in Sarcoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16581–16592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gounder, M.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; Gilligan, A.M.; Leong, H.; Ma, X.; Somaiah, N.; Chawla, S.P.; Martin-Broto, J.; Grignani, G.; Schuetze, S.M.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Pain with Selinexor in Patients with Advanced Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Authors | NCT Number | Diseases | Drug(s) | No. of Patients | Primary Endpoint | Results | Study Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdul Razak AR et al. [27] | NCT01607905 | Advanced solid tumors | Selinexor | 189 | Safety and maximum—tolerated dose | 35 mg/m2 twice a week | I |
| Grosicki S et al. [28] | NCT03110562 | Multiple myeloma | Selinexor +bortezo- Mib +desameta-sone | 457 | PFS | 13.93 vs. 9.46 months (HR 0.7 p = 0.0075) | III |
| Vergote IB et al. [42] | NCT02025985 | Advanced gynaecologic malignances | Selinexor | 114 | DCR | Ovarian 30% Endometrial 35% Cervical 24% | II |
| Kuruvilla J et al. [46] | NCT01607892 | Relapse or refractory non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | Selinexor | 79 | ORR | 31% | I |
| Gounder MM et al. [57] | NCT02606461 | Advanced unresectable dedifferentiated liposarcoma | Selinexor | 56 | PFS | 5.6 vs. 1.8 (HR 0.64 p = 0.21) | II/III |
| NCT Number | Study Title | Status |
|---|---|---|
| NCT04811196 | A study of different dosing schedules of Selinexor in sarcoma patients. | Recruiting |
| NCT03193437 | Selinexor in patients with advanced thymic epithelial tumor progressing after primary chemotherapy. | Recruiting |
| NCT04138381 | Selinexor as a single agent and in combination with Imatinib in patients with metastatic and/or unresectable GIST. | Recruiting |
| NCT04595994 | Selinexor plus gemcitabine in selected advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and osteosarcoma. | Recruiting |
| NCT03042819 | Study of Selinexor and Doxorubicin in advanced soft tissue sarcomas. | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02323880 | Selinexor in treating younger patients with recurrent or refractory solid tumors or high-grade gliomas. | Recruiting |
| NCT01986348 | A Phase 2 Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of Selinexor in patients with recurrent gliomas | Completed |
| NCT01896505 | A Phase I Trial to assess the effects of Food and Formulation on PK of KPT-330 in patients with sarcoma. | Completed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marretta, A.L.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Ribera, D.; Cannella, L.; von Arx, C.; Bracigliano, A.; Clemente, O.; Tafuto, R.; Pizzolorusso, A.; Tafuto, S. Selinexor and the Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export: A New Perspective on the Treatment of Sarcomas and Other Solid and Non-Solid Tumors. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091522
Marretta AL, Di Lorenzo G, Ribera D, Cannella L, von Arx C, Bracigliano A, Clemente O, Tafuto R, Pizzolorusso A, Tafuto S. Selinexor and the Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export: A New Perspective on the Treatment of Sarcomas and Other Solid and Non-Solid Tumors. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(9):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091522
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarretta, Antonella Lucia, Giuseppe Di Lorenzo, Dario Ribera, Lucia Cannella, Claudia von Arx, Alessandra Bracigliano, Ottavia Clemente, Roberto Tafuto, Antonio Pizzolorusso, and Salvatore Tafuto. 2021. "Selinexor and the Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export: A New Perspective on the Treatment of Sarcomas and Other Solid and Non-Solid Tumors" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 9: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091522
APA StyleMarretta, A. L., Di Lorenzo, G., Ribera, D., Cannella, L., von Arx, C., Bracigliano, A., Clemente, O., Tafuto, R., Pizzolorusso, A., & Tafuto, S. (2021). Selinexor and the Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export: A New Perspective on the Treatment of Sarcomas and Other Solid and Non-Solid Tumors. Pharmaceutics, 13(9), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091522