An Engineered IFNγ-Antibody Fusion Protein with Improved Tumor-Homing Properties
Abstract
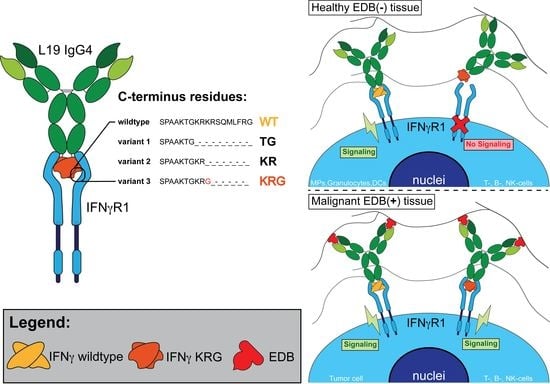
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Cloning, Expression, and Protein Purification
2.3. Protein Characterization
2.4. C-Terminus Sequence Confirmation by Intact Mass Analysis
2.5. Bioactivity Measurement
2.6. Immunofluorescence Infiltrate Study
2.7. Experimental Animals
2.8. Biodistribution Experiments
2.9. Non-Human Primate Pharmacokinetics Studies
2.10. Dose Escalation Study
2.11. Toxicity Assessment
2.12. Subcutaneous Tumor Model
2.13. Statistical Analysis
2.14. Ethical Statements
3. Results
3.1. Production and Characterization of L19-IFNγ variants
3.2. C-terminus Sequence Confirmation by Intact Mass Analysis
3.3. Generation and Biochemical Characterization of L19-IFNγ KRG
3.4. Functional Characterization of L19-IFNγ KRG
3.5. Pharmacokinetic Profiles of L19-IFNγ KRG and L19-IFNγ WT in Monkeys
3.6. Generation and Characterization of the L19-mIFNγ KRG
3.7. In Vivo Quantitative Biodistribution Profile of L19 IFNγ KRG
3.8. Dose Escalation Study and Histopathological Analysis
3.9. Therapy Experiments
3.10. Microscopic Analysis and Quantification of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, J.F.; Sadelain, M. The Journey from Discoveries in Fundamental Immunology to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiefer, J.D.; Neri, D. Immunocytokines and Bispecific Antibodies: Two Complementary Strategies for the Selective Activation of Immune Cells at the Tumor Site. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 270, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.R.; Devan, A.R.; Nair, B.; Vinod, B.S.; Nath, L.R. Harnessing the immune system against cancer: Current immunotherapy approaches and therapeutic targets. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 8075–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, D.; Sondel, P.M. Immunocytokines for cancer treatment: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 40, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berraondo, P.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in clinical cancer immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of Treatment of 255 Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Who Received High-Dose Recombinant Interleukin-2 Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutilli, E.; Feliciani, C. Adjuvant therapy for resected stage III melanoma patients: High-dose interferon-alpha versus ipilimumab combined with kinases inhibitors. Tumori J. 2012, 98, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.; Goa, K.L.; Bergmann, L.; Dummer, R.; Khayat, D. Aldesleukin (Recombinant Interleukin-2) A Review of its Pharmacological Properties, Clinical Efficacy and Tolerability in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. BioDrugs 1997, 7, 394–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, A.; Daniels, G.A.; Wong, M.K.K.; Kaufman, H.L.; Morse, M.A.; McDermott, D.F.; Clark, J.I.; Agarwala, S.S.; Miletello, G.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Contemporary experience with high-dose interleukin-2 therapy and impact on survival in patients with metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, R.; Glenn, L.; Hoen, H.; Richards, B.; Smith, J.W.; Lufkin, R.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Urba, W.J.; Curti, B.D. Durable responses and reversible toxicity of high-dose interleukin-2 treatment of melanoma and renal cancer in a Community Hospital Biotherapy Program. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silk, A.W.; Margolin, K. Cytokine Therapy. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charych, D.H.; Hoch, U.; Langowski, J.L.; Lee, S.R.; Addepalli, M.K.; Kirk, P.B.; Sheng, D.; Liu, X.; Sims, P.W.; VanderVeen, L.A.; et al. NKTR-214, an Engineered Cytokine with Biased IL2 Receptor Binding, Increased Tumor Exposure, and Marked Efficacy in Mouse Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patidar, M.; Yadav, N.; Dalai, S.K. Development of Stable Chimeric IL-15 for Trans-Presentation by the Antigen Presenting Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 646159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Fugmann, T.; Neri, D. From target discovery to clinical trials with armed antibody products. J. Proteom. 2014, 107, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielli, R.; Patuzzo, R.I.; Ruffini, P.A.; Maurichi, A.; Giovannoni, L.; Elia, G.; Neri, D.; Santinami, M. Armed antibodies for cancer treatment: A promising tool in a changing era. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 64, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, D. Antibody–cytokine fusions: Versatile products for the modulation of anticancer immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T.; Puca, E.; Silginer, M.; Hemmerle, T.; Pazahr, S.; Bink, A.; Weller, M.; Neri, D.; Roth, P. Immunocytokines are a promising immunotherapeutic approach against glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabb2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, J.R.; Wilson, C.B. Regulation of Interferon-γ During Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Adv. Immunol. 2007, 96, 41–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.W.; Goeddel, D.V. Structure of the human immune interferon gene. Nature 1982, 298, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Cross-regulation of Signaling Pathways by Interferon-γ: Implications for Immune Responses and Autoimmune Diseases. Immunity 2009, 31, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dufour, J.H.; Dziejman, M.; Liu, M.T.; Leung, J.H.; Lane, T.E.; Luster, A.D. IFN-γ-Inducible Protein 10 (IP-10; CXCL10)-Deficient Mice Reveal a Role for IP-10 in Effector T Cell Generation and Trafficking. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagpal, M.L.; Davis, J.; Lin, T. Overexpression of CXCL10 in human prostate LNCaP cells activates its receptor (CXCR3) expression and inhibits cell proliferation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2006, 1762, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, N.; Razon, H. Chemokines beyond chemo-attraction: CXCL10 and its significant role in cancer and autoimmunity. Cytokine 2018, 109, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgovanovic, D.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles of IFN-γin tumor progression and regression: A review. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojic, M.; Takeda, K.; Hayakawa, Y. The dark side of IFN-γ: Its role in promoting cancer immunoevasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abiko, K.; Matsumura, N.; Hamanishi, J.; Horikawa, N.; Murakami, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Baba, T.; Konishi, I.; Mandai, M. IFN-γ from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mimura, K.; Teh, J.L.; Okayama, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Kua, L.-F.; Koh, V.; Smoot, D.T.; Ashktorab, H.; Oike, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated with JAK-STAT pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 109, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, M.; Seyer, L.; Schadt, K.; Lynch, D.R. IFN-γ for Friedreich ataxia: Present evidence. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2015, 5, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriskandan, K.; Garner, P.; Watkinson, J.; Pettingale, K.W.; Brinkley, D.; Calman, F.M.B.; Tee, D.E.H. A toxicity study of recombinant interferon-gamma given by intravenous infusion to patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1986, 18, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.H.T.; Maher, S.G.; Young, H.A. Clinical use of interferon-γ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1182, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbinghaus, C.; Ronca, R.; Kaspar, M.; Grabulovski, D.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Engineered vascular-targeting antibody-interferon-γ fusion protein for cancer therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmerle, T.; Neri, D. The dose-dependent tumor targeting of antibody-IFNγ fusion proteins reveals an unexpected receptor-trapping mechanism in vivo. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundell, D.; Lunn, C.A.; Senior, M.M.; Zavodny, P.J.; Narula, S.K. Importance of the loop connecting A and B helices of human interferon-γ in recognition by interferon-γ receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16159–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundell, D.; Lunn, C.; Dalgarno, D.; Fossetta, J.; Greenberg, R.; Reim, R.; Grace, M.; Narula, S. The carboxyl-terminal region of human interferon 7 is important for biological activity: Mutagenic and NMR analysis. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1991, 4, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, P.S.; Mujtaba, M.G.; Paddy, M.R.; Johnson, H.M. The Carboxyl Terminus of Interferon-Contains a Functional Polybasic Nuclear Localization Sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huyghe, L.; Van Parys, A.; Cauwels, A.; Van Lint, S.; De Munter, S.; Bultinck, J.; Zabeau, L.; Hostens, J.; Goethals, A.; Vanderroost, N.; et al. Safe eradication of large established tumors using neovasculature-targeted tumor necrosis factor-based therapies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.E.; Stern, A.S.; Familletti, P.C.; Chizzonite, R.; Khan, F.R. Structural characterization of human interferon γ Heterogeneity of the carboxyl terminus. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 166, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbellari, R.; Stringhini, M.; Mock, J.; Ongaro, T.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; De Luca, R. A Novel Antibody–IL15 Fusion Protein Selectively Localizes to Tumors, Synergizes with TNF-based Immunocytokine, and Inhibits Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hober, S.; Nord, K.; Linhult, M. Protein A chromatography for antibody purification. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 848, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Trachsel, E.; Kaspar, M.; Schliemann, C.; Sommavilla, R.; Rybak, J.-N.; Rösli, C.; Borsi, L.; Neri, D. A high-affinity human monoclonal antibody specific to the alternatively spliced EDA domain of fibronectin efficiently targets tumor neo-vasculaturein vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarli, L.; Balza, E.; Viti, F.; Borsi, L.; Castellani, P.; Berndorff, D.; Dinkelborg, L.; Neri, D.; Zardi, L. A High-Affinity Human Antibody That Targets Tumoral Blood Vessels. Blood 1999, 94, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, A.W.P.; Norde, W.; van Amerongen, A. The Unfolding/Denaturation of Immunogammaglobulin of Isotype 2b and its F(ab) and F(c) Fragments. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kameoka, D.; Masuzaki, E.; Ueda, T.; Imoto, T. Effect of buffer species on the unfolding and the aggregation of humanized IgG. J. Biochem. 2007, 142, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguet, M.; Dembib, Z.; Merlin, G. Molecular Cloning and Expression of the Human Interferon-y Receptor. Cell 1988, 55, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta-Mannan, A.; Brown, R.; Key, S.; Cain, P.; Feng, Y. Pharmacokinetic Developability and Disposition Profiles of Bispecific Antibodies: A Case Study with Two Molecules. Antibodies 2022, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. The roles of IFN in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, S.D.; Holland, S.M. Defects in the interferon-g and interleukin-12 pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 203, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-gamma at the crossroads of tumor immune surveillance or evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocher, A.M.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Interferon-γ: Teammate or opponent in the tumour microenvironment? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puca, E.; Probst, P.; Stringhini, M.; Murer, P.; Pellegrini, G.; Cazzamalli, S.; Hutmacher, C.; Gouyou, B.; Wulhfard, S.; Matasci, M.; et al. The antibody-based delivery of interleukin-12 to solid tumors boosts NK and CD8 + T cell activity and synergizes with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 146, 2518–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, L.; Peissert, F.; Elsayed, A.; Weiss, T.; Look, T.; Weller, M.; Piro, G.; Carbone, C.; Tortora, G.; Matasci, M.; et al. Generation and in vivo validation of an IL-12 fusion protein based on a novel anti-human FAP monoclonal antibody. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, J.; Heery, C.R.; Kim, J.W.; Jochems, C.; Donahue, R.N.; Montgomery, A.S.; McMahon, S.; Lamping, E.; Marté, J.L.; Madan, R.A.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Trial of a Tumor-Targeted Cytokine (NHS-IL12) in Subjects with Metastatic Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.; Ping, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Yue, D.; Maimela, N.R.; Qu, J.; et al. Low-Dose IFNγ Induces Tumor Cell Stemness in Tumor Microenvironment of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 3737–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.K. The Surprising Story of IL-2: From Experimental Models to Clinical Application. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Chen, D.S. Immune escape to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade: Seven steps to success (or failure). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenga, I.; Donahue, R.N.; Lepone, L.; Bame, J.; Schlom, J.; Farsaci, B. PD-L1 and MHC-I expression in 19 human tumor cell lines and modulation by interferon-gamma treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, P102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Nitto, C.; Gilardoni, E.; Mock, J.; Nadal, L.; Weiss, T.; Weller, M.; Seehusen, F.; Libbra, C.; Puca, E.; Neri, D.; et al. An Engineered IFNγ-Antibody Fusion Protein with Improved Tumor-Homing Properties. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020377
Di Nitto C, Gilardoni E, Mock J, Nadal L, Weiss T, Weller M, Seehusen F, Libbra C, Puca E, Neri D, et al. An Engineered IFNγ-Antibody Fusion Protein with Improved Tumor-Homing Properties. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020377
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Nitto, Cesare, Ettore Gilardoni, Jacqueline Mock, Lisa Nadal, Tobias Weiss, Michael Weller, Frauke Seehusen, Chiara Libbra, Emanuele Puca, Dario Neri, and et al. 2023. "An Engineered IFNγ-Antibody Fusion Protein with Improved Tumor-Homing Properties" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020377
APA StyleDi Nitto, C., Gilardoni, E., Mock, J., Nadal, L., Weiss, T., Weller, M., Seehusen, F., Libbra, C., Puca, E., Neri, D., & De Luca, R. (2023). An Engineered IFNγ-Antibody Fusion Protein with Improved Tumor-Homing Properties. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020377