Abies holophylla Leaf Essential Oil Alleviates Allergic Rhinitis Based on Network Pharmacology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Network Construction and Prediction of Genes Associated with Allergic Rhinitis
2.2. KEGG Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Preparation of AEO
2.4. Animal Models and Drug Administration
2.5. Histopathological Examination
2.6. Nasal Sneezing and Rubbing Behavior
2.7. Serum Levels of IgE
2.8. Cell Counts for NALF
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Cell Culture
2.11. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
2.12. AEO Treatment of RPMI2650
2.13. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.14. Western Blot Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. AEO Network and Shared Targets with Allergic Rhinitis
3.2. KEGG and GO Enrichment Analysis of AEO
3.3. Histological Changes of Nasal Tissues
3.4. Effects on Nasal Sneezing and Rubbing Behavior
3.5. Effects on Serum IgE Level
3.6. Effects on Infiltration of Differential Inflammatory Cells in NALF
3.7. Cytotoxicity of AEO
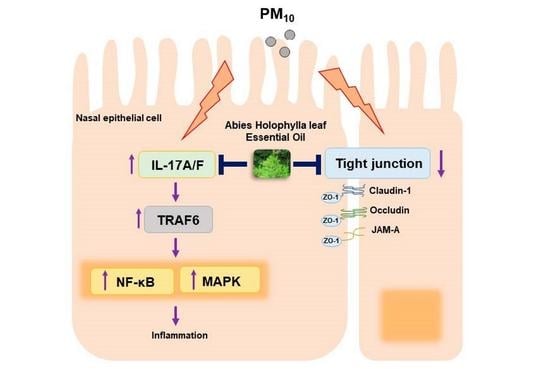
3.8. Effects on IL-17 Signaling Pathway Related Factors in the PM10-Treated Nasal Epithelial Cells
3.9. Effects on the MAPK-Related Factors in PM10-Treated Nasal Epithelial Cells
3.10. Effects on the NF-κB-Related Factors in PM10-Treated Nasal Epithelial Cells
3.11. Effects on ZO-1 Protein Expressions on Nasal Tissues
3.12. Effects on Tight Junction-Related Factors in the PM10-Treated Nasal Epithelial Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filho, N.A.R.; Satoris, R.A.; Scala, W.R. Allergic rhinitis aggravated by air pollutants in Latin America: A systematic review. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.R.; Dolen, W.K. Management of Allergic Rhinitis: A Review for the Community Pharmacist. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wu, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, B.; Cao, S.; Yan, M.; Pan, X.; Xue, T.; et al. Association between exposure to air pollution and risk of allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 205, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brożek, J.L.; Bousquet, J.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Bonini, S.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.B.; van Wijk, R.G.; Ohta, K.; Zuberbier, T.; Schünemann, H.J. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 Revision. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passali, D.; Cingi, C.; Staffa, P.; Passali, F.; Muluk, N.B.; Bellussi, M.L. The International Study of the Allergic Rhinitis Survey: Outcomes from 4 geographical regions. Asia Pac. Allergy 2018, 8, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoyte, F.C.L.; Nelson, H.S. Recent advances in allergic rhinitis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, S.M.N.; Tan, H.-T.T.; Shukri, N.M.; Ashari, N.S.M.; Wong, K.K. Nasal Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Tight Junctions Disruption in Allergic Rhinitis: Overview and Pathogenic Insights. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 663626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, P.B.; Aksun, S.; Altin, Z.; Bilgir, F.; Arslan, I.B.; Colak, H.; Ural, B.; Kahraman, D.S.; Diniz, G.; Ozdemir, B.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and Its Relationship with IL-10, IL-17, TGF-β, IFN-γ, IL 22, and IL-35. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 9131432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melum, G.R.; Farkas, L.; Scheel, C.; Van Dieren, B.; Gran, E.; Liu, Y.-J.; Johansen, F.-E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Baekkevold, E.S. A thymic stromal lymphopoietin–responsive dendritic cell subset mediates allergic responses in the upper airway mucosa. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 613–621.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, H.J.; Sutton, B.J. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters-Golden, M.; Gleason, M.M.; Togias, A. Cysteinyl leukotrienes: Multi-functional mediators in allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naclerio, R.M. The role of histamine in allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, J.; Nolte, A.; Temane, A.; Solomon, E.M. Health supplements for allergic rhinitis: A mixed-methods systematic review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 51, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, J.; Bielory, L. Complementary and Alternative Therapy (CAM) in the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, D.K.; Plesa, M.L. Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 985–992. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.; Lee, J.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.; Yoo, Y.; Jeung, E. Cytostatic effects of plant essential oils on human skin and lung cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huie, C.W. A review of modern sample-preparation techniques for the extraction and analysis of medicinal plants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 373, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kreiner, J.M.; Wong, A.R.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, A.W.H. Oral application of Chinese herbal medicine for allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytotherapy Res. 2021, 35, 3113–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Gu, Q. Current status of Chinese herbal medicine to treat allergic rhinitis in children: From the perspective of Western medicine—A narrative review. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, A.L.; Cannon, E.; Lee, S.E.; Wang, E.W.; Little, S.R. Advances in controlled drug delivery to the sinonasal mucosa. Biomaterials 2022, 282, 121430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugas, H.L.; Peters, J.I.; Williams, R.O., III. Nebulization of mycophenolate mofetil inhalation suspension in rats: Comparison with oral and pulmonary administration of Cellcept(R). Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prulière-Escabasse, V.; Michel, J.; Percodani, J.; Serrano, E.; Gilain, L.; Crampette, L.; Jankowski, R.; Stoll, D.; de Gabory, L. Consensus document for prescription of nebulization in rhinology. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2014, 131, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadgrove, N.J.; Padilla-González, G.F.; Leuner, O.; Melnikovova, I.; Fernandez-Cusimamani, E. Pharmacology of Natural Volatiles and Essential Oils in Food, Therapy, and Disease Prophylaxis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 740302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Huang, Q. Cinnamon essential oil Pickering emulsion stabilized by zein-pectin composite nanoparticles: Characterization, antimicrobial effect and advantages in storage application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 148, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Sureda, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Daglia, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Valussi, M.; Tundis, R.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; et al. Biological Activities of Essential Oils: From Plant Chemoecology to Traditional Healing Systems. Molecules 2017, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Park, K. Effect of Inhalation of Aromatherapy Oil on Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 7896081. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, L.; Yumnam, S. Terpenoids from Abies holophylla Attenuate LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in Microglial Cells by Suppressing the JNK-Related Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Subedi, L.; Ha, Y.J.; Moon, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.S. Glycosylated constituents isolated from the trunk of Abies holophylla and their anti-inflammatory and neurotrophic activity. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilada, E.; Honda, G.; Sezik, E.; Tabata, M.; Fujita, T.; Tanaka, T.; Takeda, Y.; Takaishi, Y. Traditional medicine in Turkey. V. Folk medicine in the inner Taurus Mountains. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 46, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.-H.; Zhang, S.-D.; Li, Y.-L.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Yang, X.-W.; Zeng, H.-W.; Li, H.-L.; Wang, N.; Steinmetz, A.; et al. Sesquiterpenoids and triterpenoids from Abies holophylla and their bioactivities. Phytochemistry 2012, 74, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.H.; Yang, W.M. Efficacy and mechanism of essential oil from Abies holophylla leaf on airway inflammation in asthma: Network pharmacology and in vivo study. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. Comparative analysis of chemical compositions and antimicrobial activities of essential oils from Abies holophylla and Abies koreana activities of essential oils from Abies holophylla and Abies koreana. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, D.A. Allergic rhinitis and asthma: Epidemiology and common pathophysiology. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014, 35, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiao, M.; Hu, X.; Shi, X.; Cao, S.; Qiu, F. An integrated approach based on phytochemistry, network pharmacology and metabolomics reveals the mechanism of action of Xanthium strumarium L. for allergic rhinitis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41154–41163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, A.; Yoshimoto, T. Barrier dysfunction in the nasal allergy. Allergol. Int. 2018, 67, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Lee, D.-W.; Che, M.-H. Immunomodulative Effects of Chamaecyparis obtusa Essential Oil in Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, U.; Gebbers, J.-O. Epithelial changes in seasonal allergic rhinitis throughout the year: Evidence of coexistent air pollution and local secretory IgA deficiency? ORL J. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Its Relat. Spec. 2000, 62, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.C.; Taylor, R.M.; Naclerio, R.M. The histology of allergic rhinitis and its comparison to cellular changes in nasal lavage. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalhuk, L.C.; Telles, E.Q.; Lima, M.N.; Filho, N.A.R. Nasal lavage cytology and mucosal histopathological alterations in patients with rhinitis. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 86, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-N.; Kim, S.-J.; Yoon, S.A.; Song, J.M.; Ahn, J.-S.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, A.M.K.; Yoon, J.-H. CD44v3-Positive Intermediate Progenitor Cells Contribute to Airway Goblet Cell Hyperplasia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminuma, O.; Nishimura, T.; Saeki, M.; Mori, A.; Hiroi, T. T Cell-Mediated Nasal Hyperresponsiveness in Allergic Rhinitis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Kang, H. Protective effect of Asarum sieboldii essential oil on ovalbumin induced allergic rhinitis in rat. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20191370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Lee, K.H.; Nonaka, M.; Takizawa, R. Role of mast cells and basophils in chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 20, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erjefält, J.S. Mast cells in human airways: The culprit? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, X.; Feng, C. Pharmacological Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-asthmatic Effects of Modified Guomin Decoction Determined by Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 644561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makihara, S.; Okano, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Noda, Y.; Higaki, T.; Miyateke, T.; Kanai, K.; Haruna, T.; Kariya, S.; Nishizaki, K. Local Expression of Interleukin-17a is Correlated with Nasal Eosinophilia and Clinical Severity in Allergic Rhinitis. Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 5, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Nagai, T.; Kadoki, M.; Nambu, A.; Komiyama, Y.; Fujikado, N.; Tanahashi, Y.; Akitsu, A.; Kotaki, H.; et al. Differential Roles of Interleukin-17A and -17F in Host Defense against Mucoepithelial Bacterial Infection and Allergic Responses. Immunity 2009, 30, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Liu, P.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Jin, X. Water-extracted Lonicera japonica polysaccharide attenuates allergic rhinitis by regulating NLRP3-IL-17 signaling axis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-L.; Rosenthal, M. IL-17 in lung disease: Friend or foe? Thorax 2013, 68, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newcomb, D.C.; Peebles, R.S. Th17-mediated inflammation in asthma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagliardo, R.; Chanez, P.; Profita, M.; Bonanno, A.; Albano, G.D.; Montalbano, A.M.; Pompeo, F.; Gagliardo, C.; Merendino, A.M.; Gjomarkaj, M. IκB kinase–driven nuclear factor-κB activation in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 635–645.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IL-17 cytokines in immunity and inflammation-Search Results-PubMed. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Xu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.Y.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Han, D.M.; Wang, X.D.; Zuo, K.J.; Li, H.B. Opposing roles of IL-17A and IL-25 in the regulation of TSLP production in human nasal epithelial cells. Allergy 2010, 65, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bechara, R.; Zhao, J.; McGeachy, M.J.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 receptor–based signaling and implications for disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Tsai, C.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ng, K.-K.; Chang, T.-C.; Kao, W.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Hong, J.-H. The Role of Pretreatment FDG-PET in Treating Cervical Cancer Patients With Enlarged Pelvic Lymph Node(s) Shown on MRI: A Phase 3 Randomized Trial With Long-Term Follow-Up. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 92, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.L.; Lapadat, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways Mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 Protein Kinases. Science 2002, 298, 1911–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Luo, Y.; Bian, Y.; Wang, R. Effect of artemisinin and neurectomy of pterygoid canal in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse model. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, K.; Liu, S.; Ramezanpour, M.; Cooksley, C.; Javadiyan, S.; Fujieda, S.; Wormald, P.-J.; Vreugde, S.; Psaltis, A.J. Trimellitic anhydride facilitates transepithelial permeability disrupting tight junctions in sinonasal epithelial cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 353, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, K.; Kabashima, K. Tight junctions in the development of asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarah, C.O.S.; Shukri, N.M.; Ashari, N.S.M.; Wong, K.K. Zonula occludens and nasal epithelial barrier integrity in allergic rhinitis. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günzel, D.; Yu, A.S.L. Claudins and the Modulation of Tight Junction Permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coyne, C.B.; Gambling, T.M.; Boucher, R.C.; Carson, J.L.; Johnson, L.G. Role of claudin interactions in airway tight junctional permeability. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L1166–L1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, R.S.; Vanhook, M.K.; Barozzi, N.; Toth, I.; Johnson, L.G. Specific Modulation of Airway Epithelial Tight Junctions by Apical Application of an Occludin Peptide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kojima, T.; Go, M.; Takano, K.-I.; Kurose, M.; Ohkuni, T.; Koizumi, J.-I.; Kamekura, R.; Ogasawara, N.; Masaki, T.; Fuchimoto, J.; et al. Regulation of Tight Junctions in Upper Airway Epithelium. BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2013, 947072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, A.C.; Parkos, C.A. Intracellular mediators of JAM-A-dependent epithelial barrier function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1257, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steelant, B.; Farré, R.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Belmans, J.; Dekimpe, E.; Vanheel, H.; Van Gerven, L.; Krohn, I.K.; Bullens, D.M.; Ceuppens, J.L.; et al. Impaired barrier function in patients with house dust mite–induced allergic rhinitis is accompanied by decreased occludin and zonula occludens-1 expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1043–1053.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, R.; Guoshun, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, C.; Xu, J.; Dong, W.; Hong, Z.; Yu, H.; Situ, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Nasal epithelial barrier disruption by particulate matter ≤2.5 μm via tight junction protein degradation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 38, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, G.J.; Mullin, J.; Ryan, M.P. Occludin: Structure, function and regulation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 883–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xi, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Ma, C.; Hong, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. The effect of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on tight junctions of the nasal mucosa epithelial cells in rat models with allergic rhinitis. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 28, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar]
- De Servi, B.; Ranzini, F.; Piqué, N. Protective barrier properties of Rhinosectan® spray (containing xyloglucan) on an organotypic 3D airway tissue model (MucilAir): Results of an in vitro study. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| IL17A | TCCAGAAGGCCCTCAGACTA | AGCATCTTCTCGACCCTGAA |
| IL17F | GTGCCAGGAGGTAGTATGAAGC | ATGTCTTCCTTTCCTTGAGCATT |
| CLDN1 (Claudin-1) | CTTCATTCTCGCCTTCCT | TGACAGCCATCCTCATCTT |
| TJP1 (ZO-1) | GGAGAGGTGTTTCGTGTTGT | ACTGCTCAGCCCTGTTCTTA |
| OCLN (Occludin) | TATGCCCTCTGCAACCAA | CACCGCTGCTGTAACGAG |
| F11R (JAM-A) | CTTCGATCCTGTGTCAGCTT | TCTATAGGCGAACCAGATGC |
| GAPDH | CCATCACCATCTTCCAGGAG | CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTG |
| Category | Description | p-Value | Background Genes | Common Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathways | IL-17 signaling pathway | 3.39 × 10−18 | 92 | 18 |
| Tight junction | 0.003 | 156 | 5 | |
| GO process | Cellular response to chemical stimulus | 2.07 × 10−37 | 2919 | 99 |
| Response to external stimulus | 2.94 × 10−25 | 2310 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, J.Y.; Park, N.; Kim, M.H.; Yang, W.M. Abies holophylla Leaf Essential Oil Alleviates Allergic Rhinitis Based on Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041195
Chung JY, Park N, Kim MH, Yang WM. Abies holophylla Leaf Essential Oil Alleviates Allergic Rhinitis Based on Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041195
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Jae Yoon, Nayoung Park, Mi Hye Kim, and Woong Mo Yang. 2023. "Abies holophylla Leaf Essential Oil Alleviates Allergic Rhinitis Based on Network Pharmacology" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041195
APA StyleChung, J. Y., Park, N., Kim, M. H., & Yang, W. M. (2023). Abies holophylla Leaf Essential Oil Alleviates Allergic Rhinitis Based on Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041195