Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Arid or Semiarid Region of Northern Xinjiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Field Measurements and Data Used
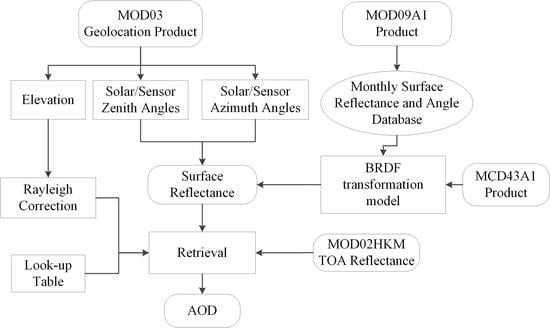
3. Methodology
3.1. Construction of Surface Database
3.2. BRDF Correction Surface Reflectance
3.3. Aerosol Parameter Determination
3.4. Rayleigh Correction for Elevation Effect
3.5. Error Indicators
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution of AOD
4.2. Validation
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.X.; Sharratt, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.S.; Yang, W.Y. Dust deposition and ambient PM 10 concentration in Northwest China: Spatial and temporal variability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamtimin, B.; Meixner, F.X. Air pollution and meteorological processes in the growing dryland city of urumqi (Xinjiang, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Atmosphere—Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, R.J.; Mason, R.M. Aerosol research and inhalation epidemiological study (ARIES): Air quality and daily mortality statistical modeling—Interim results. J. Air Waste Manag. 2000, 50, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, H.C.; Wang, T.; Baumann, K.; Guo, H. Influence of regional pollution outflow on the concentrations of fine particulate matter and visibility in the coastal area of southern china. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6463–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Ezzati, M.; Dockery, D.W. Fine particulate air pollution and life expectancies in the united states: The role of influential observations. J. Air Waste Manag. 2013, 63, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.D.; Sheng, H.J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, C.Y. Observation study on the size distribution of sand dust aerosol particles over Yinchuan, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 157645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.Y.; Du, W.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Gao, Q.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, M.X. Aerosol optical properties affected by a strong dust storm over central and northern china. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, R.B.; Tian, X.P.; Wei, J. Analysis of the temporal and spatial variation of aerosols in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region with a 1 km aod product. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Sinyuk, A.; Ginoux, P.; Holben, B. A long-term record of aerosol optical depth from toms observations and comparison to aeronet measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados, A.I.; Kondragunta, S.; Ciren, P.; Knapp, K.R. Goes aerosol/smoke product (GASP) over north america: Comparisons to aeronet and modis observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from ozone monitoring instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidot, J.; Santer, R.; Aznay, O. Evaluation of the meris aerosol product over land with aeronet. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 7603–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffler, M.; Popp, C.; Hauser, A.; Fontana, F.; Wunderle, S. Validation of a modified AVHRR aerosol optical depth retrieval algorithm over central Europe. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N. Multiangle imaging spectroradiometer global aerosol product assessment by comparison with the aerosol robotic network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Holben, B.N.; Zhang, J. Global and regional evaluation of over-land spectral aerosol optical depth retrievals from seawifs. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The collection 6 modis aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.M.; Liu, H.Q.; Laszlo, I.; Kondragunta, S.; Remer, L.A.; Huang, J.F.; Huang, H.C. Suomi-NPP VIIRS aerosol algorithms and data products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12673–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. Modis 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L. Comparison and evaluation of different modis aerosol optical depth products over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in china. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of modis aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.H.; Wang, Z.F.; Tao, J.H.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.C.; Xu, X.G.; Zhu, H. How do aerosol properties affect the temporal variation of MODIS AOD bias in Eastern China? Remote Sens. (Basel) 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; de Haan, J.F.; Stammes, P. A database of spectral surface reflectivity in the range 335-772 nm derived from 5.5 years of GOME observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.R.; Celarier, E.A. Earth surface reflectivity climatology at 340–380 nm from toms data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 28003–28011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. Aeronet—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobelspiesse, K.D.; Pietras, C.; Fargion, G.S.; Wang, M.H.; Frouin, R.; Miller, M.A.; Subramaniam, A.; Balch, W.M. Maritime aerosol optical thickness measured by handheld sun photometers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, M.; Mims, F.M.; Hagerup, S.; Anderson, S.E.; Baker, A.; Kia, J.; Walkup, T. Design, calibration, and performance of microtops II handheld ozone monitor and sun photometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 14573–14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Mi, X.T.; Guo, Y.M.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Gan, P.; Zhou, X.Y.; Jia, C.; et al. A universal dynamic threshold cloud detection algorithm (UDTCDA) supported by a prior surface reflectance database. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7172–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Kotchenova, S. Mod09 User’s Guide (J/OL). Available online: http://modis-sr.ltdri.org (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Bilal, M.; Tian, X.P.; Jia, C.; Guo, Y.M.; Mi, X.T. Aerosol optical depth retrieval over bright areas using landsat 8 oli images. Remote Sens. (Basel) 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.L.; Leroy, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. A bidirectional reflectance model of the earths surface for the correction of remote-sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 20455–20468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. An algorithm for the retrieval of albedo from space using semiempirical brdf models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.O.; Breon, F.M. Towards a generalized approach for correction of the BRDF effect in modis directional reflectances. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.T.D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J. Second Simulation of a Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum-Vector (6SV). Available online: http://6s.ltdri.org/files/tutorial/6S_Manual_Part_1.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2017).
- Tanre, D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Holben, B.N.; Chatenet, B.; Karnieli, A.; Lavenu, F.; Blarel, L.; Dubovik, O.; Remer, L.A.; Smirnov, A. Climatology of dust aerosol size distribution and optical properties derived from remotely sensed data in the solar spectrum. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18205–18217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.F.; Philip, G.M. A refinement of inverse distance weighted interpolation. Geoprocessing 1985, 2, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Miishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D. Light-scattering by polydispersions of randomly oriented spheroids with sizes comparable to wavelengths of observation. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 7206–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodhaine, B.A.; Wood, N.B.; Dutton, E.G.; Slusser, J.R. On rayleigh optical depth calculations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucholtz, A. Rayleigh-scattering calculations for the terrestrial atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angstrom, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adames, A.F.; Reynolds, M.; Smirnov, A.; Covert, D.S.; Ackerman, T.P. Comparison of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer ocean aerosol retrievals with ship-based sun photometer measurements from the around the americas expedition. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.P.; Sun, L. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth over arid areas from modis data. Atmosphere (Basel) 2016, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I.; Holben, B.N. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of modis aerosol products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.D.; Mao, J.; Li, C.C.; Holben, B.N. Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the earth observing system-terra moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.C.; Li, R.R.; Flynn, L. The modis 2.1-mu m channel—Correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Xie, H.J.; Liang, T.G. Evaluation of modis snow cover and cloud mask and its application in northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Site | Instrument | Lon. (°E) | Lat. (°N) | Elevation (m) | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dahuangshan | Microtops II | 88.645 | 44.041 | 1018 | 2014/7/10 | 2014/8/24 |
| Wucaiwan | CE-318 | 88.099 | 44.776 | 450 | 2014/7/15 | 2014/8/21 |
| Data Name | Date | Tile | N | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOD09A1 | 2010–2014 | H23-H25, V04-V05 | 240 | Build surface reflectance and angle information database |
| MCD43A1 | 2014/07/10–2014/08/24 | H23-H25, V04-V05 | 276 | Build BRDF correction model |
| MOD02HKM | 2014/07/10–2014/08/24 | 55 | Calculate the top of the atmosphere reflectance | |
| MOD03 | 2014/07/10–2014/08/24 | 55 | Obtain geolocation data | |
| MOD04 | 2014/07/10–2014/08/24 | 55 | Validation |
| Category | EVI | A1 | A2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sparse vegetation | EVI < 0.15 | 0.203 | 0.037 |
| Median vegetation | 0.15 < EVI < 0.60 | 0.438 | 0.173 |
| Dense vegetation | EVI > 0.60 | 0.762 | 0.143 |
| Parameter | Number | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Band | 1 | Band 3 (Blue band) |
| AOD at 550 nm | 15 | 0.0, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.2, 1.5 |
| Surface reflectance | 18 | 0.0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.10, 0.11, 0.12, 0.13, 0.14, 0.15, 0.18, 0.20 |
| Solar zeniths (°) | 14 | 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78 |
| Satellite zeniths (°) | 14 | 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78 |
| Relative azimuths (°) | 19 | 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180 |
| Aerosol Optical Properties | Date/Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 July | 3 August | 4 August | 21 August | |
| Ångström exponent (440–870 nm) | 0.467 | 0.409 | 0.441 | 0.443 |
| Real part of RI | 1.597 | 1.541 | 1.548 | 1.592 |
| Imaginary part of RI | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.010 |
| Site | Count | R | Absolute Error | Relative Error (%) | r (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New | DB | New | DB | New | DB | New | DB | New | DB | |
| Dahuangshan | 32 | 29 | 0.928 | 0.774 | 0.037 | 0.047 | 13.9 | 17.4 | 96.9 | 90.6 |
| Wucaiwan | 26 | 24 | 0.918 | 0.931 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 16.7 | 15.7 | 96.2 | 96.2 |
| Total | 58 | 53 | 0.928 | 0.871 | 0.032 | 0.036 | 15.1 | 16.6 | 96.6 | 92.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Arid or Semiarid Region of Northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020197
Tian X, Liu S, Sun L, Liu Q. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Arid or Semiarid Region of Northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020197
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xinpeng, Sihai Liu, Lin Sun, and Qiang Liu. 2018. "Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Arid or Semiarid Region of Northern Xinjiang, China" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020197
APA StyleTian, X., Liu, S., Sun, L., & Liu, Q. (2018). Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth in the Arid or Semiarid Region of Northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020197