China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
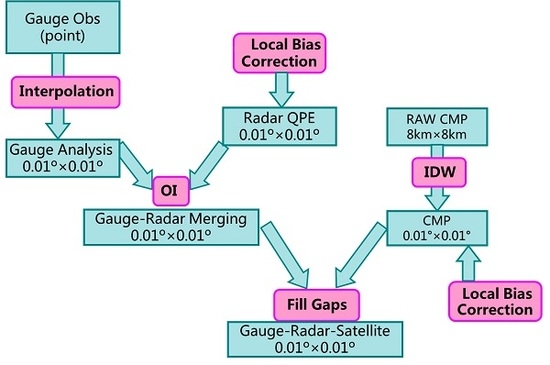
2.1. Merging Data
2.1.1. AWS Hourly Precipitation Observations
2.1.2. Radar-Based QPE
2.1.3. Satellite-Based Precipitation Product
2.2. Independent Ground Observations and Evaluation Criteria
3. Method
3.1. Gauge-Based Precipitation Analysis
3.2. Local Bias Correction
3.3. Parameters in OI-Based Merging Method
3.3.1. Error Variance Estimate for the Radar QPE:
3.3.2. Error Correlation Estimate for the Radar QPE:
3.3.3. Error Estimate for the Observed Field:
3.3.4. Error Correlation for the Observed Field:
4. Result
4.1. The Result of LGC
4.2. Evaluation of the CMPA_1km
4.2.1. Selection of Matching Data Pairs
4.2.2. Evaluations in Heavy Rainfall Events
4.2.3. Evaluations in Summer and Winter Seasons
4.2.4. Evaluations over Different Regions
4.2.5. Evaluations of Precipitation Area
5. Conclusions and Future Research Recommendations
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, M.; Liu, R.; Wen, Y.; Hong, Y. Can near-real-time satellite precipitation products capture rainstorms and guide flood warning for the 2016 summer in South China? IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, A.L.; Mullen, S.L. Spatiotemporal variability of hourly precipitation over the eastern contiguous United States from stage iv multisensor analyses. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battan, L.J. Radar observations of the atmosphere. Atmos. Phys. 1973, 99, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. Cmorph 8 km: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Joyce, R.; Wu, S.; Yoo, S.H.; Yarosh, Y.; Sun, F.; Lin, R. Reprocessed, bias-corrected cmorph global high-resolution precipitation estimates from 1998. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1617–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Tang, L.; Sapiano, M.; Maggioni, V.; Wu, H. Modeling errors in daily precipitation measurements: Additive or multiplicative? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Krajewski, W.F. Estimation of the mean field bias of radar rainfall estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 30, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Breidenbach, J.P. Real-time correction of spatially nonuniform bias in radar rainfall data using rain gauge measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumchean, S.; Seed, A.; Sharma, A. Correcting of real-time radar rainfall bias using a kalman filtering approach. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.A.; Adler, R.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.; Bowman, K.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, T.; Wolff, D. The trmm multi-satellite precipitation analysis (tmpa): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.D.; Peterslidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B. Real-time bias reduction for satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Xiong, A.Y. A conceptual model for constructing high-resolution gauge-satellite merged precipitation analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S. Multi-radar multi-sensor (mrms) quantitative precipitation estimation: Initial operating capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Vasiloff, S.; Kaney, B.; Arthur, A.; Van Cooten, S.; Kelleher, K.; Kitzmiller, D.; Ding, F. National mosaic and multi-sensor qpe (nmq) system: Description, results, and future plans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 92, 1321–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Anagnostou, E.; Kalogiros, J.; Anagnostou, M. Passive microwave rainfall error analysis using high-resolution x-band dual-polarization radar observations in complex terrain. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 12–17 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostou, M.N.; Kalogiros, J.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Derin, Y.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Satellite Rainfall Error Analysis with the Use of High-Resolution X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar Observations over the Italian Alps; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Shen, Y.; Du, Z. Tracing the source of the errors in hourly imerg using a decomposition evaluation scheme. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihua, R.; Ping, Z.; Qiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, L.; Yang, Y.; Zou, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhe, C.; et al. Quality control procedures for hourly precipitation data from automatic weather stations in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 36, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Jun, L.I.; Xiaohui, J.U.; Zhao, Y.; Zhipeng, L.I.; Zhang, W.; Hongkang, L.I. Development of three-step quality control system of real-time observation data from aws in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2015, 41, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, Y. Cinrad radar quantitative precipitation estimation group system. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 4, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Simanton, J.R.; Osborn, H.B. Reciprocal-distance estimate of point rainfall. J. Hydraul. Div. 1980, 106, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Yatagai, A.; Chen, M.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. A gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, L.S. Objective Analysis of Meteorological Fields; Gidromet: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 1963; 242p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Shi, W.; Xie, P.; Silva, V.B.S.; Kousky, V.E.; Wayne Higgins, R.; Janowiak, J.E. Assessing objective techniques for gauge-based analyses of global daily precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Neilson, R.P.; Phillips, D.L. A statistical-topographic model for mapping climatological precipitation over mountainous terrain. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pei, C.; Guo, Z. Evaluations on Chinese next generation radars coverage and terrain blockage based on srtm data. Clim. Environ. Res. 2011, 16, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.L.; Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S. Uncertainty quantification of satellite precipitation estimation and monte carlo assessment of the error propagation into hydrologic response. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 2643–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Xu, X.D. Regional characteristics of the interdecadal turning of winter/summer climate modes in Chinese mainland. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciach, G.J.; Krajewski, W.F.; Villarini, G. Product-error-driven uncertainty model for probabilistic quantitative precipitation estimation with nexrad data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1325–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Kitzmiller, D.; Wu, S. Evaluation of radar precipitation estimates from the national mosaic and multisensor quantitative precipitation estimation system and the wsr-88d precipitation processing system over the conterminous United States. J. Jpn. Soc. Hydrol. Water Resour. 2012, 13, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J. The global precipitation measurement (gpm) mission: An overview. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Hong, Y.; Yu, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Saharia, M. Uncertainty analysis of five satellite-based precipitation products and evaluation of three optimally merged multi-algorithm products over the tibetan plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6843–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| MWR Precip. (mm/d) | Benchmark Precip. (mm/d) | CC | RMSE (mm/d) | Bias (mm/d) | Sample Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean | 3.365 | 3.728 | 0.857 | 5.686 | −0.362 | 74,390 |
| Warm Season (May–September) | 5.092 | 5.469 | 0.839 | 7.803 | −0.376 | 31,249 |
| Cold Season (October–April) | 2.114 | 2.467 | 0.895 | 3.412 | −0.352 | 43,141 |
| ≥ Threshold | < Threshold | |
|---|---|---|
| g ≥ Threshold | Hits (H) | Misses (M) |
| g < Threshold | False alarms (F) | Correct negatives (C) |
| a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05° | 2.73 | 1.13 | 0.28 |
| 0.10° | 2.43 | 1.08 | 0.17 |
| 0.25° | 1.74 | 1.19 | 0.31 |
| Radar QPE | CMORPH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without LGC | With LGC | Without LGC | With LGC | |
| Bias (mm/h) | −0.340 | 0.095 | −0.108 | 0.208 |
| Relative Bias (%) | −18.3 | 5.100 | −5.400 | 10.400 |
| RMSE (mm/h) | 4.447 | 2.219 | 4.931 | 2.798 |
| CC | 0.424 | 0.879 | 0.324 | 0.828 |
| CC | RMSE (mm/6 h) | Bias (mm/6 h) | Relative Bias (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge Analysis | 0.843 | 2.643 | 0.506 | 44.61 |
| Radar QPE | 0.512 | 3.687 | −0.374 | −32.95 |
| CMORPH | 0.474 | 3.904 | 0.058 | 5.15 |
| CMPA-1km | 0.882 | 2.158 | 0.263 | 23.19 |
| NSSL MRMS (1 km) | 0.855 | 2.1 | --- | --- |
| Winter (December–February) | Summer (June–August) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RMSE (mm/6 h) | Bias (mm/6 h) | Relative Bias (%) | CC | RMSE (mm/6 h) | Bias (mm/6 h) | Relative Bias (%) | |
| Gauge Analysis | 0.8705 | 1.1189 | 0.0660 | 12.04 | 0.9418 | 1.7984 | −0.0146 | −1.37 |
| Radar QPE | 0.6789 | 1.7950 | 0.0246 | 4.48 | 0.7416 | 3.8509 | −0.3727 | −35.11 |
| CMORPH | 0.4473 | 1.9252 | −0.3461 | −63.15 | 0.5324 | 5.1322 | 0.1300 | 12.24 |
| CMPA-1km | 0.7998 | 1.4468 | 0.1006 | 18.36 | 0.9257 | 2.0446 | −0.0500 | −4.71 |
| Winter (December–February) | Summer (June–August) | |||||||
| ETS | TS | POD | FAR | ETS | TS | POD | FAR | |
| Gauge Analysis | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 0.15 |
| Radar QPE | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.29 |
| CMORPH | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.44 |
| CMPA-1km | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.18 |
| Region I | Winter (December–February) | Summer (June–August) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | |
| (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | |||||
| Gauge analysis | -- | 0.163 | 0.015 | -- | 0.926 | 1.268 | −0.052 | −7.37 |
| Radar QPE | -- | 1.076 | 0.093 | -- | 0.715 | 2.311 | −0.147 | −20.86 |
| CMORPH | -- | 0.000 | 0.000 | -- | 0.575 | 2.736 | −0.083 | −11.77 |
| CMPA-1km | -- | 1.077 | 0.098 | -- | 0.898 | 1.449 | 0.008 | 1.19 |
| Region II | Winter (December–February) | Summer (June–August) | ||||||
| CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | |
| (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | |||||
| Gauge analysis | 0.725 | 0.165 | 0.013 | 58.94 | 0.896 | 1.741 | −0.060 | −7.98 |
| Radar QPE | 0.612 | 0.213 | 0.025 | 111.80 | 0.777 | 2.544 | −0.091 | −12.00 |
| CMORPH | 0.033 | 0.318 | −0.002 | −7.64 | 0.455 | 4.368 | 0.198 | 26.13 |
| CMPA-1km | 0.704 | 0.178 | 0.017 | 75.53 | 0.872 | 1.934 | −0.061 | −8.07 |
| Region III | Winter (December–February) | Summer (June–August) | ||||||
| CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | CC | RMSE | Bias | Relative Bias (%) | |
| (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | (mm/6 h) | |||||
| Gauge analysis | 0.916 | 1.090 | 0.093 | 11.01 | 0.953 | 1.872 | 0.017 | 1.32 |
| Radar QPE | 0.746 | 1.904 | 0.003 | 0.36 | 0.743 | 4.550 | −0.560 | −43.89 |
| CMORPH | 0.474 | 2.313 | −0.529 | −62.41 | 0.554 | 5.698 | 0.111 | 8.70 |
| CMPA-1km | 0.877 | 1.366 | 0.127 | 14.93 | 0.939 | 2.155 | −0.048 | −3.73 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Hong, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.; Maguire, L. China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020264
Shen Y, Hong Z, Pan Y, Yu J, Maguire L. China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020264
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yan, Zhen Hong, Yang Pan, Jingjing Yu, and Lane Maguire. 2018. "China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020264
APA StyleShen, Y., Hong, Z., Pan, Y., Yu, J., & Maguire, L. (2018). China’s 1 km Merged Gauge, Radar and Satellite Experimental Precipitation Dataset. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020264