Siamese-GAN: Learning Invariant Representations for Aerial Vehicle Image Categorization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Feature Extraction
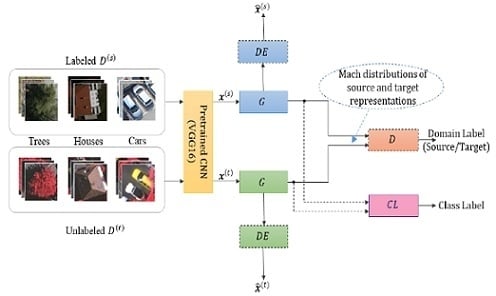
3.2. Siamese-GAN Architecture
3.3. Network Optimization
| Algorithm. Siamese-GAN. |
| Input: Source images: and target images: |
| Output: Target class labels |
|
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets Used for Creating the Cross-Domain Datasets
4.2. Cross-Domain Datasets Description
4.3. Experimental Setup
4.4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikäinen, M.; Harwood, D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognit. 1996, 29, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, Y. Pyramid of spatial relatons for scene-level land use classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L. Bag-of-visual-words scene classifier with local and global features for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Li, W.; Chen, C.; Du, Q. Scene classification using local and global features with collaborative representation fusion. Inf. Sci. (Ny) 2016, 348, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Tang, P.; Huo, L.Z. Land-use scene classification using a concentric circle-structured multiscale bag-of-visual-words model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4620–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriyadat, A.M. Unsupervised feature learning for aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhalfi, M.L.; Melgani, F.; Bazi, Y.; Alajlan, N. Land-use classification with compressive sensing multifeature fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, L. Scene classification based on the multifeature fusion probabilistic topic model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6207–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Bu, S.; Ren, J. Effective and efficient midlevel visual elements-oriented land-use classification using vhr remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4238–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, C.; Tan, Y.; Shang, K.; Tian, J. Unsupervised multilayer feature learning for satellite image scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H. Unsupervised feature learning via spectral clustering of multidimensional patches for remotely sensed scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L. Dirichlet-derived multiple topic scene classification model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2108–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Dahl, G.E.; Hinton, G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, P.J.S.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Quirita, V.H.A.; Happ, P.N. Single sample face recognition from video via stacked supervised auto-encoder. In Proceedings of the 29th Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI) Conference, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 4–7 October 2016; pp. 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Brosch, T.; Tam, R. Efficient training of convolutional deep belief networks in the frequency domain for application to high-resolution 2D and 3D Images. Neural Comput. 2015, 27, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S. Deep reconstruction models for image set classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, G.E. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 1096–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Farabet, C.; Couprie, C.; Najman, L.; LeCun, Y. Learning hierarchical features for scene labeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luus, F.P.S.; Salmon, B.P.; van den Bergh, F.; Maharaj, B.T.J. Multiview deep learning for land-use classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2448–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Ni, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q. Deep Learning based feature selection for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Su, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J. Deep filter banks for land-use scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Scene classification via a gradient boosting random convolutional network framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, G.J.; England, M.R.; Starms, W.A.; Marcum, R.A.; Davis, C.H. Training deep convolutional neural networks for land-cover classification of high-resolution imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, K.; Penatti, O.A.B.; dos Santos, J.A. Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmanis, D.; Datcu, M.; Esch, T.; Stilla, U. Deep learning earth observation classification using imagenet pretrained networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.; Bazi, Y.; Alajlan, N.; Alhichri, H.; Melgani, F. Using convolutional features and a sparse autoencoder for land-use scene classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1977–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fan, B.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Aggregating rich hierarchical features for scene classification in remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. EARTH Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4104–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Mao, Z.; Lin, J.; Guo, W. Land-use classification via extreme learning classifier based on deep convolutional features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaib, S.; Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Yao, H. Deep feature fusion for VHR remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4775–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.; Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F.; Alhichri, H.; Alajlan, N.; Zuair, M. Domain adaptation network for cross-scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4441–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1784 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Tan, W.R.; Chan, C.S.; Aguirre, H.; Tanaka, K. ArtGAN: Artwork Synthesis with Conditional Categorial Gans. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.03410 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Metaxas, D. Stackgan: Text to Photo-Realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03242 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04802 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Lin, D.; Fu, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Sun, X. MARTA GANs: Unsupervised representation learning for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Generative Adversarial networks-based semi-supervised learning for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, P.L.; Sappa, A.D.; Vintimilla, B.X. Infrared image colorization based on a triplet DCGAN architecture. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Skinner, K.A.; Eustice, R.M.; Johnson-Roberson, M. WaterGAN: Unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Tuzel, O. Coupled Generative Adversarial Networks. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.07536 (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Tzeng, E.; Hoffman, J.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.05464 (accessed on 17 February 2017).
- Bousmalis, K.; Silberman, N.; Dohan, D.; Erhan, D.; Krishnan, D. Unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1612.05424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Kou, L.; Zhang, D. Learning domain-invariant subspace using domain features and independence maximization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Feng, J.; Saenko, K. Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, Arizona, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 2058–2065. [Google Scholar]













| Class | Number of Images per Dataset of Size: 224 × 224 Pixels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto | Trento | Vaihingen | Potsdam | |
| Trees | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Grass | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Houses | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Bare soil | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Roads | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Cars | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Water | 120 | - | 120 | 120 |
| Solar Panels | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Train Tracks | 120 | 120 | 120 | - |
| Total | 1080 | 960 | 1080 | 960 |
| Datasets | SVM | NN | Siamese-GAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto→Vaihingen | 63.89 | 64.72 | 82.69 |
| Toronto→Potsdam | 68.96 | 69.17 | 84.27 |
| Toronto→Trento | 68.65 | 70.94 | 91.46 |
| Vaihingen→Toronto | 65.64 | 67.41 | 88.98 |
| Vaihingen→Potsdam | 61.35 | 65.10 | 88.33 |
| Vaihingen→Trento | 61.88 | 71.77 | 91.46 |
| Potsdam→Toronto | 72.19 | 70.83 | 92.71 |
| Potsdam→Vaihingen | 84.48 | 78.75 | 98.44 |
| Potsdam→Trento | 86.55 | 80.24 | 87.62 |
| Trento→Toronto | 68.23 | 70.21 | 91.56 |
| Trento→Vaihingen | 67.40 | 69.90 | 98.75 |
| Trento→Potsdam | 73.57 | 70.83 | 87.86 |
| AA [%] | 70.23 | 70.82 | 90.34 |
| Datasets | Regularization Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | |
| Toronto→Vaihingen | 75.74 | 78.06 | 85.74 | 83.06 | 83.61 | 82.69 |
| Toronto→Potsdam | 73.85 | 83.85 | 84.27 | 84.58 | 86.56 | 84.27 |
| Toronto→Trento | 73.12 | 91.98 | 92.4 | 91.46 | 92.08 | 91.46 |
| Vaihingen→Toronto | 72.96 | 88.24 | 88.52 | 89.16 | 88.06 | 88.98 |
| Vaihingen→Potsdam | 67.5 | 88.65 | 87.6 | 88.33 | 88.54 | 88.33 |
| Vaihingen→Trento | 78.75 | 84.79 | 92.71 | 92.6 | 91.98 | 91.46 |
| Potsdam→Toronto | 76.25 | 91.98 | 91.76 | 92.5 | 93.23 | 92.71 |
| Potsdam→Vaihingen | 90.83 | 98.12 | 98.23 | 98.12 | 98.54 | 98.44 |
| Potsdam→Trento | 85 | 85.83 | 87.02 | 87.02 | 87.14 | 87.62 |
| Trento→Toronto | 76.15 | 91.46 | 91.77 | 92.7 | 91.04 | 91.56 |
| Trento→Vaihingen | 87.6 | 98.12 | 98.65 | 98.44 | 98.85 | 98.75 |
| Trento→Potsdam | 76.9 | 89.76 | 89.52 | 88.57 | 89.05 | 87.86 |
| AA [%] | 77.89 | 89.24 | 90.68 | 90.55 | 90.72 | 90.34 |
| Datasets | Mini-Batch Size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | |
| Toronto→Vaihingen | 74.9 | 78.06 | 86.67 | 93.06 | 91.57 | 82.69 |
| Toronto→Postdam | 70.1 | 79.79 | 85.1 | 86.77 | 84.27 | 84.27 |
| Toronto→Trento | 71.67 | 83.44 | 90.73 | 93.02 | 85.83 | 91.46 |
| Vaihingen→Toronto | 73.15 | 78.98 | 88.8 | 89.44 | 89.07 | 88.98 |
| Vaihingen→Postdam | 62.5 | 71.15 | 86.04 | 87.29 | 86.77 | 88.33 |
| Vaihingen→Trento | 72.5 | 86.25 | 93.75 | 86.25 | 84.16 | 91.46 |
| Postdam→Toronto | 72.81 | 87.29 | 90.52 | 92.19 | 93.02 | 92.71 |
| Postdam→Vaihingen | 84.48 | 96.56 | 98.23 | 97.92 | 98.44 | 98.44 |
| Postdam→Trento | 72.62 | 83.57 | 89.17 | 88.33 | 87.74 | 87.62 |
| Trento→Toronto | 55.63 | 89.48 | 91.04 | 91.46 | 91.46 | 91.56 |
| Trento→Vaihingen | 75.83 | 97.7 | 97.19 | 97.5 | 98.75 | 98.75 |
| Trento→Postdam | 73.45 | 81.67 | 88.81 | 90.36 | 87.74 | 87.86 |
| AA [%] | 71.47 | 84.50 | 90.50 | 91.13 | 89.90 | 90.34 |
| Time [minutes] | 15.82 | 8.57 | 4.83 | 3.71 | 3.05 | 2.84 |
| Datasets | DAN | CORAL | MIDA | ADDA | Siamese-GAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto→Vaihingen | 90.00 | 74.25 | 70.00 | 68.51 | 82.69 |
| Toronto→Potsdam | 79.89 | 72.81 | 70.83 | 73.22 | 84.27 |
| Toronto→Trento | 88.12 | 83.12 | 66.77 | 72.08 | 91.46 |
| Vaihingen→Toronto | 77.59 | 79.35 | 77.50 | 77.87 | 88.98 |
| Vaihingen→Potsdam | 91.14 | 81.66 | 81.04 | 76.04 | 88.33 |
| Vaihingen→Trento | 82.08 | 77.50 | 75.10 | 69.27 | 91.46 |
| Potsdam→Toronto | 88.54 | 72.70 | 76.14 | 75.41 | 92.71 |
| Potsdam→Vaihingen | 84.06 | 86.00 | 88.43 | 82.49 | 98.44 |
| Potsdam→Trento | 87.14 | 84.28 | 86.04 | 86.91 | 87.62 |
| Trento→Toronto | 86.77 | 82.39 | 72.91 | 79.68 | 91.56 |
| Trento→Vaihingen | 84.68 | 80.41 | 81.56 | 79.58 | 98.75 |
| Trento→Potsdam | 85.83 | 82.26 | 79.76 | 75.71 | 87.86 |
| AA [%] | 85.48 | 79.72 | 77.17 | 76.39 | 90.34 |
| Time [minutes] | 7.18 | 2.54 | 1.77 | 3.03 | 2.84 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bashmal, L.; Bazi, Y.; AlHichri, H.; AlRahhal, M.M.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N. Siamese-GAN: Learning Invariant Representations for Aerial Vehicle Image Categorization. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020351
Bashmal L, Bazi Y, AlHichri H, AlRahhal MM, Ammour N, Alajlan N. Siamese-GAN: Learning Invariant Representations for Aerial Vehicle Image Categorization. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleBashmal, Laila, Yakoub Bazi, Haikel AlHichri, Mohamad M. AlRahhal, Nassim Ammour, and Naif Alajlan. 2018. "Siamese-GAN: Learning Invariant Representations for Aerial Vehicle Image Categorization" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020351
APA StyleBashmal, L., Bazi, Y., AlHichri, H., AlRahhal, M. M., Ammour, N., & Alajlan, N. (2018). Siamese-GAN: Learning Invariant Representations for Aerial Vehicle Image Categorization. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020351