Investigating Subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Datasets and Methodology
3.1. InSAR Datasets
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. PS-InSAR Processing Methodology
3.2.2. Decomposition of Sentinel-1 Data into 2D Displacement Rates
4. Results
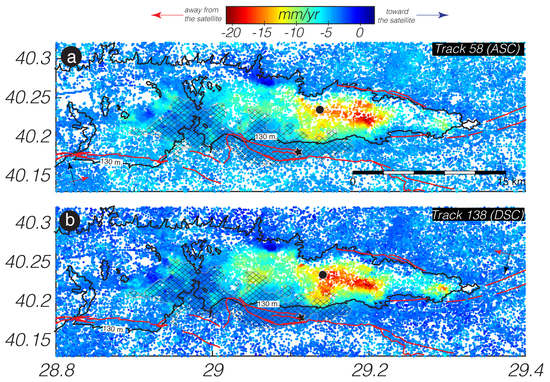
InSAR-Derived Land Subsidence Maps
5. Discussion
5.1. Self-Consistency Checking between the Ascending and Descending InSAR Observations
5.2. Water Table Variations and InSAR Time Series
5.3. Compressibility of the Aquifer in the Bursa Plain
5.4. Lithological and Tectonic Control over Land Subsidence
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kutoglu, H.S.; Kemaldere, H.; Deguchıi, T.; Berber, M. Discovering a pull-apart basin using InSAR in Bursa, Turkey. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunori, C.A.; Bignami, C.; Albano, M.; Zucca, F.; Samsonov, S.; Groppelli, G.; Norini, G.; Saroli, M.; Stramondo, S. Land subsidence, Ground Fissures and Buried Faults: InSAR Monitoring of Ciudad Guzmán (Jalisco, Mexico). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8610–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G.; Tomás, R.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Ruiz Hernández, J.M.; Fernández Merodo, J.A.; Marchamalo, M.; Martínez, R. Mapping groundwater level and aquifer storage variations from InSAR measurements in the Madrid aquifer, Central Spain. J. Hydrol. 2017, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. PSInSAR analysis in the Pisa Urban Area (Italy): A case study of subsidence related to stratigraphical factors and urbanization. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Farolfi, G.; Rosi, A.; Raspini, F.; Casagli, N. Subsidence Evolution of the Firenze–Prato–Pistoia Plain (Central Italy) Combining PSI and GNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Wang, C.T.; Chu, C.Y.; Kao, J.R. Mapping geo-hazard by satellite radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 2835–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Martínez, J.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Hernández-Marín, M.; Ortiz-Lozano, J.Á.; Zermeño-de-León, M.E. Application of insar and gravimetry for land subsidence hazard zoning in Aguascalientes, Mexico. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17035–17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.P.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Azañón, J.M.; Closson, D.; Caló, F.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Jabaloy, A.; Ruano, P.; Mateos, R.M.; Notti, D.; et al. Evaluation of the SBAS InSAR Service of the European Space Agency’s Geohazard Exploitation Platform (GEP). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Solari, L.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Monserrat, O.; Bianchini, S.; Herrera, G.; Crosetto, M.; Sarro, R.; González-Alonso, E.; Mateos, R.M.; et al. A Methodology to Detect and Update Active Deformation Areas Based on Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitoun, D.G.; Wakshal, E. The Subsidence Phenomenon throughout the World in Land Subsidence Analysis in Urban Areas: The Bangkok Metropolitan Area Case Study; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2013; pp. 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changxing, S.; Dian, Z.; Lianyuan, Y.; Bingyuan, L.; Zulu, Z.; Ouyang, Z. Land subsidence as a result of sediment consolidation in the Yellow River Delta. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evinemi, I.E.; Adepelumi, A.A.; Adebayo, O. Canal structure subsidence investigation using ground penetrating radar and geotechnical techniques. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnqvist, T.E.; Wallace, D.J.; Storms, J.E.; Wallinga, J.; Van Dam, R.L.; Blaauw, M.; Derksen, M.S.; Cornelis, J.W.; Meijneken, C.; Snijders, E.M.A. Mississippi Delta subsidence primarily caused by compaction of Holocene strata. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asselen, S. The contribution of peat compaction to total basin subsidence: Implications for the provision of accomodation space in organic-rich deltas. Basin Res. 2011, 23, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.L. Present situation of land subsidence and its mechanism in China. Global View of Engineering Geology and the Environment. In Proceedings of the International Symposium and 9th Asian Regional Conference of IAEG (AREG2013), Beijing, China, 24–25 September 2013; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR measurements of compaction and subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Quiroz, P.; Doin, M.P.; Tupin, F.; Briole, P.; Nicolas, J.M. Time series analysis of Mexico City subsidence constrained by radar interferometry. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.K.; Doubre, C.; Weber, C.; Gourmelen, N.; Masson, F. Recent land subsidence caused by the rapid urban development in the Hanoi region (Vietnam) using ALOS InSAR data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitelli, G.; Bonsignore, F.; Unguendoli, M. Levelling and GPS networks to monitor ground subsidence in the Southern Po Valley. J. Geodyn. 2000, 30, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.P.; Abe, K.; Ootaki, O. GPS-measured land subsidence in Ojiya city, Niigata prefecture, Japan. Eng. Geol. 2003, 67, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourmelen, N.; Amelung, F.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. Mining-related ground deformation in Crescent Valley, Nevada: Implications for sparse GPS networks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, C.J.; Alley, W.M. Ground-Water-Level Monitoring and the Importance of Long-Term Water-Level Data (No. 1217-2002); US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ireland, R.L.; Poland, J.F.; Riley, F.S. Land Subsidence in the San Joaquin Valley, California, as of 1980; US Geological Survey Professional, US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Poland, J.F. Guidebook to Studies of Land Subsidence Due to Ground-Water Withdrawal; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Evseev, A.; Asanov, V.; Lomakin, I.; Tsayukov, A. Experimental and theoretical studies of undermined strata deformation during room and pillar mining. In Geomechanics and Geodynamics of Rock Masses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Carbognin, L.; Brancolini, G. Using high resolution data to reveal depth-dependent mechanisms that drive land subsidence: The Venice coast, Italy. Tectonophysics 2009, 474, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, M.L.; Panda, B.B.; Meyers, R.A.; Lommler, J.C. Using InSAR to detect subsidence at brine wells, sinkhole sites, and mines. Carbonates Evaporites 2013, 28, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, C.R.; Mei, S. Mapping and monitoring coal mine subsidence using LiDAR and InSAR. In Proceedings of the GeoEdmonton2008, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 1127–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Zebker, H.A.; Goldstein, R.M. Topographic mapping from interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 4993–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rabaute, T. Radar interferometry: Limits and potential. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Holzer, T.; Vadon, H. Land subsidence caused by the East Mesa geothermal field, California, observed using SAR interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, E.J.; Blom, R.G.; Goldstein, R.M. Rapid subsidence over oil fields measured by SAR interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3215–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, P.; Stow, R. Detecting mining subsidence from space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Wdowinski, S.; Dixon, T.H.; Amelung, F.; Kim, J.W.; Won, J.S. Measurements and predictions of subsidence induced by soil consolidation using persistent scatterer InSAR and a hyperbolic model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslan, G.; Cakır, Z.; Ergintav, S.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Analysis of Secular Ground Motions in Istanbul from a Long-Term InSAR Time-Series (1992–2017). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnec, C.; Delacourt, C. Three years of mining subsidence monitored by SAR interferometry, near Gardanne, France. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikan, S.; Arıkan, M.; Sanli, F.B.; Çakir, Z. Monitoring of coal mining subsidence in peri-urban area of Zongundak city (NWTurkey) with persistent scatterer interferometry using ALOS-PALSAR. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykhus, R.P.; Lu, Z. InSAR detects possible thaw settlement in the Alaskan Arctic Coastal Plain. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 34, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temtime, T.; Biggs, J.; Lewi, E.; Hamling, I.; Wright, T.; Ayele, A. Spatial and temporal patterns of deformation at the Tendaho geothermal prospect, Ethiopia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 357, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baer, G.; Magen, Y.; Nof, R.N.; Raz, E.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Shalev, E. InSAR Measurements and Viscoelastic Modeling of Sinkhole Precursory Subsidence: Implications for Sinkhole Formation, Early Warning, and Sediment Properties. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Zebker, H.; Galloway, D.; Amelung, F. Seasonal subsidence and rebound in Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Herrera, G.; Delgado, J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Mulas, J. A ground subsidence study based on DInSAR data: Calibration of soil parameters and subsidence prediction in Murcia City (Spain). Eng. Geol. 2009, 111, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderhead, A.I.; Therrien, R.; Rivera, A.; Martel, R.; Garfias, J. Simulating pumping-induced regional land subsidence with the use of InSAR and field data in the Toluca Valley, Mexico. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G.; Marchamalo, M.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Martínez, R. A quasi-elastic aquifer deformational behavior: Madrid aquifer case study. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turkish Statistical Institute, TUIK. Available online: http://www.tuik.gov.tr/HbGetirHTML.do?id=27587 (accessed on 26 November 2018).
- Serbetci, Z. Examination of Agro-Tourism Potential: Bursa Plain Plain. J. Int. Soc. Res. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, H.H.; Tüysüz, O. The Bursa–Gönen Depression, NW Turkey: A complex basin developed on the North Anatolian Fault. Geol. Mag. 2013, 150, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, H.H.; Tüysüz, O.; Karakaş, A.; Taş, K.Ö. Morphotectonic evidence from the southern branch of the North Anatolian Fault (NAF) and basins of the south Marmara sub-region, NW Turkey. Quat. Int. 2013, 292, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursa Environment Project Report on Hydrology and Water Quality Modelling; Institute of Hydrology: Wallingford, UK, 1991; p. 14.
- Gok, E.; Polat, O. An assessment of the seismicity of the Bursa region from a temporary seismic network. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenlohr, T. Die Thermalwässer der ArmutluHalbinsel (NW-Türkei) und deren Beziehung zu Geologie und aktiver Tektonik. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH-Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 1995; p. 11340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbach, T. Deep groundwater circulation in the tectonically active area of Bursa, Northwest Anatolia, Turkey. Geothermics 1997, 26, 251–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, N.; Akıncı, A.; Eyidogan, H. Site amplification of S-waves in Bursa City and its vicinity, Northwestern Turkey: Comparison of different approaches. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, Ö.; Duman, T.Y.; Özalp, S.; Elmaci, S.; Olgun, S.; Saroglu, F. Active Fault Map of Turkey with and Explanatory Text. In General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration; Special Publication Series-30; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Expansion (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Reilinger, R.; McClusky, S.; Vernant, P.; Lawrence, S.; Ergintav, S.; Cakmak, R.; Ozener, H.; Kadirov, F.; Guliev, I.; Stepanyan, R.; et al. GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- B.U. KOERI-RETMC (Boğaziçi University Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute—Regional Earthquake-Tsunami Monitoring Center)—Earthquake Catalogue. Available online: http://www.koeri.boun.edu.tr/sismo/2/earthquake-catalog/ (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, Bursa, The View of Bursa Plain from the Hills of Mount Uludag. Available online: https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bursa (accessed on 26 November 2018).
- Sandwell, D.; Mellors, R.; Tong, X.; Wei, M.; Wessel, P. Open Radar Interferometry Software for Mapping Surface Deformation. Eos Trans. AGU 2011, 92, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.; Rosen, P.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Alsdorf, D. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A Multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2011, 514, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Walters, R.J.; Wright, T.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Parker, D.J. Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrea, U. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Zhong, L. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Shamshiri, R.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M.; Wetzel, H.U.; Akbari, B.; Nahavandchi, H.; Roessner, S.; Arabi, S. Quantifying groundwater exploitation induced subsidence in the Rafsanjan plain, southeastern Iran, using InSAR time-series and in situ measurements. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focareta, M.; Marcuccio, S.; Votto, C.; Ullo, S.L. Combination of Landsat 8 and Sentinel 1 data for the characterization of a site of interest. A Case Study: The Royal Palace of Caserta. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology, Benevento, Italy, 21–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi, P.; Martel, R.; Rivera, A.; Huang, J.; Pavlic, G.; Calderhead, A.I.; Chaussard, E.; Garfias, J.; Salas, J. Groundwater depletion in Central Mexico: Use of GRACE and InSAR to support water resources management. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5985–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Longuevergne, L.; Martel, R.; Rivera, A.; Brouard, C.; Chaussard, E. Quantitative mapping of groundwater depletion at the water management scale using a combined GRACE/InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; García-Cárdenas, R.P.; Herrera, G.; Barra, A.; López Molina, A.; Tessitore, S.; Staller, A.; Ortega-Becerril, A.J.; García-García, R.P. Interpolation of GPS and geological data using InSAR deformation maps: Method and application to land subsidence in the alto guadalentín aquifer (SE Spain). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zou, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. Vertical Displacements Driven by Groundwater Storage Changes in the North China Plain Detected by GPS Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, F.; Notti, D.; Galve, J.P.; Abdikan, S.; Görüm, T.; Pepe, A.; Balik Şanli, F. Dinsar-based detection of land subsidence and correlation with groundwater depletion in Konya Plain, Turkey. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, K.M.; Bense, V.F. Hydrogeology: Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi, P.; Martel, R.; Galloway, D.L.; Longuevergne, L.; Rivera, A. Assessing groundwater depletion and dynamics using GRACE and InSAR: Potential and limitations. Groundwater 2016, 54, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aslan, G.; Cakir, Z.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Investigating Subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010085
Aslan G, Cakir Z, Lasserre C, Renard F. Investigating Subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleAslan, Gokhan, Ziyadin Cakir, Cécile Lasserre, and François Renard. 2019. "Investigating Subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data" Remote Sensing 11, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010085
APA StyleAslan, G., Cakir, Z., Lasserre, C., & Renard, F. (2019). Investigating Subsidence in the Bursa Plain, Turkey, Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sensing, 11(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010085