Infrared Hyperspectral and Ultraviolet Remote Measurements of Volcanic Gas Plume at MT Etna during IMAGETNA Campaign
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. IMAGETNA Campaign
2.2. Lightweight SIBI Imager
2.3. Filament Imager
2.4. Hyper-Cam LWIR
2.4.1. Instrument Description
2.4.2. Retrieval Methodology
- The additional temperature inside the plume compared to ambient air Δ T plume = 1 K
- The thickness of the plume Tk plume = 400 m
- The altitude of the plume centre (where gas and particulate due to Etna emission is supposed to be maximum) Z plume = 3.2 km
- One scaling factor for the initial profiles of each molecular species (H2O, CO2, O3, N2O, CO, and CH4) except SO2;
- One scaling factor of the SO2 Volume Mixing Ratio (VMR) in the centre of the plume (SO2 VMR outside the plume is fixed at the climatological value), with a linear variation of the VMR from the scaling factor from the centre to the edge;
- Two parameters to consider the spectral dependence of the optical thickness due to particles;
2.5. FTIR Instrument
2.6. UV Camera
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Results of SIBI and Filament Imagers
3.2. Results of Hyper-Cam LWIR
3.2.1. IR Brightness Temperature Spectra: Hyper-Cam LWIR versus FTIR
3.2.2. Hyper-Cam LWIR Data Retrieval
3.2.2.1. Radiance Spectra Retrieved with LARA
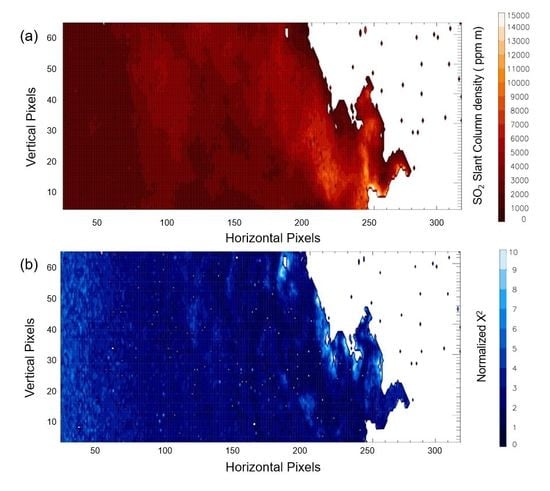
3.2.2.2. SO2 SCD Retrieved from Hyper-Cam LWIR Measurements
3.2.3. Sensitivity Tests on Retrieval Parameters
4. Discussion
UV SO2 SCD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luterbacher, J.; Pfister, C. The year without a summer. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, C.; Fischer, T.P.; Scaillet, B. Volcanic Degassing: Process and Impact. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 111–179. [Google Scholar]
- Robock, A.; Oppenheimer, C. Volcanism and the Earth’s Atmosphere. In Geophysical Monograph Series, 1st ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 139. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, P.J.; Plank, T.; Edmonds, M.; Hairu, E.H. Volatiles in Magmas. In The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes, 2nd ed.; Sigurdsson, H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, P.; Carbonnelle, J.; Dajlevic, D.; Le Bronec, J.; Morel, P.; Robe, M.C.; Maurenas, J.M.; Faivre-Pierret, R.; Martin, D.; Sabroux, J.C.; et al. Eruptive and diffuse emissions of CO2 from Mount Etna. Nature 1991, 351, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Oppenheimer, C.; Allard, P.; Shinohara, H.; Tsanev, V.; Carn, S.; Lardy, M.; Garaebiti, E. First estimate of volcanic SO2 budget for Vanuatu island arc. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2012, 211–212, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Jacob, D.J. Anthropogenic and natural contributions to tropospheric sulfate: A global model analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 18691–18699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graf, H.-F.; Feichter, J.; Langmann, B. Volcanic sulfur emissions: Estimates of source strength and its contribution to the global sulfate distribution. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 10727–10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, D.S.; Johnson, C.E.; Collins, W.J.; Derwent, R.G. The tropospheric sulphur cycle and the role of volcanic SO2. Geol. Soc. 2003, 213, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Minnis, P.; Harrison, E.F.; Stowe, L.L.; Gibson, G.G.; Denn, F.M.; Doelling, D.R.; Smith, W.L., Jr. Radiative Climate Forcing by the Mount Pinatubo Eruption. Science 1993, 259, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carn, S.A.; Clarisse, L.; Prata, A.J. Multi-decadal satellite measurements of global volcanic degassing. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2016, 11, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, B.G.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A.M.; Carn, S.A.; Hermann, M.; Heue, K.-P.; van Velthoven, P.F.J.; Zahn, A. Influence of the 2008 Kasatochi volcanic eruption on sulfurous and carbonaceous aerosol constituents in the lower stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L12813:1–L12813:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tsuda, T.; Vernier, J.-P. Effect of recent minor volcanic eruptions on temperatures in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sol-Terr. Phys. 2015, 129, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, P.; Zanetel, C.; di Sarra, A.; Salerno, G.; Tapparo, A.; Meloni, D.; Pace, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Briole, P.; Legras, B. The impact of Mount Etna sulfur emissions on the atmospheric composition and aerosol properties in the central Mediterranean: A statistical analysis over the period 2000-2013 based on observations and Lagrangian modelling. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, M. New geochemical insights into volcanic degassing. Philos. T. R. Soc. A 2008, 366, 4559–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salerno, G.G.; Burton, M.; Di Grazia, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Oppenheimer, C. Coupling between Magmatic Degassing and Volcanic Tremor in Basaltic Volcanism. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 157:1–157:12. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, A.J.; Elias, T.; Gerlach, T.M.; Stokes, J.B. Implications for eruptive processes as indicated by sulfur dioxide emission from Kïlauea volcano, Hawaii, USA, 1979-1997. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2001, 108, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltabiano, T.; Burton, M.; Giammanco, S.; Allard, P.; Bruno, N.; Muré, F.; Romano, R. Volcanic Gas Emissions from the Summit Craters and Flanks of Mt. Etna, 1987–2000. Geophy. Monog. Ser. 2004, 143, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Galle, B.; Johansson, M.; Rivera, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kihlman, M.; Kern, C.; Lehmann, T.; Platt, U.; Arellano, S.; Hidalgo, S. Network for Observation of Volcanic and Atmospheric Change (NOVAC)—A global network for volcanic gas monitoring: Network layout and instrument description. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D05304:1–D05304:19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.M.; Varey, R.H.; Millán, M.M. Remote sensing of sulphur dioxide. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatt, S.L.; Lane, A.L. A compilation of the absorption cross-section of SO2 from 106 to 403 nm. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1993, 50, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, P.; Carbonnelle, J.; Métrich, N.; Loyer, H.; Zettwoog, P. Sulphur output and magma degassing budget of Stromboli volcano. Nature 1994, 368, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Jones, G.; Stix, J.; Hickson, C. The COSPEC Cookbook: Making SO2 Measurements at Active Volcanoes. In Methods in Volcanology 1; IAVCEI: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb, G.S.; Millan, M.M. Theory, Applications, and Results of the Long-Line Correlation Spectrometer. IEEE T. Geosci. Electron. 1970, 8, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, R.E.; Malinconico, L.L.; Williams, S.N. Use of the correlation spectrometer at volcanoes. In Volcanic Events; Tazieff, H., Sabroux, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 1, pp. 424–444. [Google Scholar]
- Salerno, G.G.; Burton, M.R.; Oppenheimer, C.; Caltabiano, T.; Tsanev, V.I.; Bruno, N. Novel retrieval of volcanic SO2 abundance from ultraviolet spectra. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2009, 181, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluth, G.J.S.; Shannon, J.M.; Watson, I.M.; Prata, A.J.; Realmuto, V.J. Development of an ultra-violet digital camera for volcanic SO2 imaging. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2007, 161, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Burton, M. The SO2 camera: A simple, fast and cheap method for ground-based imaging of SO2 in volcanic plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24804:1–L24804:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Lübcke, P.; Kuhn, J.; Bobrowski, N.; Prata, F.; Burton, M.; Kern, C. Quantitative imaging of volcanic plumes—Results, needs, and future trends. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2015, 300, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.; Burton, M.; Oppenheimer, C. Remote measurements of volcanic gas compositions by solar occultation spectroscopy. Nature 1998, 396, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S.P.; Goff, F.; Counce, D.; Siebe, C.; Delgado, H. Passive infrared spectroscopy of the eruption plume at Popocatepetl volcano, Mexico. Nature 1998, 396, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spina, A.; Burton, M.; Salerno, G.G. Unravelling the processes controlling gas emissions from the central and northest craters of Mt Etna. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2010, 198, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notsu, K.; Mori, T.; Igarashi, G.; Tohjima, Y.; Wakita, H. Infrared spectral radiometer: A new tool for remote measurement of SO2 of volcanic gas. Geochem. J. 1993, 27, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J.; Bernardo, C. Retrieval of volcanic ash particle size, mass and optical depth from a ground-based thermal infrared camera. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2009, 186, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, P.; Burton, M.; Muré, F. Spectroscopic evidence for a lava fountain driven by previously accumulated magmatic gas. Nature 2005, 433, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spina, A.; Burton, M.; Allard, P.; Alparone, S.; Muré, F. Open-path FTIR spectroscopy of magma degassing processes during eight lava fountains on Mount Etna. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 2015, 413, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.E.; Watson, I.M. Observations of volcanic emissions from space: current and future perspectives. Nat. Hazards 2010, 54, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, N.; Campion, R.; Clarisse, L.; Brenot, H.; van Gent, J.; Dils, B.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Coheur, P.-F.; Van Roozendael, M.; et al. Volcanic SO2 fluxes derived from satellite data: a survey using OMI, COME-2, IASI and MODIS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5945–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J.; Bernardo, C. Retrieval of sulfur dioxide from a ground-based thermal infrared imaging camera. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2807–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrieli, A.; Porter, J.N.; Wright, R.; and Lucey, P.G. Validating the accuracy of SO2 gas retrievals in the thermal infrared (8-14 µm). Bull. Volcanol. 2017, 79, 80:1–80:18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briottet, X.; Boucher, Y.; Dimmeler, A.; Malaplate, A.; Cini, A.; Diani, M.; Bekman, H.; Scwering, P.; Skauli, T.; Kasen, I.; et al. Military applications of hyperspectral imagery. In Proceedings of the Targets and Backgrounds XII: Characterization and Representation, Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando (Kissimmee), FL, USA, 17–21 April 2006; Volume 6239, pp. 62390B:1–62390B:8. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl-Vallon, F.; Riese, M.; Maucher, G.; Lengel, A.; Hase, F.; Preusse, P.; Spang, R. Instrument concept and preliminary performance analysis of GLORIA. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riese, M.; Oelhaf, H.; Preusse, P.; Blank, J.; Ern, M.; Friedl-Vallon, F.; Fischer, H.; Guggenmoser, T.; Höpfner, M.; Hoor, P.; et al. Gimballed Limb Observer for Radiance Imaging of the Atmosphere (GLORIA) scientific objectives. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ungermann, J.; Kaufmann, M.; Hoffmann, L.; Preusse, P.; Oelhaf, H.; Friedl-Vallon, F.; Riese, M. Towards a 3-D tomographic retrieval for the air-borne limb-imager GLORIA. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1647–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pola Fossi, A.; Ferrec, Y.; Roux, N.; D’almeida, O.; Guerineau, N.; Sauer, H. Miniature and cooled hyperspectral camera for outdoor surveillance applications in the mid-infrared. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1901–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakat, E.; Vincent, G.; Rommeluère, S.; Eradès, C.; Lefebvre, S.; Cauty, F.; Collin, S.; Druart, G.; Pelouard, J.-L.; Haïdar, R. Analysis of propellant combustion with real-time multispectral infrared camera. In Proceedings of the Infrared Technology and Applications XXXIX, International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE Defense Security and Sensing, Baltimore, ML, USA, 29 April–3 May 2013; Volume 8704, pp. 87042R:1–87042R:5. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, P.; Savary, S.; Rolland, M.; Villemaire, A.; Chamberland, M.; Farley, V.; Brault, L.; Giroux, J.; Allard, J.-L.; Dupuis, E.; et al. Standoff gas identification and quantification from turbulent stack plumes with an imaging Fourier-transform spectrometer. In Proceedings of the Advanced Environmental, Chemical, and Biological Sensing Technologies VII, SPIE Defense Security and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7673, pp. 76730H:1–76730H:12. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrec, Y. Spectro-imagerie aéroportée par transformation de Fourier avec un interféromètre statique à décalage latéral: réalisation et mise en oeuvre. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris Sud, Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.; Abrams, M.; Brault, J. Fourier Transform Spectrometry; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Pola Fossi, A. Miniaturisation d’une caméra hyperspectrale infrarouge. Ph.D. Thesis, Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales, Université Paris, Palaiseau, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shogenji, R.; Kitamura, Y.; Yamada, K.; Miyatake, S.; Tanida, J. Multispectral imaging using compact compound optics. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakat, E.; Vincent, G.; Ghenuche, P.; Bardou, N.; Dupuis, C.; Collin, S.; Pardo, F.; Haïdar, R.; Pelouard, J.-L. Free-standing guided-mode resonance band-pass filters: from 1D to 2D structures. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 13082–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payan, S.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Jeseck, P.; Hawat, T.; Durry, G.; Lefèvre, F. First direct simultaneous HCl and ClONO2 profile measurements in the Arctic Vortex. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2663–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, S.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Bureau, J. Comparison of Retrieved L2 Products from Four Successive Versions of L1B Spectra in the Thermal Infrared Band of TANSO-FTS over the Arctic Ocean. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, A.; Bösch, H.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Dorf, M.; Engel, A.; Payan, S.; Pfeilsticker, K. Observational constraints on the kinetics of the ClO-BrO and ClO-ClO ozone loss cycles in the Arctic winter stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L05801:1–L05801:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelain, D.; Payan, S.; Deng, W.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Hurtmans, D.; Mantz, A.W. Measurement of the temperature dependence of line mixing and pressure broadening parameters between 296 and 90 K in the ν3 band of 12CH4 and their influence on atmospheric methane retrievals. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 2007, 244, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, S.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Oelhaf, H.; Wetzel, G.; Maucher, G.; Keim, C.; Pirre, M.; Huret, N.; Engel, A.; Volk, M.C.; et al. Validation of version-4.61 methane and nitrous oxide observed by MIPAS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keim, C.; Eremenko, M.; Orphal, J.; Dufour, G.; Flaud, J.-M.; Höpfner, M.; Boynard, A.; Clerbaux, C.; Payan, S.; Coheur, P.-F.; et al. Tropospheric ozone from IASI: Comparison of different inversion algorithms and validation with ozone sondes in the northern middle latitudes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9329–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, A.; Clerbaux, C.; Wespes, C.; Clarisse, L.; Hurtmans, D.; Payan, S.; Camy-Perret, C.; Coheur, P.-F. Characterization of methane retrievals from the IASI space-borne sounder. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7889–7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, L.S.; Gordon, I.E.; Babikov, Y.; Barbe, A.; Chris Benner, D.; Bernath, P.F.; Birk, M.; Bizzocchi, L.; Boudon, V.; Brown, L.R.; et al. The HITRAN2012 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 130, 4–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clough, S.A.; Shephard, M.W.; Mlawer, E.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Iacono, M.J.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Boukabara, S.; Brown, P.D. Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: a summary of the AER codes. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, M.; Valks, P.; Hao, N.; van Geffen, J.; Clerbaux, C.; Clarisse, L.; Coheur, P.-F.; Loyala, R.D.G.; Erbertseder, T.; Zimmer, W.; et al. Satellite monitoring of volcanic sulfur dioxide emissions for early warning of volcanic hazards. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.R.; Prata, F.; Platt, U. Volcanological applications of SO2 cameras. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2015, 200, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy, Principles and Applications, Series: Physics of Earth and Space Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu, C.; Estruch, T.; Vincent, G.; Jaeck, J.; Bardou, N.; Collin, S.; Haïdar, R. Extraordinary optical extinctions through dual metallic gratings. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagueux, P.; Farleu, V.; Chamberland, M.; Villemaire, A.; Turcotte, C.; Puckrin, E. Design and Performance of the Hyper-Cam, an Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Sensor. 2009. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/2f75/90496d218177bd059fe6bbab98ad69afc36e.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2019).
- D’Aleo, R.; Bitetto, M.; Delle Donne, D.; Tamburello, G.; Battaglia, A.; Coltelli, M.; Patanè, D.; Prestifilippo, M.; Sciotto, M.; Aiuppa, A. Spatially resolved SO2 flux emissions from Mt Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7511–7519. [Google Scholar]
- Smekens, J.F.; Gouhier, M. Observation of SO2 degassing at Stromboli volcano using a hyperspectral thermal infrared imager. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2018, 356, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Mori, T.; Kazahaya, K.; Ohwada, M.; Hirabayashi, J.; Yoshikawa, S. Effect of UV scattering on SO2 emission rate measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L17315:1–L17315:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edner, H.; Ragnarson, P.; Svanberg, S.; Wallinder, E.; Ferrara, R.; Cioni, R.; Raco, B.; Taddeucci, G. Total fluxes of sulfur dioxide from the Italian volcanoes Etna, Stromboli, and Vulcano measured by differential absorption lidar and passive differential optical absorption spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 18827–18838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibring, P.; Swartling, J.; Edner, H.; Svanberg, S.; Caltabiano, T.; Condarelli, D.; Cecchi, G.; Pantani, L. Optical monitoring of volcanic sulphur dioxide emissions – comparison between four different remote-sensing spectroscopic techniques. Opt. Laser Eng. 2002, 37, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, A.J.; Millan, M.M. The applications of optical correlation techniques to the remote sensing of SO2 plumes using sky light. Atmos. Environ. 1971, 5, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.M. Remote sensing of air pollutants. A study of some atmospheric scattering effects. Atmos. Environ. 1980, 14, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Hoff, R.M. Differential SO2 column measurements of the Mt. Pinatubo volcanic plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Deutschmann, T.; Werner, C.; Sutton, A.J.; Elias, T.; Kelly, P.J. Improving the accuracy of SO2 column densities and emission rates obtained from upward-looking UV-spectroscopic measurements of volcanic plumes by taking realistic radiative transfer into account. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D20302:1–D20302:23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, P.; Herbin, H.; Minvielle, F.; Compiègne, M.; Thieuleux, F.; Parol, F.; and Pelon, J. Remote sensing of volcanic ash plumes from thermal infrared: A case study analysis from SEVIRI, MODIS and IASI instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Instruments | Spectral Range (µm) | Spectral Resolution (cm−1) or # of Bands | Pixel Number | Instantaneous Field of View | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectro Imageur Biréfringent (SIBI) Under development | [3.7–4.8] | 14 | 640 × 512a | 1.6 mrad | [45] |
| Filament Imager Under development | [3–5] | 24 bands | 56 × 56 | 1.1 mrad 3.5° × 3.5° | [46] b |
| Hyper-Cam Imager Long Wavelength InfraRed (LWIR) | [7.7–11.8] | 1, 2, 4, 8 and 32 during this campaign | 320 × 256 | 1.4 mrad 25.6° × 20.4° | [47] TELOPS company |
| Fourier Transform InfraRed spectrometer (FTIR) OPAG 33 | [3.5–14] | 1 | 1 | 10 mrad | Bruker company |
| UltraViolet (UV) Camera | 0.310 and 0.330 | 10 nm | 1380 × 1040 | 365 µrad 28.8° × 21.9° | JAI CM-140GE-UV |
| Plume Parameters | ΔT plume (K) (Temperature Difference between the Plume and the Ambient Air) | Tk plume (m) Plume Thickness | Z plume (km) Altitude of the Plume Centre |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference parameters values | 1 | 400 | 3.2 |
| Parameters values tested | 0.5 | 65 | 2.8 |
| 5 | 200 | 3.8 | |
| 10 | 600 | 4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huret, N.; Segonne, C.; Payan, S.; Salerno, G.; Catoire, V.; Ferrec, Y.; Roberts, T.; Pola Fossi, A.; Rodriguez, D.; Croizé, L.; et al. Infrared Hyperspectral and Ultraviolet Remote Measurements of Volcanic Gas Plume at MT Etna during IMAGETNA Campaign. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101175
Huret N, Segonne C, Payan S, Salerno G, Catoire V, Ferrec Y, Roberts T, Pola Fossi A, Rodriguez D, Croizé L, et al. Infrared Hyperspectral and Ultraviolet Remote Measurements of Volcanic Gas Plume at MT Etna during IMAGETNA Campaign. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101175
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuret, Nathalie, Charlotte Segonne, Sébastien Payan, Giuseppe Salerno, Valéry Catoire, Yann Ferrec, Tjarda Roberts, Armande Pola Fossi, Delphy Rodriguez, Laurence Croizé, and et al. 2019. "Infrared Hyperspectral and Ultraviolet Remote Measurements of Volcanic Gas Plume at MT Etna during IMAGETNA Campaign" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101175
APA StyleHuret, N., Segonne, C., Payan, S., Salerno, G., Catoire, V., Ferrec, Y., Roberts, T., Pola Fossi, A., Rodriguez, D., Croizé, L., Chevrier, S., Langlois, S., La Spina, A., & Caltabiano, T. (2019). Infrared Hyperspectral and Ultraviolet Remote Measurements of Volcanic Gas Plume at MT Etna during IMAGETNA Campaign. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101175