Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Reanalysis Data
2.2.3. Gridded Drought/Soil Moisture Data
2.2.4. Statistics of Crop Yields
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. EDI Description and Standardized Calculation
2.3.2. Estimation of ET and PET
2.3.3. Comparison Drought Metrics
2.3.4. Statistical Comparisons
3. Results
3.1. Drought Index Intercomparisons
3.1.1. Climatological Characteristics
3.1.2. Evaluation of The sEDI For Detecting Historical Drought Events
3.1.3. Evaluation of The sEDI For Detecting the Impacts of Drought on Crop Yields
3.1.4. Statistical Intercomparisons
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation of Dryness Conditions in Northeast China
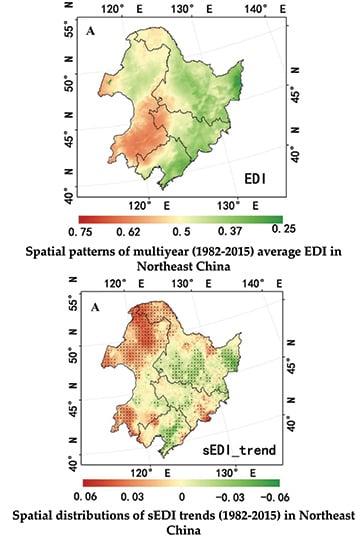
3.2.1. Mean Spatial Pattern of EDI in Northeast China
3.2.2. Characteristics of sEDI Variation in Northeast China
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. Drought modeling—A review. J. Hydrol. 2011, 403, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E.; Qian, T. A Global Data Set of Palmer Drought Severity Index for 1870–2002: Relationship with Soil Moisture and Effects of Surface Warming. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 5, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Schrier, G.V.D.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global warming and changes in drought. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lü, A.; Wu, J.; Lin, Z.; Ming, L. Drought hazard assessment and spatial characteristics analysis in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Gao, S.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y. Effects of spring drought on carbon sequestration, evapotranspiration and water use efficiency in the songnen meadow steppe in northeast China. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Guo, R.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J. Spatial and temporal analysis of drought risk during the crop-growing season over northeast China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, R.R., Jr. A Review of Twentieth-Century Drought Indices Used in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Yuan, X.; Xia, Y.; Hao, F.; Singh, V.P. An overview of drought monitoring and prediction systems at regional and global scales. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Keeping Track of Crop Moisture Conditions, Nationwide: The New Crop Moisture Index. Weatherwise 1968, 21, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.Q.; Su, B.; Krysanova, V.; Vetter, T.; Chao, G.; Tong, J. Spatial variation and trends in PDSI and SPI indices and their relation to streamflow in 10 large regions of China. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Acharya, K. Evaluation of drought and wetness episodes in a cold region (Northeast China) since 1898 with different drought indices. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 2063–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, M.J.; Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D. The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kogan, F.N. Droughts of the Late 1980s in the United States as Derived from NOAA Polar-Orbiting Satellite Data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Niyogi, D. Multi-sensor integrated framework and index for agricultural drought monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, J.Y.; Im, J.H.; Carbone, G.J. Monitoring agricultural drought for arid and humid regions using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Li, G.; Wang, C. Study on monitoring drought in China with MODIS product. Adv. Water Sci. 2005, 16, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Peters, A.J. Assessing vegetation response to drought in the northern Great Plains using vegetation and drought indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jia, G. Monitoring meteorological drought in semiarid regions using multi-sensor microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Jackson, R.D. Measuring yield-reducing plant water potential depressions in wheat by infrared thermometry. Irrig. Sci. 1981, 2, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Clarke, T.R.; Inoue, Y.; Vidal, A. Estimating crop water deficit using the relation between surface-air temperature and spectral vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mu, Q.; Huang, J. Assessing the remotely sensed Drought Severity Index for agricultural drought monitoring and impact analysis in North China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.; Wardlow, B.; Pimstein, A.; Mecikalski, J.; Kustas, W. A thermal-based evaporative stress index for monitoring surface moisture depletion. Remote Sens. Drought Innov. Monit. Approaches 2012, 145–167. Available online: https://books.google.com.hk/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=n1gqnmglvLoC&oi=fnd&pg=PA145&dq=A+thermal-based+evaporative+stress+index+for+monitoring+surface+moisture+depletion&ots=YCNl9xCiux&sig=tj-OllGPwMqO7rhMQkqWtS55aqg&redir_esc=y&hl=zh-CN&sourceid=cndr#v=onepage&q=A%20thermal-based%20evaporative%20stress%20index%20for%20monitoring%20surface%20moisture%20depletion&f=false (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Kimball, J.S.; Mcdowell, N.G.; Running, S.W. A Remotely Sensed Global Terrestrial Drought Severity Index. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.; Otkin, J.; Zhan, X.; Mo, K.; Svoboda, M.; Wardlow, B.; Pimstein, A. An Intercomparison of Drought Indicators Based on Thermal Remote Sensing and NLDAS-2 Simulations with U.S. Drought Monitor Classifications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1035–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulcre-Canto, G.; Vogt, J.; Arboleda, A.; Antofie, T. Assessment of the EUMETSAT LSA-SAF evapotranspiration product for drought monitoring in Europe. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakouchak, A.; Farahmand, A.; Melton, F.S.; Teixeira, J.; Anderson, M.C.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hain, C.R. Remote sensing of drought: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, Q.; Wang, K. Monitoring Drought over the Conterminous United States Using MODIS and NCEP Reanalysis-2 Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Yao, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Analysis of Drought in North China Based on Evapotranspiration Drought Index. Meteorol. Mon. 2013, 39, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huang, W. A drought rarity and evapotranspiration-based index as a suitable agricultural drought indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhao, S. Monitoring global land surface drought based on a hybrid evapotranspiration model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qin, Q.; Fadhil, A.M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Sui, X.; Dong, H. Evaluation of EDI derived from the exponential evapotranspiration model for monitoring China’s surface drought. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, B. MODIS-driven estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in China based on a modified Priestley–Taylor algorithm. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Satellite-derived spatiotemporal variations in evapotranspiration over northeast China during 1982–2010. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Land cover changes during agrarian restructuring in Northeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2006, 26, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Mo, X.; Meng, D. Analyzing Spatiotemporal Patterns of Meteorological Drought and Its Responses to Climate Change across Northeast China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Yang, X.; Lu, S. The contrast analysis on the average and extremum temperature trend in Northeast China. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 26, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Wang, S. Research on the Spatial-Temporal Differentiation of Precipitation in Northeast China in Recent 50 Years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2005, 2, 007. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Ma, S.; Chen, Y. The Situation and Comparative Advantage and Problems and Countermeasures of Grain Product of the Three Provinces in East-north Areas. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2006, 22, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Zhu, D. Impacts of changes in climate and its variability on food production in Northeast China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2008, 34, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.L.; Ren, G.Y. Reanalysis of Surface Air Temperature Change of the Last 100 Years over China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Zhu, Y. Climate Change in China from 1880 to 1998 and its Impact on the Environmental Condition. Clim. Chang. 2004, 50, 419–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wu, Z.; Yang, S. Temporal and spatial variations of extreme precipitation and dryness events in Northeast China in last 50 years. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 25, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, AVHRR. Available online: http://islscp2.sesda.com/ISLSCP21/data (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration, LP DAAC. Available online: http://reverb.echo.nasa.gov/reverb (accessed on 16 October 2016).
- He, J.; Yang, K. China Meteorological Forcing Dataset; Cold and Arid Regions Science Data Center: Lanzhou, China, 2011; Available online: http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn/data/7a35329c-c53f-4267-aa07-e0037d913a21 (accessed on 23 May 2017).
- Yang, K.; Jie, H.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K. On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Dool, H.V.D. Climate Prediction Center global monthly soil moisture data set at 0.5 resolution for 1948 to present. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPC Soil Moisture Data. NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, CO, USA. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/ (accessed on 14 May 2017).
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2010, 329, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer Drought Severity Index. Zhao and Running. 2009. Available online: ftp://ftp.ntsg.umt.edu/pub/NPP Science 2010/PDSI/ (accessed on 20 October 2016).
- Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) for Global Land Surface (1949–2012). National Center for Atmospheric Research, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds298.0/ (accessed on 17 July 2017).
- Kalma, J.D.; Mcvicar, T.R.; Mccabe, M.F. Estimating Land Surface Evaporation: A Review of Methods Using Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature Data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Mu, Q.; Jones, L.A.; Goetz, S.J.; Running, S.W. Satellite based analysis of northern ET trends and associated changes in the regional water balance from 1983 to 2005. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, K.; Liu, M. Spatial and Decadal Variations in Potential Evapotranspiration of China Based on Reanalysis Datasets during 1982–2010. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, C.P. Meteorological drought. US Weather Bur. Res. Pap. 1965, 45, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Keyantash, J.; Dracup, J.A. The Quantification of Drought: An Evaluation of Drought Indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. Comparing the palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index 1. Jawra J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L. China Meteorological Disaster Yearbook (2014); China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. China Statistical Data. National Bureau of statistics of China. Available online: http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=E0103&zb=A0D0Q%AE=23000-0&sj=2014: 2014 (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Sun, Q.; Liu, J. Temporal-spatial change of temperature and precipitation based on CAST in northeast China. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2014, 30, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, W.M. The Palmer Drought Severity Index: Limitations and Assumptions. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnieli, A.; Panov, N.; Goldberg, A.; Agam, N.; Anderson, M.; Pinker, R.T.; Imhoff, M.L.; Gutman, G.G. Use of NDVI and land surface temperature for drought assessment: Merits and limitations. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, K.; Zhang, W. Monitoring and Assessment of Drought Focused on Its Impact on Sorghum Yield over Sudan by Using Meteorological Drought Indices for the Period 2001–2011. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Svoboda, M.D.; Hayes, M.J.; Wilhite, D.A.; Wen, F. Appropriate application of the standardized precipitation index in arid locations and dry seasons. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 27, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Analysis on formation cause and prevention countermeasure of desertification and degeneration of Hulunbeier grassland. Pratac. Sci. 2007, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, W.; Wang, T. Drought variability in Inner Mongolia of northern China during 1960–2013 based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R. Analysis of drought and meteorological disasters in Hulun Buir Grassland. Fortune World 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Jia, N.; Zhou, W. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Nakhjiri, N. A near real-time satellite-based global drought climate data record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 044037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggs, T.; Petropoulos, G.; Velpuri, N.; Marshall, M. Remote sensing of actual evapotranspiration form Croplands. In Remote Sensing Handbook: Remote Sensing of Water Resources, Disasters, and Urban Studies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 59–99. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Bohms, S.; Verdin, J.P. A comprehensive evaluation of two MODIS evapotranspiration products over the conterminous United States: Using point and gridded FLUXNET and water balance ET. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, K.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, B.; Fisher, J.B.; Mu, Q. A satellite-based hybrid algorithm to determine the Priestley Taylor parameter for global terrestrial latent heat flux estimation across multiple biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoniello, T.; Cuomo, V.; Lanfredi, M.; Lasaponara, R.; Macchiato, M. On the relevance of accurate correction and validation procedures in the analysis of AVHRR-NDVI time series for long-term monitoring. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinzon, J.; Tucker, C. A non-stationary 1981–2012 AVHRR NDVI3g time series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6929–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.; Wardlow, B.; Pimstein, A.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Kustas, W.P. Evaluation of Drought Indices Based on Thermal Remote Sensing of Evapotranspiration over the Continental United States. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenteserrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; Lópezmoreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.C.; Zolin, C.A.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Hain, C.R.; Semmens, K.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Gao, F.; Otkin, J.A.; Tetrault, R. The Evaporative Stress Index as an indicator of agricultural drought in Brazil: An assessment based on crop yield impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zheng, H.; Lei, Z. Applicability analysis of SPEI for drought research in Northeast China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ittersum, M.K.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Van Keulen, H.; Kropff, M.J.; Bastiaans, L.; Goudriaan, J. On approaches and applications of the Wageningen crop models. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Time | Duration | Site | Hazard Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| March to June, 2004 | Four months | Western Heilongjiang Western Jilin Northwestern Liaoning | Severe drought |
| April to May, 2006 | Two months | Central and Western Heilongjiang | Moderate to Severe drought |
| January to March, 2008 | Three months | The Whole Northeast China | Severe drought |
| September, 2010 | One month | Southwestern Heilongjiang Western Jilin | Moderate to Severe drought |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Bei, X.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Jiang, B.; Shang, K.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171960
Zhang L, Yao Y, Bei X, Jia K, Zhang X, Xie X, Jiang B, Shang K, Xu J, Chen X. Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(17):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171960
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lilin, Yunjun Yao, Xiangyi Bei, Kun Jia, Xiaotong Zhang, Xianhong Xie, Bo Jiang, Ke Shang, Jia Xu, and Xiaowei Chen. 2019. "Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 17: 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171960
APA StyleZhang, L., Yao, Y., Bei, X., Jia, K., Zhang, X., Xie, X., Jiang, B., Shang, K., Xu, J., & Chen, X. (2019). Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China. Remote Sensing, 11(17), 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171960