Denoising Algorithm for the FY-4A GIIRS Based on Principal Component Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dataset and Algorithm
2.1. GIIRS Observations
2.2. Model Simulations
2.3. Theoretical Basis of the PCA-Based Denoising Algorithm (PDA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PDA Applied to Simulated Data
3.1.1. Simulation Dataset
3.1.2. PDA Performance on Simulated Data
3.2. PDA Applied to Observed Data
3.2.1. Original Observed and Simulated BT Data
3.2.2. Method for Selecting the Optimal Number of PCs
3.2.3. Selection of the Representative Channels
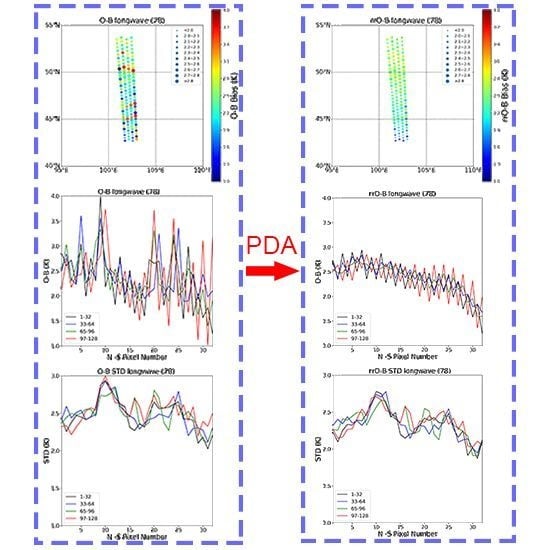
3.2.4. Statistics of the Half-Month Average Background Departures
3.2.5. Assimilation Experiment
3.2.6. Typhoon Experiment
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menzel, W.P.; Schmit, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Li, J. Satellite-based atmospheric infrared sounder development and applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, M.T.; Pagano, T.S.; Aumann, H.H.; Atlas, R.; Barnet, C.; Blaisdell, J.; Chen, L.; Divakarla, M.; Fetzer, E.J.; Goldberg, M.; et al. AIRS: Improving weather forecasting and providing new data on greenhouse gases. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, F.; Armante, R.; August, T.; Barnet, C.; Bouchard, A.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Capelle, V.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F.; et al. Hyperspectral earth observation from IASA: Five years of accomplishments. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.D.; Kilcoyne, H.; Cikanek, H.; Mehta, A. Joint polar satellite system the United States next generation civilian polar-orbiting environment satellite system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13463–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marshall, J.; Jung, J.; Derber, J.; Chahine, M.; Treadon, R.; Lord, S.J.; Goldberg, M.; Wolf, W.; Liu, H.C.; Joiner, J.; et al. Improving global analysis and forecasting with AIRS. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Han, H.; Li, J.L.; Zheng, J. On the assimilation of satellite sounder data in cloudy skies in the numerical weather prediction models. J. Meteorol. Res. 2016, 30, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, T.; Bonavita, M.; Thépaut, J.-N. The role of satellite data in the forecasting of Hurricane Sandy. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, J.; Li, J.L.; Li, Z.L.; Schmit, T.J.; Bai, W.G. Advanced infrared sounder subpixel cloud detection with imagers and its impact on radiance assimilation in NWP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, J.; Goldberg, M.D.; Schmit, T.J.; Lim, A.H.N.; Li, Z.L.; Han, H.; Li, J.L.; Ackerman, S.A. Assimilation of thermodynamic information from advanced infrared sounders under partially cloudy skies for regional NWP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5469–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, J.; Li, Z.L.; Lim, A.H.N.; Li, J.L.; Schmit, T.J.; Goldberg, M.D. The impact of Cross-track Infrared Sounder (CrIS) Cloud Cleared Radiances on Hurricane Joaquin (2015) and Matthew (2016) Forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 13201–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalon, G.; Cayla, F.; Diebel, D. IASI—An advanced sounder for operational meteorology. In Proceedings of the IAF 52nd International Astronautical Congress, Toulouse, France, 1–5 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, F.; Atkinson, N.C.; English, S.J.; Eyre, J.R. Assimilation of IASI at the Met Office and assessment of its impact through observing system experiments. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, F.; Collard, A.; Guidard, V.; Randriamampianina, R.; Schwaerz, M. Assimilation of IASI radiances at European NWP centres. In Proceedings of the Workshop on the assimilation of IASI data in NWP, ECMWF, Reading, UK, 6–8 May 2009; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, A.D.; McNally, A.P. The assimilation of Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer radiances at ECMWF. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wei, C.Y.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, FengYun-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.L.; Otkin, J.; Schmit, T.J.; Liu, C.-Y. Warning information in a preconvection environment from the geostationary advanced infrared sounding system—A simulation study using IHOP case. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Schmit, T.J. Applications of full spatial resolution space-based advanced infrared soundings in the preconvection environment. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Lim, A.; Li, J.L.; Schmit, T.J.; Atlas, R.; Boukabara, S.-A.; Hoffman, R.N. Value-added impact of geostationary hyperspectral infrared sounders on local severe storm forecasts-via a quick regional OSSE. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, A.D.; McNally, A.P.; Hilton, F.I.; Healy, S.B.; Atkinson, N.C. The use of principal component analysis for the assimilation of high-resolution infrared sounder observations for numerical weather prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, P.; Revercomb, H.E.; Sromovsky, L.A. A principal component noise filter for high spectral resolution infrared measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Antonelli, P. Application of principal component analysis to high-resolution infrared measurement compression and retrieval. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Revercomb, H.; Cromp, M.; Gu, D.G.; Johnson, D.; Mooney, D.; Scott, D.; Strow, L.; Bingham, G.; Borg, L. Suomi NPP CrIS measurements, sensor data record algorithm, calibration and validation activities, and record data quality. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12734–12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, X.L. Bias characterization of CrIS radiances at 399 selected channels with respect to NWP model simulations. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.Y.; Han, W.; Gao, Z.Q.; Di, D. The evaluation of GIIRS longwave temperature sounding channels using 4D-Var. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.D.; Lu, H.J.; Jin, Z.Y.; Tian, W.H.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B. The operational global four-dimensional variational data assimilation system at the China Meteorological Administration. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 1882–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Xue, J.S.; Yang, X.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Shen, X.S.; Hu, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, L.R.; Chen, J.B. New generation of multi-scale NWP system (GRAPES): General scientific design. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, D.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Bai, W.G.; Wu, C.Q.; Menzel, W.P. Enhancing the fast radiative transfer model for FengYun-4 GIIRS by using local training profile. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deco, G.; Obradovic, D. An Information-Theoretic Approach to Neural Computing; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Auligne, T.; McNally, A.P.; Dee, D.P. Adaptive bias correction for satellite data in a numerical weather prediction system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.W.; Wen, H.Y. Study on Method and Experiment of Hyper-spectral Atmospheric Infrared Sounder Channel Selection. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2014, 29, 795–802, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.L.; Zeng, Z. A quality control procedure for GPS radio occultation data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroziers, G.; Berre, L.; Chapnik, B.; Poli, P. Diagnosis of observation, background and analysis-error statistics in observation space. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 3385–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Channel | Before Reconstruction E | After Reconstruction Err | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 3 | 0.808 | 0.844 | −4.46% |
| Channel 4 | 0.623 | 0.663 | −6.42% |
| Channel 6 | 0.586 | 0.609 | −3.92% |
| Channel 9 | 0.552 | 0.575 | −4.17% |
| Channel 11 | 0.682 | 0.694 | −1.76% |
| Channel 12 | 0.623 | 0.641 | −2.89% |
| Channel 15 | 0.699 | 0.704 | −0.72% |
| Channel 27 | 0.700 | 0.697 | 0.43% |
| Channel 70 | 4.552 | 4.526 | 0.57% |
| Channel 72 | 3.206 | 3.198 | 0.25% |
| Channel 73 | 0.773 | 0.633 | 18.11% |
| Channel 75 | 2.398 | 2.405 | −0.29% |
| Channel 77 | 3.701 | 3.667 | 0.92% |
| Channel 78 | 2.292 | 2.148 | 6.28% |
| Channel 79 | 4.183 | 4.030 | 3.66% |
| Channel 80 | 1.042 | 0.900 | 13.63% |
| Channel 82 | 2.370 | 2.363 | 0.30% |
| Channel 83 | 2.042 | 1.904 | 6.76% |
| Channel 84 | 2.378 | 2.374 | 0.17% |
| Channel 85 | 1.002 | 0.946 | 5.59% |
| Channel 86 | 1.692 | 1.619 | 4.31% |
| Channel 87 | 0.681 | 0.624 | 8.37% |
| Channel 88 | 1.910 | 1.830 | 4.19% |
| Channel 89 | 4.197 | 4.021 | 4.19% |
| Channel 90 | 0.827 | 0.690 | 16.57% |
| Channel 91 | 2.192 | 2.056 | 6.20% |
| Channel 111 | 1.648 | 1.597 | 3.09% |
| Channel 112 | 0.956 | 0.936 | 2.09% |
| Channel 113 | 0.730 | 0.713 | 2.33% |
| Channel | Before Reconstruction E | After Reconstruction Err | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 3 | 0.614 | 0.614 | 0.04% |
| Channel 4 | 0.554 | 0.555 | −0.15% |
| Channel 6 | 0.547 | 0.536 | 2.14% |
| Channel 9 | 0.517 | 0.525 | −1.65% |
| Channel 11 | 0.628 | 0.633 | −0.72% |
| Channel 12 | 0.577 | 0.585 | −1.27% |
| Channel 15 | 0.584 | 0.600 | −2.66% |
| Channel 27 | 0.739 | 0.727 | 1.61% |
| Channel 70 | 4.074 | 4.101 | −0.66% |
| Channel 72 | 2.819 | 2.881 | −2.18% |
| Channel 73 | 0.798 | 0.792 | 0.80% |
| Channel 75 | 2.095 | 2.086 | 0.42% |
| Channel 77 | 3.135 | 3.130 | 0.16% |
| Channel 78 | 1.427 | 1.382 | 3.18% |
| Channel 79 | 3.659 | 3.555 | 2.83% |
| Channel 80 | 1.038 | 1.041 | −0.36% |
| Channel 82 | 1.997 | 1.994 | 0.11% |
| Channel 83 | 1.231 | 1.235 | −0.39% |
| Channel 84 | 2.015 | 2.000 | 0.73% |
| Channel 85 | 0.814 | 0.791 | 2.91% |
| Channel 86 | 1.454 | 1.403 | 3.55% |
| Channel 87 | 0.771 | 0.759 | 1.55% |
| Channel 88 | 1.383 | 1.378 | 0.40% |
| Channel 89 | 3.600 | 3.607 | −0.21% |
| Channel 90 | 0.771 | 0.750 | 2.71% |
| Channel 91 | 1.777 | 1.705 | 4.05% |
| Channel 111 | 1.535 | 1.512 | 1.46% |
| Channel 112 | 1.017 | 0.993 | 2.41% |
| Channel 113 | 0.826 | 0.797 | 3.42% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, S.; Han, W.; Gao, Z.; Yin, R.; Zheng, Y. Denoising Algorithm for the FY-4A GIIRS Based on Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222710
Fan S, Han W, Gao Z, Yin R, Zheng Y. Denoising Algorithm for the FY-4A GIIRS Based on Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(22):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222710
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Sihui, Wei Han, Zhiqiu Gao, Ruoying Yin, and Yu Zheng. 2019. "Denoising Algorithm for the FY-4A GIIRS Based on Principal Component Analysis" Remote Sensing 11, no. 22: 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222710
APA StyleFan, S., Han, W., Gao, Z., Yin, R., & Zheng, Y. (2019). Denoising Algorithm for the FY-4A GIIRS Based on Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sensing, 11(22), 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222710