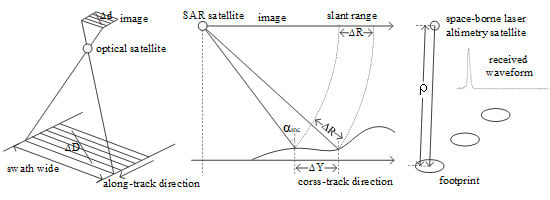
Figure 1.
The imaging mechanism of optical and SAR satellite: (a) the central projection of optical satellite. (b) The slant range projection of SAR satellite.
Figure 1.
The imaging mechanism of optical and SAR satellite: (a) the central projection of optical satellite. (b) The slant range projection of SAR satellite.
Figure 2.
The image point extraction for GLAS footprint: (a) digital orthophotograph model (DOM), (b) high-resolution (HR) optical image, and (c) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. The image points calculated by back-projection are indicated by a green cross. The final image points located in obvious texture area are indicated by a red cross. The circle footprint with a diameter of 70 m is marked by a green ellipse (the line resolution is 0.331 m and sample resolution is 0.562 m). The geometric accuracies of the used DOM, HR optical image, and SAR image were about 0.3, 30, and 5 m, respectively.
Figure 2.
The image point extraction for GLAS footprint: (a) digital orthophotograph model (DOM), (b) high-resolution (HR) optical image, and (c) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. The image points calculated by back-projection are indicated by a green cross. The final image points located in obvious texture area are indicated by a red cross. The circle footprint with a diameter of 70 m is marked by a green ellipse (the line resolution is 0.331 m and sample resolution is 0.562 m). The geometric accuracies of the used DOM, HR optical image, and SAR image were about 0.3, 30, and 5 m, respectively.
Figure 3.
An illustration of the coverage area of the experimental data.
Figure 3.
An illustration of the coverage area of the experimental data.
Figure 4.
Experimental data for combined geopositioning: (a) GF2-1, (b) GF2-2, (c) GF2-3, (d) GF6-1, (e) GF6-2, (f) GF3-1, and (g) GF3-2.
Figure 4.
Experimental data for combined geopositioning: (a) GF2-1, (b) GF2-2, (c) GF2-3, (d) GF6-1, (e) GF6-2, (f) GF3-1, and (g) GF3-2.
Figure 5.
The reference evaluation data: (a) DOM and (b) digital elevation models (DEM).
Figure 5.
The reference evaluation data: (a) DOM and (b) digital elevation models (DEM).
Figure 6.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GF3: (a) GF2 geopositioning, (b) GF3 geopositioning. (c) GF2 + GF3-1 combined geopositioning, (d) GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning, and (e) GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning with the same weight. Check points (CKPs) are represented by circles. The plane error and altitude error are represented by the vectors marked by the solid line and the dotted line, respectively.
Figure 6.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GF3: (a) GF2 geopositioning, (b) GF3 geopositioning. (c) GF2 + GF3-1 combined geopositioning, (d) GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning, and (e) GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning with the same weight. Check points (CKPs) are represented by circles. The plane error and altitude error are represented by the vectors marked by the solid line and the dotted line, respectively.
Figure 7.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF6 and GF3: (a) GF6 geopositioning, (b) GF6 + GF3-1 combined geopositioning, (c) GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning, and (d) GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning with the same weight.
Figure 7.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF6 and GF3: (a) GF6 geopositioning, (b) GF6 + GF3-1 combined geopositioning, (c) GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning, and (d) GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 combined geopositioning with the same weight.
Figure 8.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning: (a) plane geometric accuracy analysis with different offset parameters, (b) altitude geometric accuracy analysis with different offset parameters, (c) plane geometric accuracy analysis with different scale and rotation parameters, and (d) altitude geometric accuracy analysis with different scale and rotation parameters.
Figure 8.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning: (a) plane geometric accuracy analysis with different offset parameters, (b) altitude geometric accuracy analysis with different offset parameters, (c) plane geometric accuracy analysis with different scale and rotation parameters, and (d) altitude geometric accuracy analysis with different scale and rotation parameters.
Figure 9.
Evaluation of the GLAS footprint extraction with the proposed criterion. The GLAS footprints are marked with red points.
Figure 9.
Evaluation of the GLAS footprint extraction with the proposed criterion. The GLAS footprints are marked with red points.
Figure 10.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GLAS combined geopositioning: (a) with one GLAS footprint, (b) with four GLAS footprints, (c) with nine GLAS footprints and (d) with four height control points. The GLAS footprints and height control points are represented as triangles. The plane error and altitude error are represented by the vectors marked with the solid line and the dotted line, respectively.
Figure 10.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF2 and GLAS combined geopositioning: (a) with one GLAS footprint, (b) with four GLAS footprints, (c) with nine GLAS footprints and (d) with four height control points. The GLAS footprints and height control points are represented as triangles. The plane error and altitude error are represented by the vectors marked with the solid line and the dotted line, respectively.
Figure 11.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF6 and GLAS combined geopositioning: (a) with one GLAS footprint, (b) with four GLAS footprints, (c) with nine GLAS footprints, and (d) with four height control points.
Figure 11.
Geometric accuracy analysis of GF6 and GLAS combined geopositioning: (a) with one GLAS footprint, (b) with four GLAS footprints, (c) with nine GLAS footprints, and (d) with four height control points.
Figure 12.
Geometric accuracy improvement analysis: (a) GF3, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning and (b) GF2 with four GCPs.
Figure 12.
Geometric accuracy improvement analysis: (a) GF3, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning and (b) GF2 with four GCPs.
Figure 13.
Geometric accuracy improvement analysis: (a) GF6, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning and (b) GF6 with four GCPs.
Figure 13.
Geometric accuracy improvement analysis: (a) GF6, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning and (b) GF6 with four GCPs.
Table 1.
Geopositioning error sources of optical satellite and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite.
Table 1.
Geopositioning error sources of optical satellite and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite.
| Error | Error Source of Optical Satellite | Error Source of SAR Satellite |
|---|
| Along-track offset error | Time error, along-track position error, pitch angle error, along-track detector errors | Drift error of spacecraft time, along-track position error, radial position error, velocity error |
| Along-track linear or scale error | Lens distortion, focal length error, position error along the sub-satellite direction | Relative error of stable local oscillator, along-track velocity error |
| Cross-track offset error | Cross-track position error, roll angle error, cross-track detector errors, atmosphere refraction error | Delay error between signal transmitter and signal receiver, cross-track position error, radial position error, atmospheric delay |
| Cross-track linear or scale error | Cross-track lens distortion, focal length error, position error along the sub-satellite direction | Incident angle error, radial position error, atmospheric delay |
Table 2.
The criterion for Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) footprint extraction.
Table 2.
The criterion for Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) footprint extraction.
| Characteristic | Condition |
|---|
| Altitude difference compared with GDEM2 | <20 |
| GLA01 product | Number of peaks of received waveform | =1 |
| Sigma of Gaussian of received waveform | ≤3.2 |
| GLA14 product | Attitude quality indicator | =0 |
| Surface reflectance parameter | <1 |
| Saturation correction flag | =0 |
Table 3.
Satellite parameters of GF2, GF6, and GF3.
Table 3.
Satellite parameters of GF2, GF6, and GF3.
| | GF2 | GF6 | GF3 |
|---|
| Orbit altitude | 631 km | 644.5 km | Orbit altitude | 506 km |
| Orbit type | SunSync | SunSync | Orbit type | SunSync |
| Life | 5–8 years | 8 years | Life | 8 years |
| | B1: 450–520 nm | B1: 450–520 nm | | |
| | B2: 520–590 nm | B2: 520–600 nm | | |
| Spectral range | B3: 630–690 nm | B3: 630–690 nm | Band | C |
| | B4: 770–890 nm | B4: 760–900 nm | | |
| | Pan: 450–900 nm | Pan: 450–900 nm | | |
| Field of view () | 2.1 | 8.6 | Incident angle () | 10–60 |
| | | | Scanning angle () | ±20 |
| Resolution (m) | 0.81 | 2 | Imaging mode | Spotlight mode (1, 10 × 10) |
| Swath width (km) | 45 | 90 | (Resolution (m), | Hyperfine strip model (3, 30) |
| | | | swath width (km)) | Fine strip mode 1 (5, 50) |
| | | | | Fine strip mode 2 (10, 100) |
| | | | | Standard strip model (25, 130) |
| | | | | Narrow scan mode (50, 300) |
| | | | | Wide scan mode (100, 500) |
| | | | | Full polarization strip model 1 (8, 30) |
| | | | | Full polarization strip model 2 (25, 40) |
| | | | | Wave imaging mode (10, 5 × 5) |
| | | | | Global observation model (500, 650) |
| | | | | Extended incident angle model (25, 130 or 80) |
Table 4.
Description of experimental data for combined geopositioning.
Table 4.
Description of experimental data for combined geopositioning.
| Image | Acquisition Date | Pass | Incident Angle () | Size (pixels) | Resolution (m) |
|---|
| GF2-1 | 2 February 2015 | DEC | 15.502 | 29,200 × 27,620 | 0.81 × 0.81 |
| GF2-2 | 21 September 2015 | DEC | −8.403 | 29,200 × 27,620 | 0.81 × 0.81 |
| GF2-3 | 26 August 2016 | DEC | −12.444 | 29,200 × 27,620 | 0.81 × 0.81 |
| GF6-1 | 13 March 2019 | DEC | −0.004 | 44,500 × 48,312 | 2 × 2 |
| GF6-2 | 17 March 2019 | DEC | −0.003 | 44,500 × 48,312 | 2 × 2 |
| GF3-1 | 9 April 2017 | DEC | 43.796–44.342 | 30,642 × 13,544 | 0.34 × 0.56 |
| GF3-2 | 16 April 2017 | ASC | 39.224–39.881 | 33,760 × 13,382 | 0.33 × 0.56 |
| Reference data | Resolution (m) | Accuracy (m) | Range | | |
| DOM | 0.271 | 0.251 | Lat: 37.3408–37.5170 | | |
| DEM | 1.806 | 0.273 | Lon: 118.3691–118.8056 | | |
Table 5.
Geometric accuracy of GF2, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning.
Table 5.
Geometric accuracy of GF2, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning.
| | Experimental Data | Average | RMSE (m) | | MAX (m) |
|---|
| | Convergent Angle () | Plane | Altitude | | Plane | Altitude |
|---|
| A | GF2 | 18.630 | 13.085 | 75.857 | | 17.489 | 80.069 |
| GF3 | 73.140 | 1.532 | 3.272 | | 2.684 | 5.597 |
| GF2 + GF3-1 | 27.644 | 11.977 | 16.095 | | 13.763 | 20.732 |
| GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 | 34.845 | 1.724 | 3.784 | | 3.279 | 8.903 |
| GF2 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 (with the same weight) | 34.845 | 8.107 | 6.061 | | 11.191 | 8.952 |
| B | GF2 + one GLAS footprint | - | 14.129 | 3.208 | | 17.507 | 6.404 |
| GF2 + four GLAS footprints | - | 13.890 | 2.865 | | 17.410 | 5.842 |
| GF2 + nine GLAS footprints | - | 13.945 | 2.882 | | 17.447 | 5.560 |
| GF2 + four height control points | - | 13.974 | 1.805 | | 17.264 | 4.367 |
| C | GF2 + GF3 + four GLAS footprints | - | 1.587 | 1.985 | | 3.455 | 7.424 |
| GF2 + four control points | - | 1.945 | 1.803 | | 4.885 | 3.789 |
Table 6.
Geometric accuracy of GF6, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning.
Table 6.
Geometric accuracy of GF6, GF3, and GLAS combined geopositioning.
| | Experimental Data | Average | RMSE (m) | | MAX (m) |
|---|
| | Convergent Angle () | Plane | Altitude | | Plane | Altitude |
|---|
| A | GF6 | 5.16 | 12.878 | 35.901 | | 14.643 | 53.549 |
| GF6 + GF3-1 | 26.20 | 10.079 | 20.524 | | 11.654 | 34.517 |
| GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 | 37.43 | 2.823 | 9.186 | | 4.131 | 19.543 |
| GF6 + GF3-1 + GF3-2 (with the same weight) | 37.43 | 5.280 | 9.528 | | 7.143 | 20.989 |
| B | GF6 + one GLAS footprint | - | 11.570 | 11.542 | | 13.400 | 21.641 |
| GF6 + four GLAS footprints | - | 11.558 | 11.519 | | 13.388 | 21.710 |
| GF6 + nine GLAS footprints | - | 11.512 | 11.418 | | 17.447 | 5.560 |
| GF6 + four height control points | - | 11.620 | 12.490 | | 13.414 | 24.435 |
| C | GF6 + GF3 + four GLAS footprints | - | 2.908 | 7.669 | | 4.343 | 15.877 |
| GF6 + four control points | - | 1.737 | 9.290 | | 3.761 | 20.144 |
Table 7.
Geometric accuracy with different offset parameters for GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning. The first column relates to GF2 and the first row relates to GF3.
Table 7.
Geometric accuracy with different offset parameters for GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning. The first column relates to GF2 and the first row relates to GF3.
| | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 |
|---|
| | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude |
|---|
| 10 | 1.802 | 3.720 | 2.135 | 4.035 | 3.277 | 4.699 | 6.599 | 7.952 | 9.304 | 19.376 |
| 30 | 1.823 | 3.732 | 1.743 | 3.747 | 1.724 | 3.784 | 2.232 | 3.970 | 5.432 | 4.854 |
| 50 | 1.839 | 3.735 | 1.766 | 3.727 | 1.720 | 3.716 | 1.718 | 3.670 | 3.727 | 3.538 |
| 100 | 1.847 | 3.736 | 1.780 | 3.718 | 1.736 | 3.686 | 1.616 | 3.547 | 2.669 | 3.018 |
| 150 | 1.848 | 3.737 | 1.783 | 3.717 | 1.740 | 3.682 | 1.611 | 3.525 | 2.488 | 2.926 |
| 200 | 1.849 | 3.737 | 1.784 | 3.716 | 1.742 | 3.681 | 1.611 | 3.517 | 2.330 | 2.895 |
Table 8.
Geometric accuracy with different scale and rotation parameters for GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning.
Table 8.
Geometric accuracy with different scale and rotation parameters for GF2 and GF3 combined geopositioning.
| | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
|---|
| | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude | Plane | Altitude |
|---|
| 1 | 1.588 | 4.550 | 1.718 | 4.210 | 2.144 | 4.042 | 3.396 | 4.199 | 4.115 | 4.346 |
| 3 | 1.607 | 4.289 | 1.643 | 4.009 | 1.862 | 3.825 | 2.872 | 3.892 | 3.951 | 4.113 |
| 5 | 1.659 | 4.232 | 1.661 | 3.975 | 1.748 | 3.786 | 2.415 | 3.772 | 3.632 | 3.997 |
| 10 | 1.707 | 4.206 | 1.707 | 3.968 | 1.724 | 3.784 | 1.976 | 3.690 | 3.037 | 3.841 |
| 15 | 1.719 | 4.202 | 1.723 | 3.968 | 1.738 | 3.790 | 1.856 | 3.658 | 2.750 | 3.749 |
| 20 | 1.723 | 4.200 | 1.730 | 3.969 | 1.746 | 3.793 | 1.808 | 3.637 | 2.600 | 3.669 |
Table 9.
GLAS footprint extraction with the proposed criteria.
Table 9.
GLAS footprint extraction with the proposed criteria.
| Criterion | Number of Data | Mean (m) | RMSE (m) |
|---|
| Original data | 5312 | −4.490 | 16.060 |
| With GDEM2 <20 | 5064 | −1.253 | 2.799 |
| With GDEM2 <20 and criterions in GLA14 product | 3257 | −1.339 | 2.615 |
| With GDEM2 <20 and criterions in GLA01 product | 3419 | −0.865 | 2.049 |
| With GDEM2 <20 and criterions in GLA14 and GLA01 products | 2272 | −0.919 | 1.969 |