Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Images
2.2.2. Validation Data
2.2.3. Other Land Cover Datasets Used for Comparison
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
3.2. Preprocessing of Remote Sensing Image
3.2.1. Calculation of Spectral Indices
3.2.2. Fusion of Landsat OLI and MODIS Images
3.3. Pixel- and Phenology-based Paddy Rice Mapping Algorithms
3.3.1. Crop Calendar
3.3.2. Maps of Rice Paddy Fields and Multi-Cropping Areas
3.4. Validation and Comparison
4. Results
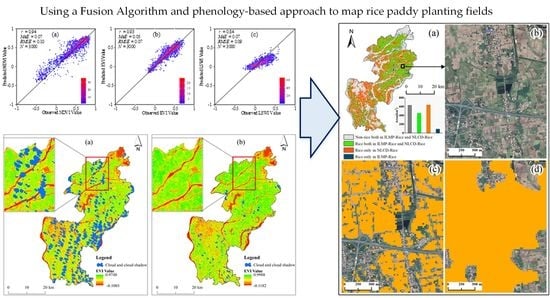
4.1. Landsat–MODIS Fusion Results
4.2. Maps of Rice Paddy Planting Area and Cropping Intensity in 2015
4.3. Accuracy Assessment of Rice Paddy Planting Areas and Cropping Intensity in 2015
4.4. Comparison between ILMP-Rice Map and NLCD-Rice Data in 2015
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. FAO Statistical Databases (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) Databases—UW-Madison Libraries. Available online: http://digital.library.wisc.edu/1711.web/faostat (accessed on 31 December 2019).
- Elert, E. Rice by the numbers: A good grain. Nature 2014, 514, S50–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, G.; Jin, C.; Kou, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Mapping paddy rice planting area in cold temperate climate region through analysis of time series Landsat 8 (OLI), Landsat 7 (ETM+) and MODIS imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, X. High resolution paddy rice maps in cloud-prone Bangladesh and Northeast India using Sentinel-1 data. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontgis, C.; Schneider, A.; Ozdogan, M. Mapping rice paddy extent and intensification in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta with dense time stacks of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xin, L.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, R. Decreasing Rice Cropping Intensity in Southern China from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, L.; Lee, T.M.; Koh, L.P.; Brook, B.W.; Gardner, T.A.; Barlow, J.; Peres, C.A.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Laurance, W.F.; Lovejoy, T.E.; et al. Primary forests are irreplaceable for sustaining tropical biodiversity. Nature 2011, 478, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Blackburn, G.A.; Huang, J.; Kindred, D.; Huang, W. Applications of satellite ‘hyper-sensing’ in Chinese agriculture: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2018, 64, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 23, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z. Mapping Early, Middle and Late Rice Extent Using Sentinel-1A and Landsat-8 Data in the Poyang Lake Plain, China. Sensors 2018, 18, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Evolution of regional to global paddy rice mapping methods: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Ke, Y.; Chen, X. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Northeastern China Using Spatiotemporal Data Fusion and Phenology-Based Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Tan, J.; Zou, J. Regional scale mapping of fractional rice cropping change using a phenology-based temporal mixture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2703–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Alfieri, J.G.; Kustas, W.P.; Mueller, R.; Johnson, D.M.; Prueger, J.H. Toward mapping crop progress at field scales through fusion of Landsat and MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, H.K.; Song, H.H.; Wang, J.; Song, C.Q. Unified fusion of remote-sensing imagery: Generating simultaneously high-resolution synthetic spatial–temporal–spectral earth observations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, H.K. Spatio-temporal reflectance fusion via unmixing: Accounting for both phenological and land-cover changes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6213–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Lu, L. Object-Based Crop Classification with Landsat-MODIS Enhanced Time-Series Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16091–16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Mapping paddy rice planting area in rice-wetland coexistent areas through analysis of Landsat 8 OLI and MODIS images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2016, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, T. Mapping paddy rice in Jiangsu Province, China, based on phenological parameters and a decision tree model. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 13, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986–2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Biradar, C.M.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice croplands in China and India from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, L.; Xin, Q. High Resolution Mapping of Cropping Cycles by Fusion of Landsat and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Ding, C.; Liu, S. Mapping Rice Paddies in Complex Landscapes with Convolutional Neural Networks and Phenological Metrics. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, C.; Feng, Z. Mapping Rice Planted Area Using a New Normalized EVI and SAVI (NVI) Derived From Landsat-8 OLI. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, H.; et al. China’s wetland change (1990–2000) determined by remote sensing. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X. Changes in rice cropping systems in the Poyang Lake Region, China during 2004–2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.K.; Huang, B.; Zhang, M.; Cao, K.; Yu, L. A generalization of spatial and temporal fusion methods for remotely sensed surface parameters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4411–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Radeloff, V.C.; Ives, A.R. Improving the mapping of crop types in the Midwestern U.S. by fusing Landsat and MODIS satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Schwartz, M.D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, F.; Schaaf, C.B.; Tan, B.; Morisette, J.T.; Zhang, X. A Cross Comparison of Spatiotemporally Enhanced Springtime Phenological Measurements from Satellites and Ground in a Northern U.S. Mixed Forest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7513–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; He, L.; Salas, W.; Li, C.; Moore, B.; Zhao, R.; Frolking, S.; Boles, S. Quantitative relationships between field-measured leaf area index and vegetation index derived from VEGETATION images for paddy rice fields. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 23, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Biradar, C.; Czarnecki, C.; Alabi, T.; Keller, M. A Simple Algorithm for Large-Scale Mapping of Evergreen Forests in Tropical America, Africa and Asia. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E. Making better use of accuracy data in land change studies: Estimating accuracy and area and quantifying uncertainty using stratified estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Tan, Z.; Wang, G. A Rice Mapping Method Based on Time-Series Landsat Data for the Extraction of Growth Period Characteristics. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Tan, M. Paddy rice multiple cropping index changes in Southern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Metternicht, G.; Shen, W.; You, N.; Zhao, G.; Xiao, X. Are There Sufficient Landsat Observations for Retrospective and Continuous Monitoring of Land Cover Changes in China? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragettli, S.; Herberz, T.; Siegfried, T. An Unsupervised Classification Algorithm for Multi-Temporal Irrigated Area Mapping in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; Ienco, D.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Belhouchette, H.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Demarez, V. Mapping Irrigated Areas Using Sentinel-1 Time Series in Catalonia, Spain. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, N.; Baumann, M.; Ehammer, A.; Fensholt, R.; Grogan, K.; Hostert, P.; Jepsen, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Meyfroidt, P.; Mitchard, E.; et al. A Review of the Application of Optical and Radar Remote Sensing Data Fusion to Land Use Mapping and Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Ground Truth Pixels | Classified Pixels | User Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Paddies | Non-Rice | ||||
| Rice paddies | 1500 | 133 | 1633 | 91.86% | |
| Non-rice | 9 | 598 | 607 | 98.52% | |
| Ground truth pixels | 1509 | 731 | 2240 | OA = 93.66% | |
| Producer accuracy | 99.4% | 81.81% | Kappa = 0.85 | ||
| Ground Truth Pixels | Classified Pixels | User Accuracy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Cropping Rice | Double-Cropping Rice | Non-Rice | ||||
| Classified results | Single-cropping rice | 652 | 14 | 56 | 722 | 90.3% |
| Double-cropping rice | 2 | 832 | 77 | 911 | 91.33% | |
| Non-rice | 4 | 5 | 598 | 607 | 98.52% | |
| Ground truth pixels | 658 | 851 | 731 | 2240 | OA = 92.95% | |
| Producer accuracy | 99.09% | 97.77% | 81.81% | Kappa = 0.89 | ||
| Ground Truth Pixels | Classified Pixels | User Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Paddies | No-Rice | ||||
| Rice paddies | 1526 | 107 | 1633 | 93.45% | |
| Non-rice | 155 | 452 | 607 | 74.46% | |
| Ground truth pixels | 1681 | 559 | OA = 88.30% | ||
| Producer accuracy | 90.78% | 80.86% | Kappa = 0.70 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, M.; Guan, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
Ding M, Guan Q, Li L, Zhang H, Liu C, Zhang L. Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(6):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Mingjun, Qihui Guan, Lanhui Li, Huamin Zhang, Chong Liu, and Le Zhang. 2020. "Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 6: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022
APA StyleDing, M., Guan, Q., Li, L., Zhang, H., Liu, C., & Zhang, L. (2020). Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sensing, 12(6), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12061022