Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in the Three Most Developed Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Continuous Nighttime Light Data (2000–2018)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Construction of an Optimal Nighttime Light Index
2.3.2. Extracting Urban Areas by Determining Dynamic Thresholds of the NTL Image
2.3.3. Evolution Patterns of Urbanization
3. Results
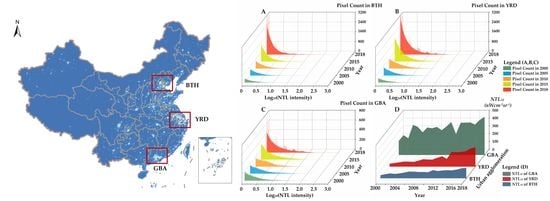
3.1. The Change in NTL Intensity during Rapid Urbanization
3.2. Variations in the Thresholds for Extracting Urban Areas
3.3. Urban Areas Derived from NTL Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution Patterns of Urban Areas
4.2. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization Based on Multiple Metrics
4.3. Limitations and Future Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects 2018: Key Facts; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anas, A.; Arnott, R.; Small, K.A. Urban spatial structure. J. Econ. Lit. 1998, 36, 1426–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Taubenböck, H.; Wurm, M.; Geiss, C.; Dech, S.; Siedentop, S. Urbanization between compactness and dispersion: Designing a spatial model for measuring 2D binary settlement landscape configurations. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Blei, A.M. The spatial structure of American cities: The great majority of workplaces are no longer in CBDs, employment sub-centers, or live-work communities. Cities 2016, 51, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Blaschke, T.; Luo, L.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.N.; Zhao, M.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban agglomerations in China during 2000–2012: A nighttime light approach. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. The History, Characteristics and prospects of regional urban cluster planning in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Region. Urban Plan. Forum 2019, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Urban ecology and sustainability: The state-of-the-science and future directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. Spatial pattern of China’s urban agglomerations: Theoretical background, formation mechanisms, and latest progress of research of dispersed regional concentration. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bonafoni, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect in a highly populated urban agglomeration area in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Important progress and prospects of china’s urbanization and urban agglomeration in the past 40 years of Reform and Opening-Up. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Gao, M.; Sun, Y. Research on the measurement and path of urban agglomeration growth effect. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portnov, B.A.; Schwartz, M. Urban clusters as growth foci. J. Reg. Sci. 2009, 49, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Roman, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Hobson, V.R.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Cocero, D. Satellite inventory of human settlements using nocturnal radiation emissions: A contribution for the global toolchest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1997, 3, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, D.J. Multi-scale analysis of the relationship between economic statistics and DMSP-OLS night light images. Giscience Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Mapping Urban Structure and Spatial Connectivity with VIIRS and OLS Night Light Imagery. In Proceedings of the Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event 2013, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 21–23 April 2013; pp. 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shuai, G.; Liu, H. Support vector data description model to map urban extent from National Polar-Orbiting Partnership Satellite-Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite nightlights and normalized difference vegetation index. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, S.; Du, J. A map spectrum-based spatiotemporal clustering method for GDP variation pattern analysis using nighttime light images of the Wuhan urban agglomeration. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Yu, C.; Meng, L. The city gravity migration of the urban agglomeration in the Middle Reach of Yangtze River based on DMSP nighttime light. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Kunming, China, 28–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Tani, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Mapping and evaluating the urbanization process in Northeast China using DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Sensors 2014, 14, 3207–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, B.; Joshi, P.K.; Seto, K.C. Monitoring urbanization dynamics in India using DMSP/OLS night time lights and SPOT-VGT data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Berrios, N.L.; Pares-Ramos, I.K.; Aide, T.M. Contrasting patterns of urban expansion in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia between 1992 and 2009. Ambio 2013, 42, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florida, R.; Mellander, C.; Gulden, T. Global metropolis: Assessing economic activity in urban centers based on nighttime satellite images. Prof. Geogr. 2012, 64, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. A robust method to generate a consistent time series from DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georg, I.; Blaschke, T.; Taubenböck, H. A global inventory of urban corridors based on perceptions and night-time light imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.J.; Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Mapping global urban areas from 2000 to 2012 using time-series nighttime light data and MODIS products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Monitoring urban clusters expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, using time-series nighttime light images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Dou, Y. Similarities and differences of city-size distributions in three main urban agglomerations of China from 1992 to 2015: A comparative study based on nighttime light data. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS nighttime light images: A meta-analysis and a systematic literature review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; He, C.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Elvidge, C.D.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C. Applications of satellite remote sensing of nighttime light observations: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Xiu, C. Normalization of time series DMSP-OLS nighttime light images for urban growth analysis with Pseudo Invariant Features. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Weng, Q.; Wang, K. Developing a new cross-sensor calibration model for DMSP-OLS and Suomi-NPP VIIRS night-light imageries. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 153, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiong, X.; Sun, C.; Chen, X.; Chiang, K. Suomi-NPP VIIRS day-night band on-orbit calibration and performance. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 036019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillger, D.; Kopp, T.; Lee, T.; Lindsey, D.; Seaman, C.; Miller, S.; Solbrig, J.; Kidder, S.; Bachmeier, S.; Jasmin, T.; et al. First-Light Imagery from Suomi NPP VIIRS. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.B.; Weiss, S.; Mills, S.; Hauss, B. Suomi NPP VIIRS day-night band on-orbit performance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12705–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W., III; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, P.K.R.; Maithani, S. Monitoring growth of built-up areas in Indo-Gangetic Plain using multi-sensor remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS ‘‘city lights’’ satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T. Paving the planet: Impervious surface as proxy measure of the human ecological footprint. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Han, L.; Du, S. Timely and accurate national-scale mapping of urban land in China using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System nighttime stable light data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.H.; Chi, W.F.; Lu, D.S.; Dou, Y.Y. A comparative analysis of megacity expansions in China and the U.S.: Patterns, rates and driving forces. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 132, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Theoretical foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Prog. Geogr. 2017, 36, 15–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. East Asia’s Changing Urban Landscape: Measuring a Decade of Spatial Growth; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.L.; Min, Z.; Cheng, Z.; XiaoMing, Z.; Chun, W.; Lu, C. Prospects of urban agglomeration in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Delta. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Tan, T. How urban agglomeration improve the emission efficiency? A spatial econometric analysis of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Li, S. Study on urban spatiotemporal expansion pattern of three first-class urban agglomerations in china derived from integrated DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1161–1174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency. Land Cover CCI Product User Guide Version 2. Tech. Rep. 2017. Available online: Maps.elie.ucl.ac.be/CCI/viewer/download/ESACCI-LC-Ph2-PUGv2_2.0.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X.; Li, H. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Huang, K.; Wang, N. Assessing spatiotemporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics in southeast asia using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.; Ichinose, T. The study on urbanization process in china based on DMSP/OLS Data: Development of a light index for urbanization level estimation. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 7, 168–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, H. Delta based on DMSP/OLS data. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2011, 3, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.; Chen, J.; Ichinose, T. Application of compound night light index derived from DMSP/OLS data to urbanization analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 893–902. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Gou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L. Detecting global urban expansion over the last three decades using a fully convolutional network. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Taubenböck, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Wurm, M. Urbanization in China from the end of 1980s until 2010-spatial dynamics and patterns of growth using EO-data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Vejre, H. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of remotely sensed region heat islands during the rapid urbanization (1995–2015) of Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y. Regional differences of China’s urban expansion from late 20th to early 21st century based on remote sensing information. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Detecting China’s urban expansion over the past three decades using nighttime light data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4095–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yao, L.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. How many metrics are required to identify the effects of the landscape pattern on land surface temperature? Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, G.; Cadenasso, M.L. Does spatial configuration matter? Understanding the effects of land cover pattern on land surface temperature in urban landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Qiao, M.J. Research on coordination of urbanization and driving forces of urban agglomeration in China based on nighttime light data. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Agro-geoinformatics (Agro-geoinformatics), Hangzhou, China, 6–9 August 2018; pp. 108–113. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ye, H.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J.; Meng, D. Coupling analysis of the thermal landscape and environmental carrying capacity of urban expansion in Beijing (China) over the past 35 years. Sustainability 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Weigand, M.; Esch, T.; Staab, J.; Wurm, M.; Mast, J.; Dech, S. A new ranking of the world’s largest cities-Do administrative units obscure morphological realities? Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; He, X.; Jendryke, M. A preliminary investigation of Luojia-1 night-time light imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Mapping urban extent using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallner, S.; Kocifaj, M. Impacts of surface albedo variations on the night sky brightness—A numerical and experimental analysis. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 239, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wurm, M.; Huang, X.; Zhong, T.; Leichtle, T.; Taubenböck, H. Urbanization that hides in the dark—Spotting China’s “ghost neighborhoods” from space. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 200, 103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Urban Agglomeration | Total Area (km2) | Core Cities | Total Population (Million) | Percentage of Urban Population (%) | GDP (Billion USD) | GDP per Capita (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration (BTH) | 218,000 | Beijing, Tianjin | 107.57 (90.26) | 65.84 (38.97) | 1282.67 (124.06) | 11,089.24 (1364.07) |
| The Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration (YRD) | 359,000 | Shanghai | 225.36 (195.53) | 67.26 (42.51) | 3195.81 (271.66) | 14,229.61 (1375.56) |
| The Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) | 56,000 | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong | 71.09 (49.99) | 84.33 (72.90) | 1653.96 (307.91) | 24,310.08 (5908.35) |
| NTL Index | Pearson Correlation Coefficients (Significance: Two-Tailed) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Metrics | Population Metrics | Land-Use Metrics | ||||||
| GDP | GDP per Capita | Proportion of Non-Agricultural Industry Product in GDP | Population Density | Urban Population Density | Ratio of Urban Population | Construction Land Area | Built-Up Area | |
| Luminous Area | 0.067 | 0.268 * | 0.088 | 0.725 | 0.329 | 0.068 | 0.507 | 0.611 |
| (0.599) | (0.028) | (0.634) | (0.096) | (0.635) | (0.836) | (0.432) | (0.371) | |
| Average NTL intensity | 0.928 ** | 0.896 ** | 0.593 ** | 0.851 ** | 0.643 ** | 0.379 * | 0.753 * | 0.803 ** |
| (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.042) | (0.017) | (0.003) | |
| Total NTL intensity | 0.830 ** | 0.892 * | 0.482 * | 0.809 ** | 0.631 ** | 0.436 | 0.648 * | 0.705 ** |
| (0.000) | (0.028) | (0.023) | (0.006) | (0.000) | (0.129) | (0.043) | (0.000) | |
| Composited NTL index | 0.855 ** | 0.830 ** | 0.477 | 0.793 ** | 0.603 | 0.357 | 0.681 * | 0.763 |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.063) | (0.000) | (0.227) | (0.085) | (0.048) | (0.067) | |
| Region | Year | Short Axis (X) (km) | Long Axis (Y) (km) | Latitude of Center Point | Longitude of Center Point | Rotation | Cohesion Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTH | 2000 | 97.95 | 219.23 | 39°03′24″ | 116°15′21″ | 23.53 | 90.12 |
| 2005 | 98.02 | 217.88 | 38°59′06″ | 116°14′50″ | 23.00 | 90.80 | |
| 2010 | 100.06 | 218.47 | 38°55′15″ | 116°16′04″ | 21.83 | 90.86 | |
| 2015 | 101.96 | 220.62 | 38°53′00″ | 116°16′53″ | 20.72 | 89.91 | |
| 2018 | 103.67 | 220.26 | 38°53′12″ | 116°18′30″ | 20.98 | 91.25 | |
| YRD | 2000 | 151.17 | 317.22 | 31°15′10″ | 119°48′34″ | 139.43 | 87.17 |
| 2005 | 154.33 | 330.65 | 31°29′16″ | 119°30′54″ | 139.10 | 86.24 | |
| 2010 | 151.84 | 320.33 | 31°33′23″ | 119°31′57″ | 138.80 | 89.18 | |
| 2015 | 146.61 | 314.32 | 31°32′07″ | 119°38′08″ | 138.57 | 91.62 | |
| 2018 | 147.85 | 309.61 | 31°31′41″ | 119°37′44″ | 138.35 | 92.83 | |
| GBA | 2000 | 72.72 | 45.65 | 22°51′45″ | 113°31′40″ | 96.82 | 93.88 |
| 2005 | 71.34 | 46.50 | 22°52′17″ | 113°34′32″ | 92.66 | 97.37 | |
| 2010 | 71.33 | 47.90 | 22°52′41″ | 113°32′04″ | 91.74 | 98.52 | |
| 2015 | 71.77 | 49.11 | 22°52′47″ | 113°30′51″ | 91.21 | 98.94 | |
| 2018 | 71.59 | 49.74 | 22°52′44″ | 113°30′11″ | 89.70 | 99.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ye, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Leng, X.; Meng, D.; Zheng, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in the Three Most Developed Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Continuous Nighttime Light Data (2000–2018). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122245
Li Y, Ye H, Gao X, Sun D, Li Z, Zhang N, Leng X, Meng D, Zheng J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in the Three Most Developed Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Continuous Nighttime Light Data (2000–2018). Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(12):2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu, Haipeng Ye, Xing Gao, Dongqi Sun, Zehong Li, Ninghui Zhang, Xuejing Leng, Dan Meng, and Ji Zheng. 2021. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in the Three Most Developed Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Continuous Nighttime Light Data (2000–2018)" Remote Sensing 13, no. 12: 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122245
APA StyleLi, Y., Ye, H., Gao, X., Sun, D., Li, Z., Zhang, N., Leng, X., Meng, D., & Zheng, J. (2021). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in the Three Most Developed Urban Agglomerations in China Based on Continuous Nighttime Light Data (2000–2018). Remote Sensing, 13(12), 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122245