Recommendations for HCHO and SO2 Retrieval Settings from MAX-DOAS Observations under Different Meteorological Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrument
2.2. Observation Site
2.3. DOAS Analysis
2.4. Ancillary Data
2.5. Error Estimation
2.6. TROPOMI Satellite Observations
2.7. EMI satellite Observations
3. Results
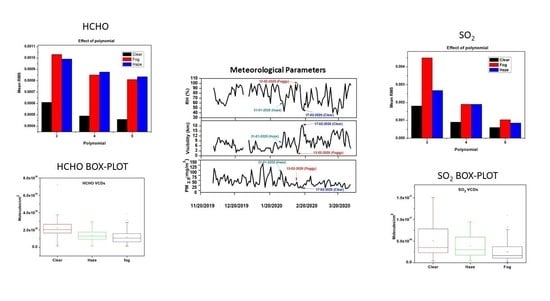
3.1. HCHO Retrieval Settings
3.2. SO2 Retrieval Settings
3.3. HCHO and SO2 Column Densities over NUIST Nanjing
3.4. Satellite Validation
3.4.1. Comparison of HCHO Columns
3.4.2. Comparison of SO2 Columns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almqvist, E. Remote sensing of gaseous air pollution. Ambio 1974, 3, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy. In Physics of Earth and Space Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, A.W.; McElroy, C.T.; Kerr, J.B. Nitrogen dioxide concentration in the atmosphere. Nature 1973, 246, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noxon, J.F. Nitrogen dioxide in the stratosphere and troposphere measured by ground-based absorption spectroscopy. Science 1975, 189, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, D.; Ehhalt, D.H.; Pätz, H.W.; Platt, U.; Röth, E.P.; Volz, A. OH–Radicals in the lower troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1976, 3, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Perner, D.; Pätz, H.W. Simultaneous measurement of atmospheric CH2O, O3, and NO2by differential optical absorption. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1979, 84, 6329–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, L.; Sihler, H.; Lampel, J.; Wagner, T.; Platt, U. Retrieval interval mapping: A tool to visualize the impact of the spectral retrieval range on differential optical absorption spectroscopy evaluations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Che, H.; Zhong, J.; Chu, Y.; Cheng, L. Temporal and spatial variations of haze and fog and the characteristics of PM2.5 during heavy pollution episodes in China from 2013 to 2018. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kumar, K.R.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over the urban-industrial megacity Nanjing in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17532–17552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Ma, J.; An, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Cui, H. Impacts of meteorological condition and aerosol chemical compositions on visibility impairment in Nanjing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Fan, S.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, F. Particle size distribution and characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during a heavy haze episode in Nanjing, China. Particuology 2015, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Ji, Y. Variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric PM2.5 during winter haze period around 2014 Chinese Spring Festival at Nanjing: Insights of source changes, air mass direction and firework particle injection. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 520, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Ullah, K.; Tan, W.; Xing, C.; Liu, H. Investigating the Effect of Different Meteorological Conditions on MAX-DOAS Observations of NO2 and CHOCHO in Hefei, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Liu, J. A new method to determine the aerosol optical properties from multiple-wavelength O4 absorptions by MAX-DOAS observation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, R.G.; Silver, J.D.; Querel, R.; Smale, D.; Rhodes, S.; Tully, M.; Jones, N.; Schofield, R. Comparison of formaldehyde tropospheric columns in Australia and New Zealand using MAX-DOAS, FTIR and TROPOMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6501–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Rood, R.; Lin, S.-J.; Müller, J.-F.; Thompson, A.M. Atmospheric sulfur cycle simulated in the global model GOCART: Model description and global properties. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 24671–24687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.-Y.; Yuan, T.-H.; Shie, R.-H.; Chen, C.-F.; Chan, C.-C. Increased incidence of allergic rhinitis, bronchitis and asthma, in children living near a petrochemical complex with SO2pollution. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- aved, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Tanvir, A.; Rehman, A.; Ji, X.; Xing, C.; Shakoor, A.; Liu, C. Investigating the Impacts of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Trace Gases Using Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3939. [Google Scholar]
- Danckaert, T.; Fayt, C.; Van Roozendael, M.; De Smedt, I.; Letocart, V.; Merlaud, A.; Pinardi, G. QDOAS Software User Manual; Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, K.; Kurucz, R. An improved high-resolution solar reference spectrum for earth’s atmosphere measurements in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, R.; Moortgat, G.K. Temperature dependence of the absorption cross sections of formaldehyde between 223 and 323 K in the wavelength range 225-375 nm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 7089–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandaele, A.C.; Hermans, C.; Simon, P.C.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R.; Fally, S.; Merienne, M.-F.; Jenouvrier, A.; Coquart, B. Measurements of the NO2 absorption cross-section from 42000 cm−1 to 10000 cm−1 (238–1000 nm) at 220 K and 294 K. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 59, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serdyuchenko, A.; Gorshelev, V.; Weber, M.; Chehade, W.; Burrows, J.P. High spectral resolution ozone absorption cross-sections–Part 2: Temperature dependence. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thalman, R.; Volkamer, R. Temperature dependent absorption cross-sections of O2–O2 collision pairs between 340 and 630 nm and at atmospherically relevant pressure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15371–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, O.C.; Hartmann, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Orphal, J. New ultraviolet absorption cross-sections of BrO at atmospheric temperatures measured by time-windowing Fourier transform spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 168, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Schmeltekopf, A.L.; Sanders, R.W. On the interpretation of zenith sky absorption measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 8311–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Ibrahim, O.; Shaiganfar, R.; Platt, U. Mobile MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric trace gases. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celarier, E.A.; Brinksma, E.J.; Gleason, J.F.; Veefkind, J.P.; Cede, A.; Herman, J.R.; Ionov, D.; Goutail, F.; Pommereau, J.-P.; Lambert, J.-C.; et al. Validation of Ozone Monitoring Instrument nitrogen dioxide columns. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, W.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Ji, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. An improved TROPOMI tropospheric HCHO retrieval over China. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6271–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, C.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, F.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. First sulfur dioxide observations from the environmental trace gases monitoring instrument (EMI) onboard the GeoFen-5 satellite. Sci. Bull. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Khokhar, M.F.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Subhani, M.A.; Rehman, A.; Tanvir, A. Investigating the impact of Glyoxal retrieval from MAX-DOAS observations during haze and non-haze conditions in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, S.F.; Richter, A.; Peters, E.; Ostendorf, M.; Schmalwieser, A.W.; Weihs, P.; Burrows, J.P. Dual ground-based MAX-DOAS observations in Vienna, Austria: Evaluation of horizontal and temporal NO2, HCHO, and CHOCHO distributions and comparison with independent data sets. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 5, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreher, K.; Van Roozendael, M.; Hendrick, F.; Apituley, A.; Dimitropoulou, E.; Frieß, U.; Richter, A.; Wagner, T.; Lampel, J.; Abuhassan, N.; et al. Intercomparison of NO2, O4, O3 and HCHO slant column measurements by MAX-DOAS and zenith-sky UV–visible spectrometers during CINDI-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2169–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Dou, K.; Fan, G.; Huang, S.; Si, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Pei, C.; Tang, F.; Yang, D.; et al. Vertical distributions of tropospheric formaldehyde, nitrogen dioxide, ozone and aerosol in southern China by ground-based MAX-DOAS and LIDAR measurements during PRIDE-GBA 2018 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A.; Heue, K.-P.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Hao, N.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Nanjing and a comparison to ozone monitoring instrument observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 10051–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; van Geffen, J.; De Smedt, I.; Alberti, C.; Cheng, Z.; Ye, S.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Munich and the comparison to OMI and TROPOMI satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4499–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Xing, C.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Xia, C.; Liu, H.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J. Tropospheric NO2, SO2, and HCHO over the East China Sea, using ship-based MAX-DOAS observations and comparison with OMI and OMPS satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 15387–15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Hu, Z. Long-term observations of tropospheric NO2, SO2 and HCHO by MAX-DOAS in Yangtze River Delta area, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hendrick, F.; Wang, P.; Tang, G.; Clémer, K.; Yu, H.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Gielen, C.; Muller, J.-F.; et al. Evaluation of tropospheric SO2 retrieved from MAX-DOAS measurements in Xianghe, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 11149–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreier, S.; Peters, E.; Richter, A.; Lampel, J.; Wittrock, F.; Burrows, J. Ship-based MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and SO2 in the South China and Sulu Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Su, W.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J. Long-distance mobile MAX-DOAS observations of NO2 and SO2 over the North China Plain and identification of regional transport and power plant emissions. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Khokhar, M.F.; Tan, W.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; Ji, X.; Tanvir, A.; Hong, Q.; Sandhu, O.; et al. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations of CHOCHO and HCHO in Beijing and Baoding, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Guo, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z. Study on pollution behavior and sulfate formation during the typical haze event in Nanjing with water soluble inorganic ions and sulfur isotopes. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Qiu, Z.; Jäkel, E.; Campbell, J.R.; Atique, L.; Huang, X.; Lolli, S. A Simplified and robust surface reflectance estimation method (SREM) for use over diverse land surfaces using multi-sensor data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanvir, A.; Javed, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Xue, R.; Wang, S.; Bin, Z. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO during COVID-19 lockdown and spring festival over Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, G.; Van Roozendael, M.; Abuhassan, N.; Adams, C.; Cede, A.; Clémer, K.; Fayt, C.; Frieß, U.; Gil, M.; Herman, J.; et al. MAX-DOAS formaldehyde slant column measurements during CINDI: Intercomparison and analysis improvement. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 6, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rix, M.; Valks, P.; Hao, N.; Loyola, D.; Schlager, H.; Huntrieser, H.; Flemming, J.; Koehler, U.; Schumann, U.; Inness, A. Volcanic SO2, BrO and plume height estimations using GOME-2 satellite measurements during the eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in May 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, Z.Y.; McLaren, R. Recommendations for spectral fitting of SO2 from MAX-DOAS measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, Y.; Mueller, S.; Knipping, E. Diagnosis of an underestimation of summertime sulfate using the Community Multiscale Air Quality model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5119–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigouroux, C.; Langerock, B.; Bauer Aquino, C.A.; Blumenstock, T.; Cheng, Z.; De Mazière, M.; De Smedt, I.; Grutter, M.; Hannigan, J.W.; Jones, N.; et al. TROPOMI–Sentinel-5 Precursor formaldehyde validation using an extensive network of ground-based Fourier-transform infrared stations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3751–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameters | Data Source | Trace Gases | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | HCHO | ||
| HCHO | 297 K, [21] | ✓ | ✓ |
| NO2 | 220 K, [22] | ✓ | ✓ |
| SO2 | 298 K, [22] | ✓ | X |
| O3 | 243 K, [23] | ✓ | ✓ |
| O3 | 223 K, [23] | ✓ | ✓ |
| O4 | 293 K, [24] | X | ✓ |
| BrO | 223 K, [25] | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ring | Calculated with QDOAS | ✓ | ✓ |
| Polynomial degree | 5 | 5 | |
| Meteorological Condition | Visibility | PM 2.5 | Relative Humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear days | >10 km | <40 µg/m3 | <80% |
| Haze days | >5 km and <10 km | >40 µg/m3 | <80% |
| Fog days | <5 km | >40 µg/m3 | >80% |
| Fitting Window | Clear Days | Foggy Days | Haze Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | |
| 336.5–359 nm | 0.0005 | 3.87 × 1015 | 0.00072 | 5.93 × 1015 | 0.00063 | 5.27 × 1015 |
| 324.5–359 nm | 0.00049 | 1.70 × 1015 | 0.00070 | 2.73 × 1015 | 0.00061 | 2.12 × 1015 |
| Fitting Window | Clear Days | Foggy Days | Haze Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | Mean RMS | Mean Fit Error | |
| 305–317 nm | 0.0019 | 3.93 × 1015 | 0.0042 | 8.93 × 1015 | 0.0026 | 5.59 × 1015 |
| 307–328 nm | 0.0008 | 1.77 × 1015 | 0.0013 | 3.87 × 1015 | 0.0009 | 2.27 × 1015 |
| 312–326 nm | 0.0010 | 2.36 × 1015 | 0.0020 | 7.34 × 1015 | 0.0011 | 4.51 × 1015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, Z.; Tanvir, A.; Bilal, M.; Su, W.; Xia, C.; Rehman, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sandhu, O.; Xing, C.; Ji, X.; et al. Recommendations for HCHO and SO2 Retrieval Settings from MAX-DOAS Observations under Different Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122244
Javed Z, Tanvir A, Bilal M, Su W, Xia C, Rehman A, Zhang Y, Sandhu O, Xing C, Ji X, et al. Recommendations for HCHO and SO2 Retrieval Settings from MAX-DOAS Observations under Different Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(12):2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122244
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Zeeshan, Aimon Tanvir, Muhammad Bilal, Wenjing Su, Congzi Xia, Abdul Rehman, Yuanyuan Zhang, Osama Sandhu, Chengzhi Xing, Xiangguang Ji, and et al. 2021. "Recommendations for HCHO and SO2 Retrieval Settings from MAX-DOAS Observations under Different Meteorological Conditions" Remote Sensing 13, no. 12: 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122244
APA StyleJaved, Z., Tanvir, A., Bilal, M., Su, W., Xia, C., Rehman, A., Zhang, Y., Sandhu, O., Xing, C., Ji, X., Xie, M., Liu, C., & Wang, Y. (2021). Recommendations for HCHO and SO2 Retrieval Settings from MAX-DOAS Observations under Different Meteorological Conditions. Remote Sensing, 13(12), 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122244