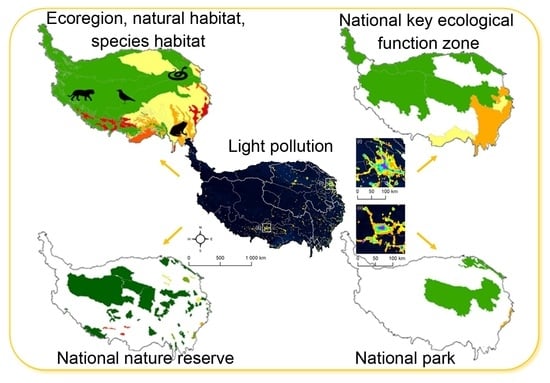
Spatiotemporal Patterns of Light Pollution on the Tibetan Plateau over Three Decades at Multiple Scales: Implications for Conservation of Natural Habitats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. Extraction of the LP Range
3.2. Validation of the LP Range
3.3. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Patterns of LP
4. Results
4.1. Validation of the LP Range
4.2. Changes in LP on the TP from 1992 to 2018
4.3. Changes in LP at Different Scales
4.4. LP for Different Habitat Typess
4.5. LP for Different Species Habitats
5. Discussion
5.1. Main Reasons for the Increase in the LP Range
5.2. Policy Implications
5.3. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longcore, T.; Rich, C. Ecological light pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encyclopædia Britannica. Light Pollution. 2020. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/light-pollution (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Peregrym, M.; Pénzesné Kónya, E.; Falchi, F. Very important dark sky areas in Europe and the Caucasus region. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svechkina, A.; Portnov, B.A.; Trop, T. The impact of artificial light at night on human and ecosystem health: A systematic literature review. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Cruse, D.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Artificial light at night causes top-down and bottom-up trophic effects on invertebrate populations. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Fournari-Konstantinidou, I.; Sourbes, L.; Koutsoubas, D.; Mazaris, A.D. Reduction of sea turtle population recruitment caused by nightlight: Evidence from the Mediterranean region. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 153, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominoni, D.; Smit, J.A.H.; Visser, M.E.; Halfwerk, W. Multisensory pollution: Artificial light at night and anthropogenic noise have interactive effects on activity patterns of great tits (Parus major). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Somers-Yeates, R.; Bennie, J.; Economou, T.; Hodgson, D.; Spalding, A.; McGregor, P.K. Light pollution is associated with earlier tree budburst across the United Kingdom. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubisic, M.; van Grunsven, R.H.A.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Manfrin, A.; Holker, F. Insect declines and agroecosystems: Does light pollution matter? Ann. Appl. Biol. 2018, 173, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, A.; Zubidat, A.E. Artificial light at night: Melatonin as a mediator between the environment and epigenome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Gao, J.; Li, L.; Hou, P. Human pressure dynamics in protected areas of China based on nighttime light. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, E.; Bongiorni, L.; Fontanini, D.; Capocchi, A.; Dal Bello, M.; Giacomelli, A.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Artificial light at night erases positive interactions across trophic levels. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massetti, L. Assessing the impact of street lighting on Platanus x acerifolia phenology. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvareninova, J.; Tuharska, M.; Skvarenina, J.; Babalova, D.; Slobodnikova, L.; Slobodnik, B.; Stredova, H.; Mindas, J. Effects of light pollution on tree phenology in the urban environment. Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2017, 25, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touitou, Y.; Reinberg, A.; Touitou, D. Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption. Life Sci. 2017, 173, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Pan, J.M. Wavelength-specific artificial light disrupts molecular clock in avian species: A power-calibrated statistical approach. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Kuester, T.; Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Baugh, K.; Jechow, A.; Hölker, F.; Bennie, J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Gaston, K.J.; Guanter, L. Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koen, E.L.; Minnaar, C.; Roever, C.L.; Boyles, J.G. Emerging threat of the 21st century lightscape to global biodiversity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Bai, W.; Ding, M.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, E.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of land use and cover change on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Ni, L.; Jiang, X.G.; Fang, S.F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.P. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Changes Along the Belt and Road Initiative Region From 1982 to 2015. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122579–122588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, W.P.; Wu, M.Q.; Liu, K.; Yu, X.M.; Gao, J. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Ecological-Economic Impacts in the Belt and Road Initiatives Mining Project: A Case Study in Sino Iron and Taldybulak Levoberezhny. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Chidthaisong, A.; Limsakul, A.; Varnakovida, P.; Ekkawatpanit, C.; Diem, P.K.; Diep, N.T.H. How do disparate urbanization and climate change imprint on urban thermal variations? A comparison between two dynamic cities in Southeast Asia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Aryal, J.; Tan, L.C.; Jin, L.; Gao, Z.H.; Wang, Y.Q. Comparison of changes in vegetation and land cover types between Shenzhen and Bangkok. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Mapping human influence intensity in the Tibetan Plateau for conservation of ecological service functions. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challéat, S.; Barré, K.; Laforge, A.; Lapostolle, D.; Franchomme, M.; Sirami, C.; Le Viol, I.; Milian, J.; Kerbiriou, C. Grasping darkness: The dark ecological network as a social-ecological framework to limit the impacts of light pollution on biodiversity. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Liang, E.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Niu, B. Response feedback of Tibetan Plateau ecosystem to climate change. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2842–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y.; Du, Y. Dynamic monitoring and analysis of ecological environment quality in Sanjiangyuan region based on Google Earth Engine platform. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X. Assessment of Night-Time Lighting for Global Terrestrial Protected and Wilderness Areas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Rehman, S.; Sajjad, H.; Tripathy, B.R.; Rani, M.; Singh, S. Analyzing trend in artificial light pollution pattern in India using NTL sensor’s data. Urban Clim. 2019, 27, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Cruz, S.A.; Smolinsky, J.A.; Buler, J.J. Light pollution is greatest within migration passage areas for nocturnally-migrating birds around the world. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morshed, M.M.; Chakraborty, T.; Mazumder, T. Measuring Dhaka‘s Urban Transformation Using Nighttime Light Data. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2022, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- China Statistical Yearbook 2001–2020; National Bureau of Statistics: Beijing, China, 2001–2020.
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalles, V.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Parker, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Pickens, A.H.; Parente, L.L.; Ferreira, L.G.; Song, X.P.; Hernandez-Serna, A.; et al. Rapid expansion of human impact on natural land in South America since 1985. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.N.; Underwood, E.C.; D’Amico, J.A.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth. BioScience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. National and Regional Functional Zones Are Planned; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Global 1:1 Million Glacier Dataset. National Cryophere Desert Data Center. 2013. Available online: http://www.ncdc.ac.cn (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Urban Distribution and Urbanization Index Dataset on the Tibetan Plateau (2019); National Data Center for Tibetan Plateau Science: Beijing, China, 2019; Available online: http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, D. Characterizing spatiotemporal patterns of air pollution in China: A multiscale landscape approach. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.R.; Clark, M.; Buchanan, G.M.; Ficetola, G.F.; Rondinini, C.; Tilman, D. Proactive conservation to prevent habitat losses to agricultural expansion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 4, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Huang, J.; Su, W.; Hu, T.; Wen, Y.; Yin, P.; Han, Y.; Xue, F. Evaluation of Light Pollution in Global Protected Areas from 1992 to 2018. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Kareiva, P.; Forman, R.T.T. The implications of current and future urbanization for global protected areas and biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J. Ecological Corridor Construction Based on Least-Cost Modeling Using Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Nighttime Light Data and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Land 2021, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, K.J.; Davies, T.W.; Bennie, J.; Hopkins, J. REVIEW: Reducing the ecological consequences of night-time light pollution: Options and developments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamrowski, R.L.; Sutton, S.G.; Tobin, R.C.; Hamann, M. Balancing artificial light at night with turtle conservation? Coastal community engagement with light-glow reduction. Environ. Conserv. 2014, 42, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. The Dynamic Analysis and Comparison of Emergy Ecological Footprint for the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: A Case Study of Qinghai Province and Tibet. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, L.; Tian, L.; Ao, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of human disturbance on vegetation cover change in Tibetan Plateau. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, T.M.; Mittermeier, R.A.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Gerlach, J.; Hoffmann, M.; Lamoreux, J.F.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Pilgrim, J.D.; Rodrigues, A.S. Global Biodiversity Conservation Priorities. Science 2006, 313, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, W.; He, G.; Jiang, W. Investigating the Spatiotemporal Variability and Driving Factors of Artificial Lighting in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Using Remote Sensing Imagery and Socioeconomic Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Category (Abbreviation) | Mammals | Birds | Reptiles | Amphibians | Nocturnal Species | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Deficient (DD) | 24 | 2 | 8 | 26 | 7 | 60 |
| Least Concern (LC) | 285 | 931 | 100 | 91 | 103 | 1407 |
| Near Threatened (NT) | 29 | 52 | 1 | 16 | 6 | 98 |
| Vulnerable (VU) | 28 | 41 | 4 | 17 | 6 | 90 |
| Endangered (EN) | 20 | 15 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 45 |
| Critically Endangered (CR) | 2 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Total | 388 | 1050 | 117 | 159 | 122 | 1714 |
| Natural Habitat | Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | |
| Grassland | 552 (46.9%) | 855 (49.9%) | 1903 (50.5%) | 4583 (51.7%) | 6860 (51.1%) | 22,144 (49.9%) | 44,424 (54.7%) |
| Forest | 90 (7.6%) | 152 (8.9%) | 695 (18.4%) | 1928 (21.8%) | 3207 (23.9%) | 13,574 (30.6%) | 21,096 (26.0%) |
| Desert | 265 (22.5%) | 352 (20.6%) | 488 (13.0%) | 785 (8.9%) | 1096 (8.2%) | 3558 (8.0%) | 7395 (9.1%) |
| Wetland | 31 (2.6%) | 35 (2.0%) | 88 (2.3%) | 163 (1.8%) | 230 (1.7%) | 611 (1.4%) | 999 (1.2%) |
| Ice | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 254 (0.3%) |
| Sum | 938 (79.6%) | 1394 (81.4%) | 3174 (84.3%) | 7459 (84.2%) | 11,393 (84.9%) | 39,887 (89.8%) | 74,168 (91.4%) |
| ID in Figure 5c | Name | Abbreviation | Major Source of Light Pollution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lalu Wetland | LW | Chengguan Distract in Lhasa city |
| 2 | Gansu Lianhua Mountain | GLM | Xiacheng town, Lianlu town |
| 3 | Xunhua Mengda | XM | Dahejia town |
| 4 | Longbao | Longbao | Longbao town |
| 5 | Black-necked crane of Brahmaputra River | BNCBR | Lhunzhub county, Maizhuokunggar county, Shigatse city, Road from Lhasa to Lhunzhub (G561), Road from Lhasa to Maizhuokunggar (G349) |
| 6 | Wolong | Wolong | Wolong town, Genda town |
| 7 | Four Girls Mountain | FGM | Siguniangshan town, Dawei town |
| 8 | Haloxylon forest in Qinghai-chaidam | HFIQC | Beijing-tibet highway (G6), Road from Beijing to Lhasa (G109) |
| 9 | Baihe | Baihe | Jiuhong road (S301) |
| 10 | Taizi mountains | TM | Songming town |
| 11 | The source region of rivers in the north of Datong | SRRND | Road from Xining to Zhangye (G227) |
| 12 | Gahai-zecha | GZ | Road from Gahai to Maqu (S204), Gaxiu village, Gahai village, Gongba village, Langmushi town |
| 13 | Gexigou | Gexigou | Yajing county, Xiangkezong |
| 14 | Duoer | Duoer | Road from Lianghekou to Maqu (S313) |
| 15 | Gongga Mountain | GM | Kangding city |
| 16 | Qinghai Lake | QL | Road from Beijing to Lhasa (G109) |
| 17 | Mangkang Yunnan snub-nosed monkey | MYSNM | Rumei town, Naxi nationality Town, Quzika Town |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Lv, C.; Pan, X.; Liu, Z.; Xia, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Light Pollution on the Tibetan Plateau over Three Decades at Multiple Scales: Implications for Conservation of Natural Habitats. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225755
Wang Y, Lv C, Pan X, Liu Z, Xia P, Zhang C, Liu Z. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Light Pollution on the Tibetan Plateau over Three Decades at Multiple Scales: Implications for Conservation of Natural Habitats. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225755
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yihang, Caifeng Lv, Xinhao Pan, Ziwen Liu, Pei Xia, Chunna Zhang, and Zhifeng Liu. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Light Pollution on the Tibetan Plateau over Three Decades at Multiple Scales: Implications for Conservation of Natural Habitats" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225755
APA StyleWang, Y., Lv, C., Pan, X., Liu, Z., Xia, P., Zhang, C., & Liu, Z. (2022). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Light Pollution on the Tibetan Plateau over Three Decades at Multiple Scales: Implications for Conservation of Natural Habitats. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5755. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225755