High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Notations
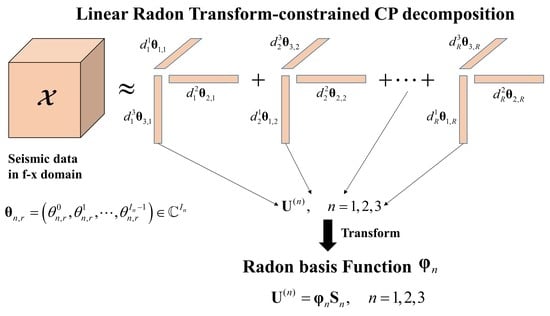
2.2. Tensor CPD Method and Linear Radon Transform
2.2.1. Tensor CPD Method
2.2.2. Linear Radon Transform
2.3. Linear Radon Transform–Constrained CPD for Tensor Completion
- 1.
- Update .
- 2.
- Update .
- 3.
- Update .
- 4.
- Update .
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis Data Experiment
3.2. Field Data Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Abma, R.; Claerbout, J. Lateral prediction for noise attenuation by t-x and f-x techniques. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornbostel, S.C. Spatial prediction filtering in the t-x and f-x domains. Geophysics 1991, 56, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulunay, N. FXDECON and complex wiener prediction filter. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1986; pp. 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H. High-dimensional center filtering method based on block matching. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 4580–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, V.E.; Sacchi, M.D. Multifrequency singular spectrum analysis. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 3193–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, V.E.; Sacchi, M.D. A randomized SVD for Multichannel Singular Spectrum Analysis (MSSA) noise attenuation. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Gan, S. Damped multichannel singular spectrum analysis for 3D random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2016, 81, V261–V270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickett, S.R. F-xy eigenimage noise suppression. Geophysics 2003, 68, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolda, T.G.; Bader, B.W. Tensor Decompositions and Applications. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 455–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, A.; Mandic, D.; Phan, A.-H.; Caiafa, C.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Q.; Lathauwer, L. Tensor Decompositions for Signal Processing Applications From Two-way to Multiway Component Analysis. Signal Process. Mag. IEEE 2014, 32, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, M.E.; Martin, C.D. Factorization strategies for third-order tensors. Linear Algebra Appl. 2011, 435, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreimer, N.; Sacchi, M.D. A tensor higher-order singular value decomposition for prestack seismic data noise reduction and interpolation. Geophysics 2012, 77, V113–V122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, N.; Stanton, A.; Sacchi, M.D. Tensor completion based on nuclear norm minimization for 5D seismic data reconstruction. Geophysics 2013, 78, V273–V284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ely, G.; Aeron, S.; Hao, N.; Kilmer, M.E. 5D seismic data completion and denoising using a novel class of tensor decompositions. Geophysics 2015, 80, V83–V95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitchcock, F.L. The Expression of a Tensor or a Polyadic as a Sum of Products. J. Math. Phys. 1927, 6, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, R.A. Foundations of the PARAFAC procedure: Models and conditions for an “explanatory” multi-model factor analysis. UCLA Work. Pap. Phon. 1970, 16, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.D.; Chang, J.-J. Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an n-way generalization of “Eckart-Young” decomposition. Psychometrika 1970, 35, 283–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sacchi, M. Incoherent noise attenuation via randomized CP decomposition. In 2017 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 5006–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, B. Vandermonde constrained CANDECOMP/PARAFAC tensor decomposition for high-dimensional seismic data reconstruction. Geophysics 2022, 87, V533–V544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ulrych, T.J. Physical Wavelet Frame Denoising. Geophysics 2003, 68, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, H. Comparisons of wavelets, contourlets and curvelets in seismic denoising. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, T.S.; Bisset, D. The Radon transform and its properties. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trad, D.; Ulrych, T.; Sacchi, M. Latest views of the sparse Radon transform. Geophysics 2003, 68, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H. High-Resolution Linear Radon Transformation with L0-norm Constraint. In Proceedings of the Beijing 2014 International Geophysical Conference & Exposition, Beijing, China, 21–24 April 2014; pp. 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Geng, J. A Robust and Efficient Sparse Time-Invariant Radon Transform in the Mixed Time–Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7558–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.J.; Böniger, U.; Verschuur, D.J. Non-linear primary-multiple separation with directional curvelet frames. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, F.; Hennenfent, G. Non-parametric seismic data recovery with Curvelet frames. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.-X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Geophysical data sparse reconstruction based on L0-norm minimization. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, C.; Han, X. 2-D TFPF based on Contourlet transform for seismic random noise attenuation. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 129, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehui, K.; Peng, Z. Seismic random noise attenuation using shearlet and total generalized variation. J. Geophys. Eng. 2015, 12, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X. AVO-preserving data reconstruction by 3D high-order sparse-parabolic Radon transform. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 4338–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tang, W. 3D high-order sparse radon transform with L1–2 minimization for multiple attenuation. Geophys. Prospect. 2022, 70, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, T.H. Enhancement of large faults with a windowed 3D Radon transform filter. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2012; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Qu, Y. The 3D conical Radon transform for seismic signal processing. Geophysics 2022, 87, V481–V504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radon, J.; Parks, P.; Clark, C. On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, B.; Neal, P.; Eric, C.; Borja, P.; Jonathan, E. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.-J.; So, H.C. Outlier-Robust Matrix Completion via Lp-Minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 66, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A.T. A New TwIST: Two-Step Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding Algorithms for Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, J.; Cai, J.F.; Guo, D.; Tang, G.; Chen, Z.; Qu, X. Vandermonde Factorization of Hankel Matrix for Complex Exponential Signal Recovery—Application in Fast NMR Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 5520–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, K. High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
Ouyang Z, Zhang L, Wang H, Yang K. High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Zhiyuan, Liqi Zhang, Huazhong Wang, and Kai Yang. 2022. "High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
APA StyleOuyang, Z., Zhang, L., Wang, H., & Yang, K. (2022). High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275