Monitoring the Impact of Heat Damage on Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
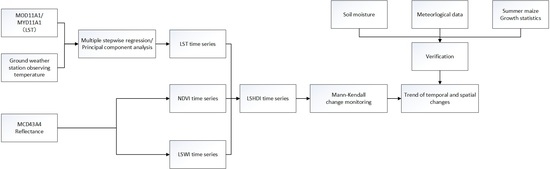
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Data Preparation
- (1)
- Remote sensing data
- (2)
- Ground observation data and statistical data
2.2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Construction of the LSHDI
2.3.1. Construction of Temperature Time-Series Data
2.3.2. Building LSHDI Time-Series Data
2.4. Monitoring of High Temperature and Heat Damage of Summer Maize Based on the LSHDI
2.4.1. Mann–Kendall Trend Monitoring
2.4.2. Mann–Kendall Mutation Detection
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the LSHDI
3.1.1. Construction and Verification of Temperature Time-Series Data
3.1.2. Performance of the LSHDI under Coarse Spatial Resolution
3.1.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Factors in the LSHDI
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Heat Damage in Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain
3.2.1. Trend of the LSHDI during the Year
3.2.2. Trend of the LSHDI between Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, J.H.; Oh, D.; Ko, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Yeom, J.M.; Cho, J. Remote Sensing-Based Evaluation of Heat Stress Damage on Paddy Rice Using NDVI and PRI Measured at Leaf and Canopy Scales. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Li, X.; Tian, B.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, H. Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought in different growth stages of soybean in Heilongjiang. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2020, 31, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huo, Z.; Wang, P.; Wu, D. Occurrence characteristics of early rice heat disaster in Jiangxi Province. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2020, 31, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Y.; Huang, R.; Mansaray, L.R.; Huang, J. Mapping high temperature damaged area of paddy rice along the Yangtze River using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 41, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Drought under global warming: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.K.; Kohne, R.W. Susceptibility of Reservoirs to Drought Using Palmer Index. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1993, 119, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Roujean, J.L.; Fan, T.; Dong, Y.; Hu, T.; Cao, B.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q. An angular normalization method for temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) in monitoring agricultural drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F. Application of vegetation index and brightness temperature for drought detection. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 15, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H. Comparisons and classification system of typical remote sensing indexes for agricultural drought. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Shi, P. An integrated agricultural drought monitoring model based on multi-source remote sensing data: Model development and application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7757–7770. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.J.; Choudhury, B.J. Satellite remote sensing of drought conditions. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 23, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Peters, A.J. Assessing vegetation response to drought in the northern Great Plains using vegetation and drought indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, M.; Nutini, F.; Brivio, P.A.; Bartholomé, E.; Stroppiana, D.; Hoscilo, A. Identification of environmental anomaly hot spots in West Africa from time series of NDVI and rainfall. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 78, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Gong, F.; Su, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, X. The Novel Microwave Temperature Vegetation Drought Index (MTVDI) Captures Canopy Seasonality across Amazonian Tropical Evergreen Forests. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F. World droughts in the new millennium from AVHRR-based vegetation health indices. Eos 2002, 83, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Parida, B.R.; Venus, V.; Saha, S.K.; Dadhwal, V.K. Analysis of agricultural drought using vegetation temperature condition index (VTCI) from Terra/MODIS satellite data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 7153–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Tansey, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Developing a fused vegetation temperature condition index for drought monitoring at field scales using Sentinel-2 and MODIS imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 168, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, A.; Rahman, A.S.; Das, J.; Hosono, T.; Kisi, O. Drought forecasting using the Prophet model in a semi-arid climate region of western India. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 1397–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Tansey, K.; Ghent, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Drought Monitoring Using the Sentinel-3-Based Multiyear Vegetation Temperature Condition Index in the Guanzhong Plain, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswambharan, S.; Kumaramkandath, I.T.; Tali, J.A. A geospatial approach in monitoring the variations on surface soil moisture and vegetation water content: A case study of Palakkad District, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Sun, X.; Wang, C. The Design of a Drought Weather Index In-surance System for Summer Maize in Anhui Province, China. J. Risk Anal. Crisis Response (JRACR) 2018, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Peng, T.; Wang, S. Decomposition of long time-series fraction of absorbed photo-synthetically active radiation signal for distinguishing heavy metal stress in rice. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusiol, L.G.T.; Sun, L.; Sun, Z.; Chen, R.; Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Song, C. In-Season Monitoring of Maize Leaf Water Content Using Ground-Based and UAV-Based Hyperspectral Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, H.S.; Odindi, J.; Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Clulow, A.; Chimonyo, V.G.; Mabhaudhi, T. A Comparative Estimation of Maize Leaf Water Content Using Machine Learning Techniques and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Based Proximal and Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Song, J. Evaluation of Global Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FAPAR) Products at 500 m Spatial Resolution. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Sun, R. Evaluation of Three Long Time Series for Global Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FAPAR) Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5509–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Liang, S.; He, T.; Jin, H. Estimation of fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation from multiple satellite data: Model development and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Zhang, T.B.; Yi, G.H.; Li, J.J.; Qin, Y.B.; Chen, Y. Erratum to: Spatio-temporal variation of Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation absorbed by vegetation in the Hengduan Mountains, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanand, S.; Behera, M.D.; Roy, P.S.; Kumar, P.; Barik, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K. Satellite Based Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation Is Congruent with Plant Diversity in India. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, L.; Sun, R.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Assessing spectral indices to estimate the fraction of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by the vegetation canopy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 8022–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Desai, A.R.; Zhu, J.; Townsend, P.A.; Huang, J. Soil moisture as an essential component for delineating and forecasting agricultural rather than meteorological drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Okujeni, A.; Brell, M.; Hostert, P. Quantifying drought effects in Central European grasslands through regression-based unmixing of intra-annual Sentinel-2 time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; McCabe, M.F. Multi-sensor remote sensing for drought characterization: Current status, opportunities and a roadmap for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Keyserlingk, J.; de Hoop, M.; Mayor, A.; Dekker, S.; Rietkerk, M.; Foerster, S. Resilience of vegetation to drought: Studying the effect of grazing in a Mediterranean rangeland using satellite time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.G.S.S.; Neto, A.R.; de Souza, L.L. Soil moisture-based index for agricultural drought assessment: SMADI application in Pernambuco State-Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X. Continental drought monitoring using satellite soil moisture, data assimilation and an integrated drought index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.; Quinn, N.; Horswell, M. Remote sensing for drought monitoring & impact assessment: Progress, past challenges and future opportunities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M. A Random Forest Model for Drought: Monitoring and Validation for Grassland Drought Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, J.; Kuleshov, Y.; Chua, Z.W.; Watkins, A.B.; Choy, S.; Sun, Q. Evaluating Satellite Soil Moisture Datasets for Drought Monitoring in Australia and the South-West Pacific. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Geng, G.; Yang, J.; Hu, H.; Sheng, L.; Lou, W. Improving Soil Moisture Estimation via Assimilation of Remote Sensing Product into the DSSAT Crop Model and Its Effect on Agricultural Drought Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Koohpayma, J.; Firozjaei, M.K.; Kakroodi, A.A. Evaluation of Seasonal, Drought, and Wet Condition Effects on Performance of Satellite-Based Precipitation Data over Different Climatic Conditions in Iran. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páscoa, P.; Gouveia, C.M.; Russo, A.C.; Bojariu, R.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Trigo, R.M. Drought Impacts on Vegetation in Southeastern Europe. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, R.; Almeida, T.S.; Mantovani, E.C.; Dias, S.H.B.; Fernandes-Filho, E.I.; da Cunha, F.F.; Venancio, L.P. Soil water content and actual evapotranspiration pre-dictions using regression algorithms and remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Mei, P. Comprehensive Assessment and Variation Characteristics of the Drought Intensity in North China Based on EID. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2022, 61, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zou, C. The change of growing season of the vegetation in Huanghe-Huaihe-Haihe Region and its responses to climate changes. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2011, 22, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J.-P.; et al. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, L.; Song, J.; Li, S. Monitoring and evaluation of high temperature and heat damage of summer maize based on remote sensing data. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2020, 31, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabinia, M.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Rack, W. Spatio-temporal analysis of the relationship between LST from MODIS and air temperature in New Zealand. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduk, A.R. Prediction and Modeling of Dry Seasons Air pollution changes using multiple linear Regression Model: A Case Study of Port Harcourt and its Environs, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 264355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Bu, J.; Wei, J.; Chen, S.; Peng, H.; Xie, J.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, X.; Xie, J. Effect of Planting Density on Grain-Filling and Mechanized Harvest Grain Characteristics of Summer Maize Varieties in Huang-huai-hai Plain. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Cai, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, B.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Effects of nitrogen application rate on summer maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water–nitrogen use efficiency under micro–sprinkling irrigation in the Huang–Huai–Hai Plain of China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guga, S.; Ma, Y.; Riao, D.; Zhi, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Drought monitoring of sugarcane and dynamic variation characteristics under global warming: A case study of Guangxi, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, D.; Dinpashoh, Y.; Kahya, E.; Choudhary, R.R.; Singh, V.P. Trends in temperature over Godavari River basin in Southern Peninsular India. Int. J. Clim. 2013, 34, 1369–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Song, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, J. Improved Spring Vegetation Phenology Calculation Method Using a Coupled Model and Anomalous Point Detection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militino, A.F.; Moradi, M.; Ugarte, M.D. On the Performances of Trend and Change-Point Detection Methods for Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nega, W.; Hailu, B.T.; Fetene, A. An assessment of the vegetation cover change impact on rainfall and land surface temperature using remote sensing in a subtropical climate, Ethiopia. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 16, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Tan, Y.; Guo, D.; Xu, B. Dynamic Monitoring of Forest Land in Fuling District Based on Multi-Source Time Series Remote Sensing Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, F. Catastrophe progression method based on M-K test and correlation analysis for assessing water resources carrying capacity in Hubei province. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018, 11, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Jin, J. Analysis of Water Yield Changes from 1981 to 2018 Using an Improved Mann-Kendall Test. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.M.; Tali, P.A.; Nanda, A.A. Seasonal Spatio-Temporal Variability in Temperature over North Kashmir Himalayas Using Sen Slope and Mann-Kendall Test. J. Climatol. Weather. Forecast. 2021, 9, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.M.; Wang, J.J.; Wu, Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Shen, S.H. Research on monitoring and modeling of rice heat injury based on satellite and meteorological station data: Case study of Jiangsu and Anhui. Res. Agric. Mod. 2017, 38, 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.D.; Cao, L.J.; Li-Quan, W.U. Investigation and analysis of heat Damage on rice at blossoming stage in anhui province in 2003. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2004, 31, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.T.; He, J.; Wang, W.C.; Chen, X.N. Simulation of maize drought degree in Xi’an City based on cusp catastrophe model. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; van Dijk, A.I.; Miralles, D.G.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; de Jeu, R.A.; Gentine, P.; Huete, A.; Parinussa, R.M.; Wang, L.; et al. Enhanced canopy growth precedes senescence in 2005 and 2010 Amazonian droughts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ross, K.W.; Liu, C.; Berry, K. Standardized Soil Moisture Index for Drought Monitoring Based on Soil Moisture Active Passive Observations and 36 Years of North American Land Data Assimilation System Data: A Case Study in the Southeast United States. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhou, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, S.; Li, Z. Contrasting Responses of Planted and Natural Forests to Drought Intensity in Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.M.; Shi, Z. Estimation and Mapping of Soil Properties Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T.K.A. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multisource Remote Sensing Data: Literature Survey, Taxonomy, Principles, Applications, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Song, J.; Han, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Reconstruction of High-Temporal- and High-Spatial-Resolution Reflectance Datasets Using Difference Construction and Bayesian Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J. Bayesian Method for Building Frequent Landsat-Like NDVI Datasets by Integrating MODIS and Landsat NDVI. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, J.; Jin, Y. Deep Learning for Feature-Level Data Fusion: Higher Resolution Reconstruction of Historical Landsat Archive. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






























| Level | Relative Humidity of the Soil (%) | LSHDI |
|---|---|---|
| Light | 50~60 | Level-1: 0.3~0.4 |
| Moderate | 40~50 | Level-2: 0.3~0.2 |
| Heavy | 30~40 | Level-3: 0.2~0.1 |
| Extreme | <30 | Level-4: <0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Song, J.; Hu, F.; Han, L.; Wang, J. Monitoring the Impact of Heat Damage on Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112773
Yang L, Song J, Hu F, Han L, Wang J. Monitoring the Impact of Heat Damage on Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112773
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lei, Jinling Song, Fangze Hu, Lijuan Han, and Jing Wang. 2023. "Monitoring the Impact of Heat Damage on Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112773
APA StyleYang, L., Song, J., Hu, F., Han, L., & Wang, J. (2023). Monitoring the Impact of Heat Damage on Summer Maize on the Huanghuaihai Plain, China. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112773