Mangrove Species Identification: Comparing WorldView-2 with Aerial Photographs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Survey
2.3. Remote Sensing Data and Pre-Processing
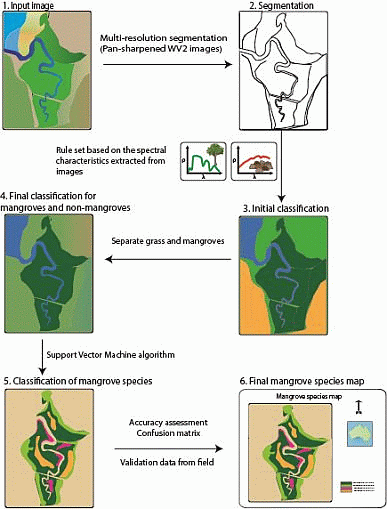
2.4. Image Classification
2.4.1. Separating Mangroves and Non-Mangroves
2.4.2. Mangrove Species Classification
2.5. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Field Survey
3.2. Separating Mangroves and Non-Mangroves
3.3. Mangrove Species Classification
3.4. Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Separating Mangroves and Non-Mangroves
4.2. Comparison of Mangrove Species Classifications
4.3. Accuracy Assessment
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Information
remotesensing-06-06064-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization, The World’s Mangroves 1980–2005; FAO Forestry Paper 153; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2007.
- Suratman, M.N. Carbon Sequestration Potential of Mangroves in Southeast Asia. In Managing Forest Ecosystems: The Challenge of Climate Change; Bravo, F., Jandl, R., LeMay, V., Gadow, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 297–315. [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon, S.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Twilley, R.R.; Kairo, J.G. Mangroves. In The Management of Natural Coastal Carbon Sinks; Laffoley, D., Grimsditch, G., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama, A.; Ong, J.E.; Poungparn, S. Allometry, biomass, and productivity of mangrove forests: A review. Aquatic Bot 2008, 89, 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, K. The Biological Diversity, Recovery from Disturbance and Rehabilitation of Mangroves in Darwin Harbour, Northern Territory. In Faculty of Education, Health & Science; Charles Darwin University: Darwin, NT, Australia, 2007; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, D.M. Present state and future of the world’s mangrove forests. Environ. Conserv 2002, 29, 331–349. [Google Scholar]
- Blasco, F.; Gauquelin, T.; Rasolofoharinoro, M.; Denis, J.; Aizpuru, M.; Caldairou, V. Recent advances in mangrove studies using remote sensing data. Mar. Freshw. Resour 1998, 49, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Green, E.P.; Cleark, C.D.; Mumby, P.J.; Edwards, A.J.; Ellis, A.C. Remote sensing techniques for mangrove mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens 1998, 19, 935–956. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, R.M.; Ellison, J.C.; Mitchell, A.; Donnelly, B.; Finlayson, M.; Milne, A.K. Use of stereo aerial photography for quantifying changes in the extent and height of mangroves in tropical Australia. Wetl. Ecol. Manag 2002, 10, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Heumann, B.W. Satellite Remote sensing of mangrove forests: Recent advances and future opportunities. Progr. Phys. Geogr 2011, 35, 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. A hybrid method toward accurate mapping of mangroves in a marginal habitat from SPOT multispectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens 1998, 19, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Held, A.; Ticehurst, C.; Lymburner, L.; Williams, N. High resolution mapping of tropical mangrove ecosystems using hyperspectral and radar remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens 2003, 24, 2739–2759. [Google Scholar]
- Nandy, S.; Kushwasha, S.P.S. Study on the utility of IRS LISS-III data and the classification techniques for mapping of Sunderban mangroves. J. Coast. Conserv 2010, 15, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.; Phinn, S. Hyperspectral data for mangrove species mapping: A comparison of pixel-based and object-based approach. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 2222–2242. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiphasa, C.; Ongsmwang, S.; Vaiphasa, T.; Skidmore, A.K. Tropical mangrove species discrimination using hyperspectral data: A laboratory study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci 2005, 65, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiphasa, C.; Skidmore, A.K.; Boer, W.F.D.; Vaiphasa, T. A hyperspectral band selector for plant species discrimination. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens 2007, 62, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sousa, W.P. Distinguishing mangrove species with laboratory measurements of hyperspectral leaf reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens 2009, 30, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzer, C.; Bluemel, A.; Gebhardt, S.; Quoc, T.V.; Dech, S. Remote sensing of mangrove ecosystems: A review. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 878–928. [Google Scholar]
- Heumann, B.W. An object-based classification of mangroves using a hybrid decision tree—support vector machine approach. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 2440–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Tso, B.; Mather, P.M. Support Vector Machines. In Classification Methods for Remotely Sensed Data, 2nd ed; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 125–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrakis, G.; Jungho, I.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. Int. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst, P.; Edmeades, B. The Mangrove Communities of Darwin Harbour: Northern Territory; Department of Lands, Planning and Environment, Northern Territory Government: Darwin, NT, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ferwerda, J.G.; Ketner, P.; McGuinness, K.A. Differences in regeneration between hurricane damaged and clear-cut mangrove stands 25 years after clearing. Hydrobiologia 2007, 591, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wightman, G. Mangrove Plant Identikit for North Australia’s Top End; Greening Australia: Darwin, NT, Australia, 2006; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, N.C. Australia’s Mangroves: The Authoritative Guide to Australia’s Mangrove Plants; University of Queensland: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2006; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- DigitalGlobe, The Benefits of the 8 Spectral Bands of WorldView-2; DigitalGlobe: Longmont, CO, USA, 2009.
- Northern Territory Government, Northern Territory Digital Data and Information; Department of Lands, Planning and the Environment: Darwin, NT, Australia, 2010.
- DigitalGlobe, DigitalGlobe Core Imagery Products Guide; DigitalGlobe: Longmont, CO, USA, 2011.
- Updike, T.; Comp, C. Radiometric Use of WorldView-2 Imagery. In Technical Note; DigitalGlobe: Longmont, CO, USA, 2010; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Amro, I.; Mateos, J.; Vega, M.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. A survey of classical methods and new trends in pansharpening of multispectral images. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.P.S.; Sides, S.C.; Anderson, J.A. Comparison of three different methods to merge multiresolution and multispectral data: Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic. J. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens 1991, 57, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, J.P.S.; Bowell, J.A. Comparison of the spectral information content of Landsat thematic mapper and SPOT for three different sites in the Phoenix, Arizona. J. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens 1988, 54, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Palubinskas, G. Fast, simple, and good pan-sharpening method. J. Appl. Remote Sens 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergraph Corporation, IMAGINE Workspace: HPF Resolution Merge Manual; Intergraph: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2013.
- Australian Government. 2013. Available online: http://www.ga.gov.au/ (accessed on 25 January 2013).
- Henrich, V.; Krauss, G.; Götze, C.; Sandow, C. Index Database. 2012. Available online: http://www.indexdatabase.de/db/i-single.php?id=126 (accessed on 29 May 2014).
- Ahamed, T.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ting, K.C. A review of remote sensing methods for biomass feedstock production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2455–2469. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, K.C.; Verbeke, L.P.C.; Ducheyne, E.I.; De Wulf, R.R. Using genetic algorithms in sub-pixel mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens 2003, 24, 4241–4247. [Google Scholar]
- Tatema, A.J.; Lewisa, H.G.; Atkinsonb, P.M.; Nixona, M.S. Super-resolution land cover pattern prediction using a Hopfield neural network. Remote Sens. Environ 2002, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.Q.; Atkinson, P.M.; Lewis, H.G. Super-resolution mapping using Hopfield neural network with panchromatic image. Int. J. Remote Sens 2011, 32, 6149–6176. [Google Scholar]
- Tatem, A.J.; Lewis, H.G.; Atkinson, P.M.; Nixon, M.S. Multiple-class land-cover mapping at the sub-pixel scale using a Hopfield neural network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinforma 2001, 3, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle, O.; Haffner, P.; Vapnik, V.N. Support vector machines for histogram-based image classification. Trans. Neural Netw 1999, 10, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Canty, M.J. Supervised Classification: Part 1. In Image Analysis, Classification, and Change Detection in Remote Sensing with Algorithm for ENVI/IDL, 2nd ed; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. Accuracy assessment and validation of remotely sensed and other spatial information. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2001, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Quoc, T.V.; Oppelt, N.; Leinenkugel, P.; Kuenzer, C. Remote sensing in mapping mangrove ecosystem—An object-based approach. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Pan-Sharpening for Improved Information Extraction. In Advances in Photogrammmetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; Taylor & Fransis: London, UK, 2008; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, D.M. Zonation and seasonality of benthic primary production and community respiration in tropical mangrove forests. Oecologia 1994, 98, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Verheyden, A.; Kairo, J.G.; Jayatissa, L.P.; Koedam, N. Capacity building in tropical coastal resource monitoring in developing countries: A re-appreciation of the oldest remote sensing method. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol 2006, 13, 62–76. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classification of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar]








| Band | Spectral Range (nm) | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|
| WorldView-2 | ||
| Panchromatic | 447–808 | 0.5 |
| Coastal | 396–458 | 2.0 |
| Blue | 442–515 | 2.0 |
| Green | 506–586 | 2.0 |
| Yellow | 584–632 | 2.0 |
| Red | 624–694 | 2.0 |
| Red-Edge | 699–749 | 2.0 |
| NIR1 | 765–901 | 2.0 |
| NIR2 | 856–1043 | 2.0 |
| Aerial photographs | ||
| Blue | 380–600 | 0.14 |
| Green | 480–700 | 0.14 |
| Red | 580–720 | 0.14 |
| Species | No. of Samples for Training (4 m2 or 16 Pixels Each) | No. of Points for Validating the Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Avicennia marina (AM) | 22 | 216 |
| Bruguiera exaristata (BE) | 14 | 106 |
| Ceriops tagal (CT) | 10 | 80 |
| Lumnitzera racemosa (LR) | 12 | 78 |
| Rhizophora stylosa (RS) | 11 | 96 |
| PS-WV2-VIS | PS-WV2-R/NIR1 | WV2-VIS | WV2-R/NIR1 | AP0.14M | AP0.5M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall accuracy | 89% | 87% | 58% | 42% | 68% | 68% |
| Kappa | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.58 |
| Image | Accuracy (%) | AM | BE | CT | LR | RS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS-WV2-VIS | Producer’s acc. | 98 | 73 | 55 | 100 | 95 |
| User’s acc. | 98 | 72 | 84 | 87 | 89 | |
| PS-WV2-R/NIR1 | Producer’s acc. | 95 | 54 | 70 | 100 | 100 |
| User’s acc. | 100 | 83 | 68 | 72 | 81 | |
| WV2-VIS | Producer’s acc. | 98 | ** | ** | 82 | 28 |
| User’s acc. | 99 | ** | ** | 13 | 19 | |
| WV2-R/NIR1 | Producer’s acc. | 94 | ** | 2 | 44 | 70 |
| User’s acc. | 98 | ** | 2 | 12 | 13 | |
| AP0.14M | Producer’s acc. | 83 | 27 | 45 | 73 | 77 |
| User’s acc. | 94 | 46 | 35 | 60 | 59 | |
| AP0.5M | Producer’s acc. | 91 | 20 | 65 | 79 | 44 |
| User’s acc. | 77 | 25 | 70 | 72 | 65 | |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Heenkenda, M.K.; Joyce, K.E.; Maier, S.W.; Bartolo, R. Mangrove Species Identification: Comparing WorldView-2 with Aerial Photographs. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6064-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076064
Heenkenda MK, Joyce KE, Maier SW, Bartolo R. Mangrove Species Identification: Comparing WorldView-2 with Aerial Photographs. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(7):6064-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076064
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeenkenda, Muditha K., Karen E. Joyce, Stefan W. Maier, and Renee Bartolo. 2014. "Mangrove Species Identification: Comparing WorldView-2 with Aerial Photographs" Remote Sensing 6, no. 7: 6064-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076064
APA StyleHeenkenda, M. K., Joyce, K. E., Maier, S. W., & Bartolo, R. (2014). Mangrove Species Identification: Comparing WorldView-2 with Aerial Photographs. Remote Sensing, 6(7), 6064-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076064