Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Data Acquisition and Pre-Processing
3. Methodology
3.1. Water Body Delineation
3.2. Water Level Mapping
3.3. Water Level Validation

4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Assessment of Satellite-Derived Water Levels



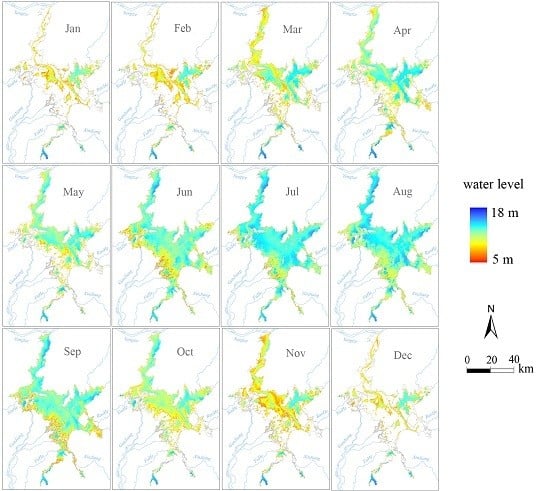
4.2. The Seasonal Water-Level Distribution Pattern

| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 6.35 | 6.21 | 7.88 | 8.63 | 8.77 | 11.89 | 13.58 | 12.51 | 11.16 | 8.53 | 6.51 | 6.11 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.50 | 3.29 | 3.94 | 3.87 | 3.75 | 2.58 | 2.48 | 2.50 | 3.08 | 3.71 | 3.28 | 3.46 |

4.3. Inter-Annual Spatial Variability of Water Levels

4.4. Water Level Gradient Variability within Poyang Lake

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beeton, A.M. Large freshwater lakes: Present state, trends, and future. Environ. Conserv. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiner, R.W. Search of Swampland: A Wetland Sourcebook and Field Guide; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, W.F. Effects of climate change on lakes. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Academic Press, Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Vassiljev, J.; Harrison, S.P.; Haxeltine, A. Recent lake-level and outflow variations at Lake Viljandi, Estonia: Validation of a coupled lake-catchment modelling scheme for climate change studies. J. Hydrol. 1995, 170, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.A. Levels at Gauging Stations: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 3-A19; 2010. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/tm3A19/ (accessed on 9 January 2013).
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Tracking fresh water from space. Science. 2003, 301, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.C. Satellite remote sensing of river inundation area, stage, and discharge: A review. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Rodriguez, E.; Letternmaier, D.P. Measuring surface water from space. Rev. Geophys. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Pappenberger, F.; Matgen, P. Estimating uncertainty associated with water stages from a single SAR image. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-François, C.; Sylvain, B.; Adalbert, A.; Muriel, B.N.; Mélanie, B. Global surveys of reservoirs and lakes from satellites and regional application to the Syrdarya river basin. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.S.; Matgen, P.; Pappenberger, F. Progress in integration of remote sensing-derived flood extent and stage data and hydraulic models. Rev. Geophys. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, Z.N.; Popescu, I.; Mynett, A. A review of applications of satellite SAR, optical, altimetry and DEM data for surface water modeling, mapping and parameter estimation. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 4857–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Calmant, S.; Cauhope, M.; Seyler, F.; Cazenave, A. Preliminary results of ENVISAT RA-2 derived water levels validation over the Amazon basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Niu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Huang, H.; Sun, F.; Li, X. Water-level changes in China’s large lakes determined from ICESat/GLAS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsen, A.; Crétaux, J-F.; Abarca-Del-Rio, R. Use of SARAL/AltiKa over mountainous lakes, intercomparison with Envisat mission. Mar. Geod. 2015, 38, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistioadi, Y.B.; Tseng, K.-H.; Shum, C.K.; Hidayat, H.; Sumaryono, M.; Suhardiman, A.; Setiawan, F.; Sunarso, S. Satellite radar altimetry for monitoring small rivers and lakes in Indonesia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ričko, M.; Birkett, C.M.; Carton, J.A.; Crétaux, J.E. Intercomparison and validation of continental water level products derived from satellite radar altimetry. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2012, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.F.; Stéphane, C.; Romanovski, V.; Shabunin, A.; Lyard, F.; Bergé Nguyen, M.; Cazenave, A.; Hernandez, Fabrice.; Perosanz, F. An absolute calibration site for radar altimeters in the continental domain: Lake Issykkul in Central Asia. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.C.; Kouraev, A.V.; Shum, C.K.; Vuglinsky, V.S.; Crétaux, J-F.; Calmant, S. The performance of altimeter waveform retrackers at Lake Baikal. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2013, 24, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Papa, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Seyler, F. Interannual variations of river water storage from a multiple satellite approach: A case study for the Rio Negro River basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baup, F.; Frappart, F.; Maubant, J. Combining high-resolution satellite images and altimetry to estimate the volume of small lakes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.F.; Nichols, J. Remote sensing of river stage using the cross-sectional inundation area-river stage relationship (IARSR) constructed from digital elevation model data. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khudhairy, D.H.A.; Leemhuis, C.; Hoffman, V.; Calaon, R.; Shepherd, I.M.; Thompson, J.R.; Gavin, H.; Gasca-Tucker, D.L. Monitoring wetland ditch water levels in the North Kent Marshes using Landsat TM imagery and ground-based measurements. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2001, 46, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.D.; Neal, J.C.; Alsdorf, D.; Schumann, G. Observing global surface water flood dynamics. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.W.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Sonenshein, R. Space-based detection of wetland’s detection of wetland’s surface water level changes from L-band SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Melack, J.M.; Dunne, T.; Mertes, A.K.; Hess, L.L.; Smith, L.C. Interferometric radar measurements of water level changes on the Amazon floodplain. Nature 2000, 404, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Birkett, C.M. Water level changes in a large Amazon Lake measured with spaceborne radar interferometry and alimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2671–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Wdowinski, S. Multitemporal multitrack monitoring of wetland water levels in the Florida Everglades using ALOS PALSAR data with interferometric processing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Trigg, M. Estimating river depth from remote sensing swath interferometry measurements of river height, slope, and width. IEEE. J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J.-B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-derived inundation areas, high precision topographic data and a river flow model toward real-time flood management. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raclot, D. Remote sensing of water levels on floodplains: a spatial approach guided by hydraulic functioning. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2553–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Matgen, P.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Black, A.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Comparison of remotely sensed water stages from LiDAR, topographic contours and SRTM. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwenzner, H.; Voigt, S. Improved estimation of flood parameters by combining space based SAR data with very high resolution digital elevation data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, M.; Harris, J.; McCartney, M.; Lew, Y.; Zhang, C. Report on Ramsar Visit to Poyang Lake Ramsar Site, PR China, Report Prepared on behalf of the Secretariat of the Ramsar Convention. 2010.
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, X. Recent declines in China’s largest freshwater lake: Trend or regime shift? Environ. Res. Lett. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Liu, Y.B. Satellite-based detection of water surface variation in China’s largest freshwater lake in response to hydro-climatic drought. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4511–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ni, L.; Xu, J.; He, L.; Fu, H.; Liu, Z. Annual dynamics of the wetland plants community in Poyang Lake in response to water-level variations. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 1057–1063. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Decharme, B.; Douville, H.; Prigent, C.; Papa, F.; Aires, F. A new river flooding scheme for global climate applications: Off-line validation over South Amercia. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillisson, J.M.; Marion, L. Water level fluctuations for managing excessive plant biomass in shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Capturing variations in inundation with satellite remote sensing in a morphologically complex, large lake. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C. An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: Comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5767–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Fang, C. Study of morphologic change in Poyang Lake basin caused by sand dredging using multi-temporal Landsat images and DEMs. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, XL-1, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.M. Effect of differing DEM creation methods on the results from a hydrological model. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P. DEM generation from laser scanner data using adaptive TIN models. Int. Arch. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, S.P.; Charles, N.K. Quantifying DEM uncertainty and its effect on topographic parameters. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Markham, B.; Dye, D.G.; Dulaney, W.; Yang, J. Normalized difference vegetation index measurements from the advanced very high resolution radiometer. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Singh, R.D.; Jain, M.K.; Lohani, A.K. Delineation of flood-prone areas using remote sensing techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.G. Application of AVHRR to monitoring a climatically sensitive playa. Case study: Chottel Djerid, southern Tunisia. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 1999, 24, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, P.; Peng, J.; Ye, C. A physical explanation of the variation in threshold for delineating terrestrial water surface from multi-temporal images: Effects of radiometric correction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5862–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. A Review of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Environmental Scientists; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2008.
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Poyang Lake rises higher than alert level. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/photo/2012-08/13/content_15670620_2.htm (accessed on 12 May 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13466-13484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71013466
Wu G, Liu Y. Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(10):13466-13484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71013466
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guiping, and Yuanbo Liu. 2015. "Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake" Remote Sensing 7, no. 10: 13466-13484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71013466
APA StyleWu, G., & Liu, Y. (2015). Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sensing, 7(10), 13466-13484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71013466